Gemfibrozil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
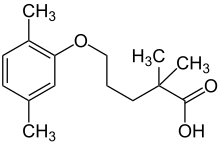
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Gemfibrozil | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 22 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white, waxy, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Fibrates (lipid lowering agents) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 250.34 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
61-63 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
158-159 ° C (2.66 Pa ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
4.7 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water, very easily soluble in dichloromethane , easily soluble in ethanol and in methanol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Gemfibrozil is an oral lipid-lowering drug (used to lower high blood lipids ). It belongs to the drug class of fibrates . Gemfibrozil was patented as a lipid lowering agent in 1969 by Parke-Davis (now Pfizer ) and is available under the trade name Gevilon and as a generic .
Mechanism of action
The drug is a ligand of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor of subtype α (PPAR α ), a receptor that is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats and also in the formation of adipose tissue . The increase in the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase also increases the breakdown of triglycerides .
Therapeutic effect
Gemfibrozil
- reduces the level of triglycerides (by 20-40%)
- reduces the level of VLDL
- moderately reduces the level of LDL (by 10–20%)
- moderately increases the level of HDL (by 5–20%).
Side effects and toxic effects
Common side effects are dizziness, headache, gastrointestinal discomfort, skin eczema and fatigue. An increase in transaminases, muscle problems, gallstone formation and hair loss can also occur, as with other fibrates.
In animal experiments there were indications of carcinogenicity at abnormal doses .
Indications
- Gemfibrozil is the drug of choice for hyperlipidemia (type III).
- Hypertriglyceridemia (Type IV): Gemfibrozil is better tolerated, even if it is less effective than niacin .
Contraindications
Gemfibrozil should only be used with caution in the presence of increased liver enzymes , advanced renal insufficiency and biliary tract disease . It is only permitted during pregnancy if there is a vital indication. There is a risk of hypoglycaemia when taken with repaglinide . When taken with statins, the common metabolic pathway via cytochrome P450 increases the risk of rhabdomyolysis .
Interactions
- Anticoagulants : Gemfibrozil enhances the effects of warfarin .
- Statins : When statins are given at the same time as fibrates (including gemfibrozil), the risk of muscle cramps , myopathy, and rhabdomyolysis increases .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet GEMFIBROZIL CRS 06/27/2013 (PDF) at EDQM , accessed on August 29, 2017.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Gemfibrozil. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 10, 2019.
- ↑ a b Gemfibrozil data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 3, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas Karow, Ruth Lang-Roth: General and special pharmacology and toxicology . P. 654.
- ↑ Red List online, accessed on February 1, 2014.
- ↑ Richard Daikeler, idols Use, Sylke Waibel: diabetes. Evidence-based diagnosis and therapy. 10th edition. Kitteltaschenbuch, Sinsheim 2015, ISBN 978-3-00-050903-2 , p. 149.
- ↑ rxlist.com: Lopid ( Memento from June 12, 2008 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Red List Online Gemfibrozol, accessed February 1, 2014.