Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (formerly also the Gulf of Guinea ) describes the part of the Atlantic Ocean that is bounded in the north and east by West Africa .
geography
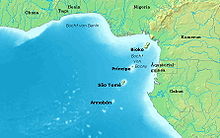
In the north and east, the Gulf of Guinea borders on the coastal land of the regions of Upper Guinea and Lower Guinea and in the south on the Angola Basin . According to the definition of the International Hydrographic Organization , it is bounded by Cape Palmas in Liberia and Cap Lopez in Gabon .
In the Gulf of Guinea are the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe , which make up the independent state of São Tomé and Príncipe , and Bioko and Annobón , which are part of Equatorial Guinea . They were created by a volcanic hot spot that also gave birth to the Cameroon Mountain on the African mainland.
In the Gulf of Guinea crosses the equator the prime meridian .
story
According to a controversial Greek account of antiquity, it is now assumed that the Punic Phoenicians in an expedition under Hanno the navigator around 470 BC. Chr. The Gulf reached.
The coast of Upper Guinea has four sections, the names of which come from the colonial times: Pepper Coast (today Liberia ), Ivory Coast (today Côte d'Ivoire ), Gold Coast (today Ghana ) and the Slave Coast (today Togo , Benin and the western part of Nigeria ). The names show which “goods” were preferred to be traded and loaded in which section of the coast.
Between 1884 and 1919, the German colonies in West Africa bordered the Gulf of Guinea. Other neighboring colonial areas included France , the United Kingdom , Portugal and Spain .
As Bight of Biafra was until 1973 the of Cameroon and the Niger Delta in Nigeria adjacent innermost part of the Gulf called, after the Biafran war , the Nigerian authorities possessed a renaming in Bight of Bonny . Another part is the Bay of Benin .
piracy
More recently, the Gulf of Guinea has become a center of piracy . In 2019, 90 percent of all kidnappings at sea recorded worldwide, followed by ransom, took place in the waters of the Gulf of Guinea. Denmark has been helping Ghana and Nigeria build anti-piracy capacities since 2016 . There are 30-40 ships of Danish shipping companies in this sea area every day. With the frigate Esbern Snarre and a Seahawk helicopter , the Kongelige Danske Marine will contribute to the security in the Gulf of Guinea from November 2021 to April 2022. As a location and information center, the Maritime Domain Awareness for Trade - Gulf of Guinea (MDAT-GoG) is also supported by the European Union .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ International Hydrographic Organization (1953): Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition (PDF; 994 kB), p. 19. Accessed February 7, 2010.
- ↑ IMB Piracy & Armed Robbery Map 2019. ICC Commercial Crime Services, accessed on May 11, 2020 .
- ↑ Kevin Ponniah: The day the pirates came. BBC News, May 10, 2020, accessed May 11, 2020 .
- ^ Kai Strell: Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea. The region on the West African coast was also a central “hotspot” for piracy in 2019 . MarineForum 5-2020, pp. 32-35.
- ↑ Andreas Knudsen: In the hotspot of piracy. Denmark is preparing to fight pirates in the Gulf of Guinea . MarineForum 10-2021, p. 35.
Coordinates: 2 ° 23 ′ 43 " N , 6 ° 24 ′ 24" E