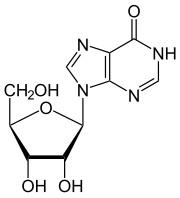
Inosine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Inosine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 N 4 O 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White dust |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Immune stimulant |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 268.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
222-226 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (2.1 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Inosine is a rare nucleoside of RNA . It consists of β- D- ribofuranose (sugar) and hypoxanthine , a base that has a purine as its basic structure, which is an intermediate product of the purine metabolism .
properties
In the tRNA, inosine pairs in the anticodon as a nucleotide in the wobble position with cytidine , uridine and adenosine . This modification was found in some tRNAs from eukaryotes, prokaryotes and chloroplasts. In so-called RNA editing , adenosine is converted into inosine by the enzyme ADAR ( adenosine deaminase acting on RNA ). In baker's yeast , the conversion of adenosine to inosine in the tRNA Ala at position 34 is catalyzed by the tRNA-specific deaminase Tad2p / 3p, a heterodimer; at position 37 this is done by Tad1p.
 A tRNA Ala from S. cerevisiae .
A tRNA Ala from S. cerevisiae .
Inosine is marked with I at position 34 here . Methylated inosine (m 1 I) is highlighted at position 37.
Inosine is used in the construction of degenerate primers for the polymerase chain reaction . It serves here as a "neutral" base that can pair with all four bases. However, the pairing is a little energetically unfavorable in all four cases and not the same for all four base pairings. The best pairing is made with cytosine , followed by adenine . The pairing with guanine and thymine are both about energetically the same and the most unfavorable.
use
Inosine is being tested for use in patients with Parkinson's disease . The intermediate product in the purine metabolism is partially converted into uric acid in the body. High uric acid levels have been linked to slower progression of Parkinson's disease.
A phase II study has now shown that there are no serious side effects during the treatment , even if high uric acid levels theoretically carry the risk of gout , kidney stones and an increased cardiovascular risk. The study showed no increased risk for any of the three diseases during inosine treatment.
Inosine is considered to be a potentially important component in chemical evolution . In experiments, inosine showed reasonable rates and accuracy in RNA copy reactions ( RNA world hypothesis ). Inosine could have served as a substitute for guanosine in the early stages of life .
Trade names
Delimmun (D), Isoprinosine (D)
See also
Web links
- Entry for Inosine in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed September 24, 2013.
- Inosine's Modification Summary in the Modomics database, accessed January 14, 2014.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Inosine, 98 +% at AlfaAesar, accessed on December 7, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Inosine data sheet from Acros, accessed on February 17, 2013.
- ↑ Gerber, AP. und Keller, W. (1999): An adenosine deaminase that generates inosine at the wobble position of tRNAs . In: Science 286 (5442); 1146-1149; PMID 10550050 ; doi : 10.1126 / science.286.5442.1146
- ↑ SC Case-Green, EM Southern: Studies on the base pairing properties of deoxyinosine by solid phase hybridization to oligonucleotides , Nucleic Acids Res. , 1994 , 22 (2), pp. 131-136 ( PMC 307762 (free full text); PMID 8121796 ).
- ^ CC Sun et al. (2012): Association of serum uric acid levels with the progression of Parkinson's disease in Chinese patients. , Chinese medical journal. Volume 125, Number 4, pp. 583-587, PMID 22490478 .
- ↑ Tua Annanmaki et al. (2011): Uric acid and cognition in Parkinson's disease: A follow-up study. , Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 17, pp. 333–337, doi : 10.1016 / j.parkreldis.2011.01.013 .
- ↑ MA Schwarzschild et al. (2014): Inosine to Increase Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Urate in Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. In: JAMA neurology 71 (2); 141-150; PMID 24366103 ; doi : 10.1001 / jamaneurol.2013.5528
- ↑ Seohyun Chris Kim, Derek K. O'Flaherty, Lijun Zhou, Victor S. Lelyveld, Jack W. Szostak: Inosine, but none of the 8-oxo-purines, is a plausible component of a primordial version of RNA. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115, 2018, p. 13318, doi : 10.1073 / pnas.1814367115 .