Jasmine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Jasmine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 16 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, viscous liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 164.24 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.9437 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Jasmone is a chemical compound from the cyclopentenone group , it is an essential component of the fragrance of the jasmine flowers , which was already used by the Romans to make perfumes.
The constitution of the compound was described independently in 1933 both by Leopold Ružička and in a publication by the scientific laboratory of Heine & Co. and confirmed with a synthesis published in 1935. In 1952 it was possible to provide evidence that the naturally occurring jasmone is the cis isomer.
presentation
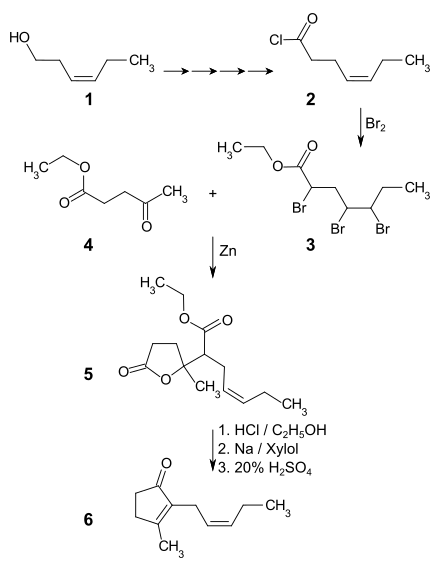
As a starting material for the first synthesis of jasmone, cis -3-hexenol 1 from Japanese peppermint oil was used. This is converted into the cis -3-hexenecarboxylic acid chloride 2 via the intermediate stages cis -3-hexene bromide, cis -3-hexenenitrile and cis -3-hexenecarboxylic acid . The acid chloride is and adjacent to the double bond to chlorocarbonyl brominated with ethanol in the Tribromethylester 3 transferred. The reaction of 3 with levulinic acid ethyl ester 4 in benzene and with iodine- activated zinc in a Reformatzki reaction gives the lactone 5 , with the double bond in the side chain being re-formed at the same time by debromination. The lactone is first reacted with hydrogen chloride in ethanol and the reaction product is then reacted with sodium in xylene . After heating with 20% strength sulfuric acid , a crude product is obtained which is purified as semicarbazone by recrystallization and from which the cis -jasmon 6 can be released with 10% strength sulfuric acid .
Isomerism
The isomeric trans -jasmon can occur as an accompanying substance to the naturally occurring cis -isomer and can in particular be present as a component in synthetically produced jasmon.
Occurrence
cis -jasmon occurs in the flowers of jasmine . The compound can be detected in American, Russian, Italian and Bulgarian, but not in Japanese peppermint oil.
Biological importance
In plants, cis -jasmon is included in the defense strategy against insects . It is released when insects infest the plants. So it attracts predators of the insects (e.g. aphids). At the same time, the compound is said to disturb the fertility of the insects.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on CIS-JASMONE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 16, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Jasmon at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 16, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d L. Ruzicka, M. Pfeiffer: About jasmine fragrances I. The constitution of jasmon . In: Helvetica Chimica Acta . tape 16 , no. 1 , 1933, pp. 1208-1214 , doi : 10.1002 / hlca.193301601153 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-366.
- ^ W. Treff, H. Werner: About the constitution of the jasmons . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 66 , no. 10 , October 11, 1933, p. 1521–1527 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19330661014 .
- ↑ a b W. Treff, H. Werner: About the synthesis of Jasmons . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 68 , no. 4 , April 3, 1935, pp. 640-644 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19350680415 .
- ↑ Leslie Crombie, Stanley H. Harper: Experiments on the synthesis of the pyrethrins. Part VIII. Stereochemistry of jasmone and identity of dihydropyrethrone . In: Journal of the Chemical Society . 1952, p. 869 , doi : 10.1039 / jr9520000869 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to (E) -Jasmon : CAS number: 6261-18-3, EC number: 228-410-7, ECHA InfoCard: 100.025.828 , PubChem : 1549019 , ChemSpider : 1266013 , Wikidata : Q27160475 .
- ↑ Ernst Steinegger, Rudolf Hansel: Textbook of Pharmacognosy and Phytopharmacy . 4th edition. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg 1988, ISBN 978-3-662-08319-2 , pp. 341 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Harry Schmidt: To the knowledge of the peppermint oil. Occurrence of Jasmon in the essential oil of Mentha piperita L . In: Chemical Reports . tape 80 , no. 6 , December 1947, p. 538 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19470800613 .
- ↑ Perfume component as plant protection - Cis-Jasmone attracts enemies of the seed-killing insects , July 30, 2002.