Lomefloxacin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
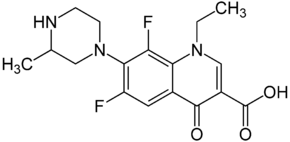
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Lomefloxacin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
( RS ) -1-Ethyl-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-7- (3-methyl-1-piperazinyl) -4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 19 F 2 N 3 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless needles [( RS ) -lomefloxacin] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Lomefloxacin is an antibacterially active drug from the group of fluoroquinolones . It is used to treat bacterial infections in ophthalmology and general medicine.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
- General medicine
Lomefloxacin is used orally for bacterial infections of the respiratory tract , the ear, nose and throat area , the skin , soft tissue and bones , the lower urinary tract, such as acute and chronic, complicated and uncomplicated infections such as pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidney), cystitis , urethritis and infections after surgical operations Interventions in the urogenital tract, used.
- Ophthalmology
In ophthalmology, lomefloxacin is used in the form of eye drops for bacterial infections of the anterior eye segment and the ocular adnexa; used for blepharoconjunctivitis , conjunctivitis and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid).
Contraindications (contraindications)
If you are hypersensitive to lomefloxacin, other quinolones or one of the pharmaceutical excipients ; bacterial keratitis ; bacterial endophthalmitis ; Exposure to sunlight or UV light; Wearing contact lenses; Children and adolescents under 18 years of age should not be treated with lomefloxacin until the end of the growth phase. There is a risk of cartilage disruption ( arthropathies ).
Drug interactions
Sucralfate and antacids containing magnesium or aluminum (for example magaldrate ) and metal cations from other sources can form chelate complexes with lomefloxacin and affect bioavailability . Such substances should therefore be taken at least four hours before or at least two hours after taking the medication. Probenecid may slow the elimination of lomefloxacin when administered concomitantly.
Meals delay the absorption of lomefloxacin when taken at the same time , but global bioavailability is not significantly affected.
Adverse effects (side effects)
Rarely temporary burning eyes immediately after use, hypersensitivity reactions with itching and pain. Long-term antibiotic therapy runs the risk of a secondary fungal infection and promotes the growth of non-sensitive bacteria.
Other Information
Chemical and pharmaceutical information
Lomefloxacin monohydrochloride is used medicinally .
Stereoisomerism
Lomefloxacin contains a stereocenter , hence there are two isomers, ( R ) -lomefloxacin and the enantiomeric ( S ) -lomefloxacin. The drug Okacin ® (D) contains the racemate [1: 1 mixture of the ( R ) form and the ( S ) form] of lomefloxacin · monohydrochloride, although the use of an enantiomer which is more effective or has fewer side effects is preferred for fundamental reasons would.
( R ) -Lomefloxacin (top) and ( S ) -Lomefloxacin (bottom)
Manufacturing
The multistep synthesis of lomefloxacin from 2,3,4-trifluoro aniline is described in the literature.
History
Lomefloxacin was patented in 1985 by Hokuriku Pharmaceutical Co. and is available from Novartis Pharma GmbH ( Okacin ® ) in the form of eye drops to treat bacterial conjunctivitis ; and from Pfizer in the oral dosage form ( Maxaquin ® ) against infections of the urinary tract, infections of the respiratory tract, infections of the skin and soft tissues.
literature
- Hermann J. Roth: Medicinal Chemistry: Targets and Drugs; 157 tables . German Apotheker-Verlag, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-7692-3483-9
Individual evidence
- ↑ Franz von Bruchhausen. Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice: Substances LZ . Gabler Wissenschaftsverlage 1999. ISBN 978-3-540-52688-9 . P. 752 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition, 2006, p. 962, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b Lomefloxacin hydrochloride data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 8, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher and Dietmar Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances, 4th edition (2000), 2 volumes published by Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9 ; online since 2003 with biannual additions and updates.
- ^ EJ Ariëns: Stereochemistry, a basis for sophisticated nonsense in pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology . In: European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26 (1984) pp. 663-668. PMID 6092093 .
- ↑ Entry on lomefloxacin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 29, 2014.
Trade names
Maxaquin (CH), Okacin (D, A, CH)
