Myristicin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
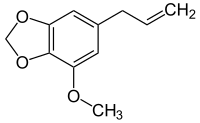
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Myristicin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 12 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Oil smelling of nutmeg |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 192.2 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.1416 (20 ° C ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
276.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5403 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Myristicin is a phenylpropanoid and an essential ingredient in nutmeg essential oil . It belongs to the group of MAO inhibitors .
Occurrence
Myristicin is part of the essential oil of some aromatic plants. It is contained in nutmeg ( Myristica fragrans ) and in many umbellifers , for example in dill ( Anethum graveolens ), lovage ( Levisticum officinale ), parsnips ( Pastinaca sp.) And parsley ( Petroselinum crispum ). In the essential oil of the Australian red family Zieria , the proportion is up to 23.4%.
Structurally related ones are safrole , elemicin and apiol .
use
Nutmeg used to be used for abortion when ground in beer. In Indonesia, the home of the nutmeg trees, a sedative was also made from the essential oil of nutmeg.
It was also used as an insecticide and disinfectant in the past due to its toxic effects on microorganisms.
Pharmacological properties
Myristicin is hallucinogenic . The psychotropic effect is due to its nature as a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor .
Myristicin, like many other phenylpropanes with a terminal methylenedioxy group, can damage DNA. It is therefore considered carcinogenic and genotoxic. Since this also happens in the zygote, it has an abortion effect.
Legal status
While mescaline and MDMA are banned, nutmeg is available over the counter. The strongly psychoactive, myristicin-containing oil is in a legal gray area.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Safrol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-382.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on myristicin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Myristicin data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ Peter Nuhn: Naturstoffchemie , S. Hirzel Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 1990, p. 528, ISBN 3-7776-0473-9 .
- ↑ a b Alexander Shulgin: Possible implication of myristicin as a psychotropic substance . In: Nature . No. 210 , 1966, pp. 380-384 .
- ↑ a b c Christian Rätsch: Encyclopedia of psychoactive plants . Aarau 2007.
- ↑ a b Michael Wink, Coralie Wink, Ben-Erik van Wyk: Handbook of poisonous and psychoactive plants . Stuttgart 2008.
- ↑ Stein, Hentschel: Nutmeg (myristicin) poisoning - report on a fatal case and a series of cases reported by a poison information center . In: Forensic science international . No. 118 , 2001, p. 87-90 .
literature
- Shulgin, Alexander: Psychotropic Phenylisopropylamines derived from Apiole and Dillapiole , in: Nature , 1967 , Vol. 215, pp. 1494-1495; PMID 4861200 .
Web links
- Fragrance dictionary: Myristicin ( Memento from March 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive )

