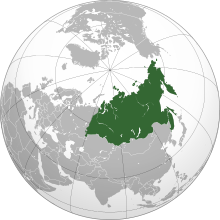
North asia
North Asia is a large region in the north of the continent of Asia .
There are two different delimitations:
- mostly the Asian part of Russia , consisting of the Urals federal districts (Asian part), Siberia and the Far East ; this area is often referred to as a whole as Siberia .
- sometimes also Mongolia , which is usually assigned to East Asia .
In the west, North Asia borders the European part of Russia. This limit is determined by the watershed of the Ural formed. In the south, North Asia is bounded by the states of Central Asia and China and possibly by Mongolia. The northern border is formed by the Arctic Ocean , the eastern border by the Pacific Ocean .
history
The Mongol Empire , established in the 13th century, also encompassed the south of North Asia. After the fall of the Golden Horde around 1500, Russian Cossacks , traders and colonists invaded the east, founded settlements and traded, especially in furs and precious metals.
In 1582 the Cossacks conquered the Tatar Khanate of Sibir near today's Tobolsk ; around 1600 the last Khan fled. The advance of the Cossacks took place along the Siberian rivers and in 1607 they reached the Yenisei , in 1632 the Lena , until they reached the Pacific in 1636 . However, the Siberian peoples such as the Buryats , Khanty and Koryaks offered resistance and so the Russian conquest of Siberia dragged on until the beginning of the 18th century.
In 1689 the Russians and Chinese signed the Treaty of Nercink , in 1727 the Treaty of Kjachta , in both of which borders and trade were regulated. A research expedition led Bering to Kamchatka, other important discoverers were Gerhard Friedrich Müller and Johann Georg Gmelin . In 1829 Alexander von Humboldt also traveled through Siberia.
Khabarovsk was founded in 1858 and - according to the Aigun treaty with China - Vladivostok in 1860. In 1891, the symbolic first groundbreaking for the Trans-Siberian Railway , which was open for the first time in autumn 1904, took place.
1915 was the second Treaty of Kyakhta , the Outer Mongolia autonomous rights . In 1921 the Soviet Union installed a puppet government in Outer Mongolia , which in 1924 proclaimed the Mongolian People's Republic as a Soviet satellite state .
As early as 1920, Soviet Russia had founded the Far Eastern Republic as a " buffer state " .
For the history see also the history of Siberia and the history of the Russian Far East .