Phentolamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
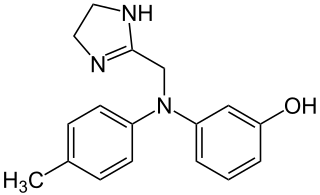
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Phentolamine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 19 N 3 O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, crystalline, slightly hygroscopic powder (phentolamine mesilate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 281.35 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
174-175 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
7.7 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Easily soluble in water and ethanol 96%, practically insoluble in dichloromethane (phentolamine mesilate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Phentolamine is a medicinal substance that cancels out the effects of certain endogenous messenger substances ( hormones , neurotransmitters ) and thereby primarily has the effect of expanding arteries.
Pharmacologically, it is a substance from the group of non-selective alpha blockers . As competitive antagonists of α 1 - and α 2 -adrenoceptors , alpha blockers abolish the effects of catecholamines , such as adrenaline and noradrenaline .
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Phentolamine lowers blood pressure, increases heart rate and decreases venous tone. In intensive care medicine, it is used in adults at a dosage of 50 to 500 µg / min.
Pheochromocytoma
The drug is used to treat blood pressure crises in pheochromocytoma - a tumor that produces catecholamines ( noradrenaline , adrenaline and metanephrine ) - for example, during preoperative preparation and surgical intervention.
Phentolamine inhibition test
The phentolamine inhibition test , also known as the phentolamine suppression test , is a diagnostic function test to determine autonomous catecholamine production, as occurs, for example, in pheochromocytoma. It is carried out if the findings are unclear. Suppression means that the release of hormones is inhibited or suppressed. In the Regitin test - as it is also called - phentolamine is administered to those affected and the pheochromocytoma is detected on the basis of the drop in systolic blood pressure after the intravenous injection of phentolamine.
Use as an antidote
In the case of intoxication by indirect sympathomimetics such as cocaine , amphetamine and amphetamine-like substances, a blockade of the alpha receptors is indicated if the patient's sedation alone is not sufficient. The antidote phentolamine is the drug of choice for the treatment of tachycardia and arterial hypertension . A beta blockade alone can lead to severe hypertensive complications due to the unimpeded effect on the alpha receptors.
Erectile dysfunction
Phentolamine is indicated in combination with papaverine or with aviptadil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction .
Dentistry
The in dentistry commonly used local anesthetics are usually with epinephrine as a vasoconstrictor combined to the blood vessels constrict and prevent the anesthetic does not drain away too quickly from the injection site. As a side effect of local dental anesthesia , hours after the treatment, paresthesia (false sensation) of the lip, tongue or both organs (loss of sensation, burning, tingling) up to general numbness or numbness ( sensory disturbances) can occur.
Phentolamine mesilate causes the anesthetic to drain off by widening the blood vessels and the associated increased blood flow rate (abolition of the epinephrine effect). In clinical trials, the drug reduced the time it took to regain lip sensation to 75 to 85 minutes, more than half. Novalar Pharmaceuticals , a small drug company from San Diego , received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for this dental indication (trade name OraVerse ) in May 2008 . It has been approved in Germany since the beginning of 2011 and has been available in stores since 2013.
Contraindications (contraindications)
Phentolamine must not be used if you are known to be hypersensitive to the drug . An absolute contraindication is hypotension , a myocardial infarction (heart attack), also in the anamnesis , coronary insufficiency, angina pectoris or other indications of a coronary disease, gastritis and a peptic ulcer .
See also
literature
- Ernst Mutschler among others: Mutschler - drug effects textbook of pharmacology and toxicology . 9th edition. Scientific Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8047-1952-1 .
- Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. (1st edition 1986) 5th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 1999, ISBN 3-540-65024-5 , pp. 65-69 and 76.
Trade names
- OraVerse (USA)
- Regitin (Switzerland), no longer in trade
- with papaverine: Androskat (A, NL)
- with Aviptadil: Invicorp (DK)
Web links
- MeSH phentolamine
- FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Division of Anesthesia, Analgesia and Rheumatology Products: Phentolamine Mesylate, OraVerse Clinical Review May 5, 2008 (PDF; 4.9 MB)
- FDA - Clinical Pharmacology Review of OraVerse; NV-101 (PDF; 3.8 MB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 5TH EDITION . tape 5.0-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b Entry on phentolamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ Sean Sweetman (Ed.): Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 35th Edition: Book and CD-ROM Package . Pharmaceutical Press, ISBN 0-85369-704-3 .
- ↑ a b Datasheet Phentolamine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 19, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. 1999, p. 76.
- ^ Dossier on pheochromocytoma .
- ↑ Antidotes in poisoning from the Swiss Toxicological Information Center 2008 (PDF; 233 kB).
- ↑ EV Hersh et al .: Reversal of soft-tissue local anesthesia with phentolamine mesylate in adolescents and adults. In: J Am Dent Assoc . 2008 Aug; 139 (8), pp. 1080-1093, PMID 18682623 .
- ↑ M. Tavares et al .: Reversal of soft-tissue local anesthesia with phentolamine mesylate in pediatric patients. In: J Am Dent Assoc. 2008 Aug; 139 (8), pp. 1095-1104, PMID 18682624 .
- ↑ OraVerse - the current status of the ZMK.