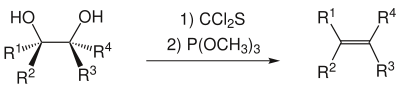Thiophosgene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thiophosgene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Thiocarbonyl chloride |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CCl 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red to orange-red liquid with an unpleasant odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 114.98 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.5 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
73 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes in water and alcohol |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5442 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Thiophosgene is an orange-red to red, malodorous liquid. It is the sulfur analog ( thio compound ) of phosgene and can be used for analogous reactions , such as the introduction of a thio carbonyl group . Since working with gaseous phosgene should be avoided if possible because of its high toxicity, the use of liquid thiophosgene is often advisable for reasons of easier handling and the lower outlay on equipment.
Manufacturing
Thiophosgene can be synthesized from trichloromethanesulfenyl chloride and iron (III) chloride as a catalyst in xylene at 140 ° C.
The reaction can also be carried out in benzene or toluene with zinc chloride or aluminum chloride as a catalyst .
properties
Thiophosgene is a red, foul-smelling and poisonous liquid. In water, the compound hydrolyzes to hydrochloric acid and carbon oxide sulfide , which further reacts to hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide .
The hydrolysis is much slower than with phosgene . When thiophosgene is heated it is disproportionated to carbon disulfide and carbon tetrachloride .
Thiophosgene sometimes reacts violently and strongly exothermically with nucleophilic solvents such as B. alcohols , amines and acids and bases. The compound can be photochemically dimerized to 2,2,4,4-tetrachloro-1,3-dithietane.
Thiophosgene forms flammable vapor-air mixtures at higher temperatures. The compound has a flash point of 63 ° C.
use
Thiophosgene is used for the production of dyes , pesticides , fungicides and nematicides . It was also used in the past to manufacture chemical warfare agents . In synthetic organic chemistry, it is used as a reagent for the production of thiocarbonyl compounds. It reacts with amines to form isothiocyanates , substituted thioureas or thiocarbamoyl chlorides .
The reaction with 1,2-diols enables the stereoselective production of alkenes in a Corey-Winter elimination .
The compound can also react as a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions . With bisphenol A , polythiocarbonates result.
toxicology
Thiophosgene is a highly toxic and caustic compound. The vapors are very irritating to the eyes, the respiratory tract, the lungs and the skin. The formation of pulmonary edema is possible. The compound is a lung irritant. An inhalation can lead to life-threatening conditions. Contact with the liquid causes very severe irritation to the skin or eyes. It is assumed that life-threatening doses are absorbed through the skin, which makes the strictest skin protection measures necessary when handling.
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 .
- Sharma, S .: Thiophosgene in Organic Synthesis . In: Synthesis , 11, 1978, 803-820; doi : 10.1055 / s-1978-24896 (review article in English, free full text)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on thiophosgene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Entry on thiophosgene. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 2, 2017.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-88.
- ↑ Entry on Thiocarbonyl chloride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Patent US2668853 : Production of thiophosgene. Filed October 12, 1950 , published February 9, 1954 , applicant: Sharples Chemicals, inventor: Edward F. Orwoll.
- ↑ a b L. Roth, U. Weller: Hazardous chemical reactions , entry for thiophosgene, status 81. Supplementary delivery 4/2017, ecomed Verlag Landsberg / Lech, ISBN 978-3609195872 .
- ↑ Schönberg, A .; Stephenson, A .: About the constitution of the photodimeric thiophosgene (23rd part. About organic sulfur compounds) in Ber. German. chem. Ges. 66B (1933) 567-571, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19330660425 .
- ↑ Krebs, B .; Beyer, H .: The crystal and molecular structure of the dimeric thiophosgene in Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 365 (1969) 199-210, doi : 10.1002 / zaac . 19693650315 .
- ↑ a b c e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis , 1999-2013, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., entry for Thiophosgene, doi : 10.1002 / 047084289X.rt103.pub2