Tebbe reagent
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
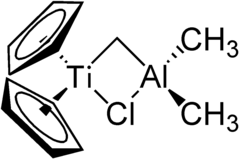
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tebbe reagent | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
μ-chlorobis (cyclopentadienyl) - (dimethylaluminum) -μ-methylene titanium ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 18 AlClTi | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 284.62 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.93 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
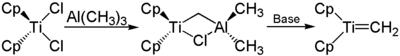
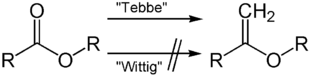
The Tebbe reagent (after Frederick Nye Tebbe , Fred Tebbe for short) is an organometallic compound that is used for the methylenation of ketones or esters , the Tebbe methylenation . It is a two-core bridged complex with a titanium and an aluminum core. Two cyclopentadienyl residues are bound to the titanium core, which is linked to the aluminum core via a methylene group and a chlorine bridge . There are still two methyl residues on the aluminum core . The Tebbe reagent is a pyrophoric red solid and is therefore only handled under protective gas . It is mostly commercially available as a solution (for example: in toluene ).
Manufacturing
Tebbe reagent is prepared from titanocene dichloride (Cp 2 Cl 2 Ti) and trimethylaluminum by stirring for three days at room temperature. The Schrock carbene actually required for methylenation can be obtained from this in situ by treatment with mild bases (for example pyridine ).
Reaction mechanism
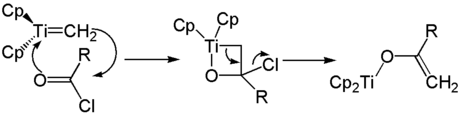
The Schrock carbene obtained by adding a base initially adds to the carbonyl component to form an Oxatitana cyclobutane . After ring opening, the methylenated product is obtained.
Similar to the case of phosphorus in the Wittig reagent , the affinity of titanium for oxygen is the driving force behind the reaction.
Range of use
In contrast to other olefinations (see Wittig reaction , Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction ), the use of the Tebbe reagent is limited to the introduction of methylene groups. However, when using the Tebbe reagent, esters can also be used which cannot be converted, for example, with the Wittig reaction.
Another area of application for the Tebbe reagent is the synthesis of titanium enolates . The oxatitanium acyclobutane derivative obtained from a carboxylic acid chloride and the Tebbe reagent decomposes to form the titanium enolate with elimination of the chloride ion .
Alternatives to the Tebbe reagent are the Petasis reagent and the Lombardo reagent .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Tebbe reagent data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 6, 2010 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b mattmatter: µ-Chlorobis (cyclopentadienyl) (dimethylaluminum) -µ-methylenetitanium ( Memento from January 31, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 184 kB).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ FN Tebbe, GW Parshall, GS Reddy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1978 , 100 , pp. 3611-3613.
- ↑ WA Herrmann, Advances in Organometallic Chemistry , 1982 , 20 , pp. 195-197.