Tiaprofenic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
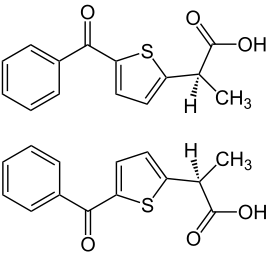
| 1: 1 mixture of two stereoisomers: ( R ) -form (top) and ( S ) -form (bottom) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Tiaprofenic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 12 O 3 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 260,31 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
96 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
3.0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water, easily soluble in acetone , dichloromethane and ethanol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tiaprofenic acid (trade name Surgam ; manufacturer Sanofi ) is a derivative of arylpropionic acid from the active ingredient group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory / anti-inflammatory drugs , which is used in the symptomatic treatment of inflammatory pain, swelling and fever.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Tiaprofenic acid is suitable for the symptomatic therapy of pain and inflammation in:
- Chronic arthritis , especially rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's disease) and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases of the spine
- Irritation in degenerative joint and spinal diseases (arthrosis and spondyloarthrosis )
- Acute arthritis, including gout attack
- Painful swelling or inflammation after injury
- Inflammatory fibromyalgia
- For wound care after surgical excision (e.g. for lipomas )
Contraindications (contraindications)
Hypersensitivity to the drug, acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Severe liver and kidney dysfunction , bronchial asthma , chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD or respiratory infections , allergic rhinitis (hay fever), gastrointestinal bleeding or other active bleeding . The use of tiaprofenic acid is not suitable for the treatment of children and adolescents under 18 years of age as there are insufficient data on safety and efficacy for this age group.
Drug interactions
The combined use of tiaprofenic acid with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including COX-2 inhibitors ) should be avoided. When taking anticoagulants such as phenprocoumon at the same time , the bleeding tendency can be increased. The simultaneous administration of tiaprofenic acid and methotrexate (agent for severe forms of polyarthritis) can lead to increased undesirable side effects of methotrexate. The effects of diuretics and antihypertensive agents can be weakened by tiaprofenic acid. In combination with loop diuretics ( e.g. furosemide ), kidney dysfunction can occur. If potassium-sparing dehydrating agents ( e.g. triamterene ) are administered at the same time , the potassium level in the blood serum increases with the risk of cardiac arrhythmias . The effects of medicines used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure may be weakened.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis can negatively affect pregnancy and embryo-fetal development . Data from epidemiological studies indicate an increased risk of miscarriages as well as cardiac malformations and gastroschisis after the use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. Animal studies have shown that the administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor leads to increased pre- and post-implantation loss and embryo-fetal lethality. In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular malformations, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the organogenesis phase . For the reasons mentioned, therapy with tiaprofenic acid is contraindicated in the third trimester of pregnancy .
There are no studies as to whether tiaprofenic acid is excreted in breast milk during breastfeeding . There is insufficient experience with the safety of the infant. The use of the drug during breastfeeding is not recommended.
Special patient groups (diabetics, kidney patients)
Since the Qo value of tiaprofenic acid is high (Qo = 0.55), no dose adjustment is necessary in the case of slightly impaired renal function. However, NSAIDs can lead to acute kidney failure if the maintenance of renal blood flow depends on renal prostaglandins. The risk of developing kidney failure is increased, among other things, with pre-existing renal insufficiency or with co-medication with ACE inhibitors . Accordingly, caution should be exercised in the case of severe kidney function impairments.
Adverse effects (side effects)
Often there are phototoxic and photoallergic reactions of the skin, very rarely photosensitization . Irritation and inflammation of the urinary bladder, stomatitis, inflammation of the tongue ( glossitis ), mediastinitis (esophageal lesions ), discomfort in the lower abdomen, constipation ( constipation ), increased transaminases , pancreatitis, sensory disorders, taste disorders, psychotic reactions , palpitations, chest pain, arterial hypertension , Heart failure, allergic vasculitis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis .
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Tiaprofenic is a Phenylpropionsäurederivat and belongs to the pharmacotherapeutic group of active substances of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which is on the prostaglandin synthesis inhibition proved in animal experiments in the usual models of inflammation to be effective. Tiaprofenic acid reduces inflammation-related pain, swelling and fever in humans. It also acts as a platelet aggregation inhibitor and inhibits adenosine diphosphate and collagen-induced platelet aggregation.
Absorption and distribution in the body (pharmacokinetics)
After oral administration , tiaprofenic acid is largely absorbed in the stomach and then completely from the small intestine . The metabolism takes place hepatically, the pharmacologically largely inactive metabolites are mainly eliminated renally , but also completely in the bile . The plasma half-life is 1.5–2.7 hours in healthy individuals; it is increased to 5.8 and 4.7 hours in patients with kidney disease and in old age. The plasma protein binding is 98-99%. Maximum plasma levels are reached after 1–3 hours after oral administration. The required therapeutically effective plasma concentration should be greater than 5 µg / ml. The absolute bioavailability after oral administration is around 100%.
toxicology
Symptoms of an overdose are central nervous disorders with headache , drowsiness and unconsciousness , as well as abdominal pain , nausea , vertigo (dizziness) and vomiting. Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract and functional disorders of the liver and kidneys are possible. It can also lead to hypotension (drop in blood pressure), respiratory depression and cyanosis . There is no specific antidote . Therapeutic measures for oral overdose consist primarily of vomiting or gastric lavage to remove toxins. Control and balancing of the water-electrolyte balance and the close-knit control of the vital functions are also part of the elementary aid. The LD 50 value for the mouse is 690 mg · kg −1 after oral administration.
Chemistry and isomerism
Tiaprofenic acid is chiral , i.e. it contains a stereocenter. There are thus two enantiomers , the ( R ) form and the ( S ) form. The commercial preparations contain the drug as a racemate (1: 1 mixture of enantiomers).
literature
- Ernst Mutschler et al .: Mutschler - drug effects textbook of pharmacology and toxicology . 8th edition. Scientific Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8047-1763-2 .
- Patent US2004067914 : R-NSAID esters and their use.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 5TH EDITION . tape 5.0-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b Entry on tiaprofenic acid in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Entry on tiaprofenic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on 2-fluoropyridine at TCI Europe, accessed on November 1, 2016.
- ↑ Surgam Data Sheet ( Memento from July 1, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) at Medsave, accessed on April 21, 2013 (PDF; 68 kB).
- ↑ Interactions with phenprocoumon - increased effectiveness - increased risk of bleeding Pharmacy of the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz clinic
- ↑ a b c Surgam® specialist information from Aventis Pharma Deutschland GmbH .13. November 2007
- ↑ Dose adjustment in case of renal insufficiency with Dosing ( Memento of July 20, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Phototoxic and photoallergic reactions ( Memento from April 2, 2010 in the Internet Archive ). Guidelines of the German Dermatological Society (DDG).
- ↑ Defense against dangers: Systemically used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices BfArM .
- ↑ W. Forth, D. Henschler, W. Rummel: General and special pharmacology and toxicology . 9th edition. URBAN & FISCHER, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-437-42521-8 .
- ↑ Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 9, Pg. 715, 1975 .