Air Force Research Laboratory: Difference between revisions
m →Organization: Ref clean-up |
m →Directed Energy Directorate: Replaced AF ref for Starfire with non-AF |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
The Directed Energy Directorate "is the Air Force's center of excellence for high power microwave technology and the Department of Defense's center of expertise for laser development, including semiconductor, gas, chemical and solid-state lasers."<ref name="factsheet" /> The current Director of the Directed Energy Directorate is Susan Thornton.<ref name="bios" /> |
The Directed Energy Directorate "is the Air Force's center of excellence for high power microwave technology and the Department of Defense's center of expertise for laser development, including semiconductor, gas, chemical and solid-state lasers."<ref name="factsheet" /> The current Director of the Directed Energy Directorate is Susan Thornton.<ref name="bios" /> |
||
The [[Starfire Optical Range]] at [[Kirtland AFB]], [[North Oscura Peak]] on [[White Sands Missile Range]], and the [[Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing observatory]] (AMOS) are also operated by divisions of the Directed Energy Directorate in addition to their facilities at the Directorate's headquarters at Kirtland AFB.<ref name="factsheet" /> The Starfire Optical Range is used to research various topics of advanced tracking using lasers as well as studies of atmospheric physics which examines atmospheric effects which can distort laser beams.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www. |
The [[Starfire Optical Range]] at [[Kirtland AFB]], [[North Oscura Peak]] on [[White Sands Missile Range]], and the [[Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing observatory]] (AMOS) are also operated by divisions of the Directed Energy Directorate in addition to their facilities at the Directorate's headquarters at Kirtland AFB.<ref name="factsheet" /> The Starfire Optical Range is used to research various topics of advanced tracking using lasers as well as studies of atmospheric physics which examines atmospheric effects which can distort laser beams.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.engadget.com/2006/06/28/starfire-optical-range-a-death-ray-for-sciences-sake/ | title=Starfire Optical Range -- a death ray for science's sake | accessdate=2008-07-20 | last=Miller | first=Paul | date=2006-06-28 | publisher=Engadget}}</ref> [[North Oscura Peak]] is used to research the various technologies necessary to facilitate successful tracking and destruction of an incoming missile via a laser and is used frequently for laser-based missile defense tests.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/facility/oscura.htm | title=Oscura Range | author=GlobalSecurity.org | publisher=GlobalSecurity.org | accessdate=2008-07-19}}</ref> AMOS provides space observation capabilities and computational resources to AFRL, the Department of Defense and other agencies of the US Government.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/track/amos.htm | title=Air Force Maui Optical Station | author=Federation of American Scientists | accessdate=2008-07-19}}</ref> |
||
Directed Energy projects typically fall into two categories: [[laser]] and [[microwave]]. Laser projects range from completely non-lethal targeting lasers to [[dazzler (weapon)| dazzler]]s such as the [[Saber 203]] used by US forces during the [[Somali Civil War]] and the more recent [[Personnel Halting and Stimulation Response rifle| PHaSR]] dazzler<ref name="phasr">{{cite web | url=http://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=dn8275 | title=US military sets laser PHASRs to stun | accessdate=2008-07-02 | last=Knight | first=Will | date=2005-11-07 | publisher=New Scientist}}</ref> to powerful missile defense lasers such as the [[chemical oxygen iodine laser]] (COIL) used in the [[Boeing YAL-1| YAL-1A]] project now led by the [[Missile Defense Agency]].<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/space/systems/abl.htm | title=Airborne Laser | accessdate=2008-07-17 | author=GlobalSecurity.org | publisher=GlobalSecurity.org}}</ref> A continuation of the Airborne Laser experiment is also being conducted in the form of the [[Advanced Tactical Laser]], which is a [[Air Force Special Operations Command | Special Forces]] demonstrator project to mount a COIL system in a tactical [[Lockheed AC-130 | AC-130]] aircraft.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.popsci.com/scitech/article/2004-06/advanced-tactical-laser | title=Advanced Tactical Laser | date=2004-06-01 | accessdate=2008-07-17 | last=Adams | first=Eric | publisher=Popular Science}}</ref> Microwave technologies are being advanced for use against both electronics and personnel. One example of an anti-personnel microwave project is the "less-than-lethal" [[Active Denial System]] which uses high powered microwaves to penetrate less than a millimeter into the target's skin where the nerve endings are located.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1540562/US-unveils-%27heat-gun%27.html | accessdate=2008-07-17 | title=US unveils 'heat gun' | last=Hooper | first=Duncan | publisher=Daily Telegraph | date=2007-01-26}}</ref> |
Directed Energy projects typically fall into two categories: [[laser]] and [[microwave]]. Laser projects range from completely non-lethal targeting lasers to [[dazzler (weapon)| dazzler]]s such as the [[Saber 203]] used by US forces during the [[Somali Civil War]] and the more recent [[Personnel Halting and Stimulation Response rifle| PHaSR]] dazzler<ref name="phasr">{{cite web | url=http://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=dn8275 | title=US military sets laser PHASRs to stun | accessdate=2008-07-02 | last=Knight | first=Will | date=2005-11-07 | publisher=New Scientist}}</ref> to powerful missile defense lasers such as the [[chemical oxygen iodine laser]] (COIL) used in the [[Boeing YAL-1| YAL-1A]] project now led by the [[Missile Defense Agency]].<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/space/systems/abl.htm | title=Airborne Laser | accessdate=2008-07-17 | author=GlobalSecurity.org | publisher=GlobalSecurity.org}}</ref> A continuation of the Airborne Laser experiment is also being conducted in the form of the [[Advanced Tactical Laser]], which is a [[Air Force Special Operations Command | Special Forces]] demonstrator project to mount a COIL system in a tactical [[Lockheed AC-130 | AC-130]] aircraft.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.popsci.com/scitech/article/2004-06/advanced-tactical-laser | title=Advanced Tactical Laser | date=2004-06-01 | accessdate=2008-07-17 | last=Adams | first=Eric | publisher=Popular Science}}</ref> Microwave technologies are being advanced for use against both electronics and personnel. One example of an anti-personnel microwave project is the "less-than-lethal" [[Active Denial System]] which uses high powered microwaves to penetrate less than a millimeter into the target's skin where the nerve endings are located.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1540562/US-unveils-%27heat-gun%27.html | accessdate=2008-07-17 | title=US unveils 'heat gun' | last=Hooper | first=Duncan | publisher=Daily Telegraph | date=2007-01-26}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 22:09, 20 July 2008
| Air Force Research Laboratory | |
|---|---|
 Emblem of AFRL | |
| Active | October 1997-Present |
| Country | United States |
| Branch | Air Force |
| Type | Research and development |
| Size | 4,200 civilian 1,200 military (2006) |
| Part of | Air Force Materiel Command |
| Garrison/HQ | Wright-Patterson Air Force Base |
| Commanders | |
| Commander | Maj Gen Curtis Bedke |
| Vice-Commander | Col David Glade |
The United States Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to the development of warfighting technologies.[1] It was "stood up" at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio on October 31, 1997 as a consolidation of 13 Air Force laboratory facilities and the Rome Air Development Center under a unified command. The Laboratory is composed of 8 Technical Directorates, 1 Wing, and the Office of Scientific Research. It controls the entire Air Force science and technology research budget which was $2.4 billion in 2006.[2]
Mission Statement
AFRL's published mission statement is[1]:
- Leading the discovery, development and integration of affordable aerospace warfighting technologies;
- Planning and executing the Air Force science and technology program;
- Provide warfighting capabilities to United States air, space and cyberspace forces.
History
The path to a consolidated Air Force Research Laboratory began with the passage of the Goldwater-Nichols Act which was designed to streamline the use of resources by the Department of Defense.[3] In addition to this Act, the end of the Cold War began a period of budgetary and personnel reductions within the armed forces in preparation for a "stand-down" transition out of readiness for a global war with the Soviet Union.[4] Prior to 1990, the Air Force laboratory system spread research out into 13 different laboratories and the Rome Air Development Center which each reported up two separate chains of command: a product center for personnel, and the Air Force Systems Command Director of Science & Technology for budgetary purposes.[5] Bowing to the constraints of a reduced budget and personnel, the Air Force merged the existing research laboratories into four "superlabs" in December 1990.[6] During this same time period, the Air Force Systems Command and Air Force Logistics Command merged to form Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) in July 1992.[7]
| Pre-Merger | Post-Merger |
|---|---|
| Weapons Laboratory, Kirtland AFB, NM | Phillips Laboratory Kirtland AFB |
| Geophysics Laboratory, Hanscom AFB, MA | |
| Astronautics Laboratory, Edwards AFB, CA | |
| Avionics Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | Wright Laboratory Wright-Patterson AFB |
| Electronics Technology Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | |
| Flight Dynamics Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | |
| Material Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | |
| Aero Propulsion and Power Laboratory Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | |
| Armament Laboratory, Eglin AFB, FL | |
| Rome Air Development Center, Griffiss AFB, NY | Rome Laboratory Griffiss AFB, NY |
| Human Resources Laboratory, Brooks AFB, TX | Armstrong Laboratory Brooks AFB, TX |
| Harry G. Armstrong Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH | |
| Drug Testing Laboratory, Brooks AFB, TX | |
| Occupational and Environmental Health Laboratory, Brooks AFB, TX |
While the initial consolidation of Air Force laboratories reduced overhead and budgetary pressure, another push towards a unified laboratory structure came in the form of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 1996, Section 277. This section instructed the Department of Defense to produce a five-year plan for consolidation and restructuring of all defense laboratories.[9] The currently existing laboratory structure was created in October 1997 through the consolidation of Phillips Laboratory headquartered in Albuquerque, New Mexico, Wright Laboratory in Dayton, Ohio, Rome Laboratory (formerly Rome Air Development Center) in Rome, New York, and Armstrong Laboratory in San Antonio, Texas and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR).[10] The single laboratory concept was developed and championed by Maj Gen Richard Paul, then Director of Science & Technology for AFMC and Gen Henry Viccellio Jr, then Commander, AFMC.[11]

With the merger of the laboratories into a single entity, the history offices at each site ceased to maintain independent histories and all history functions were transferred to a central History Office located at AFRL HQ at Wright-Patterson AFB.[12] In homage to the predecessor laboratories, the new organization named four of the research sites after the laboratories and assured that each laboratories' history would be preserved as inactivated units.[13]
Organization
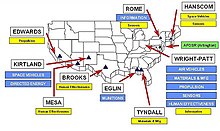
The laboratory is divided into 8 Technical Directorates, one wing, and the Office of Scientific Research based on different areas of research. AFOSR is primarily a funding body for external research while the other directorates perform research in-house or under contract to external entities.[1]
A directorate is roughly equivalent to a military wing. Each directorate is composed of a number of divisions and typically has at least three support divisions in addition to its research divisions.[14] The Operations and Integration Division provides the directorate with well-conceived and executed business computing, human resource management, and business development services while the Financial Management Division manages the financial resources and the Procurement Division provides an in-house contracting capability.[15] The support divisions at any given location frequently work together to minimize overhead at any given research site. Each division is then further broken down into branches, roughly equivalent to a military squadron.
Superimposed on the overall AFRL structure are the eight detachments. Each detachment is composed of the AFRL military personnel at any given geographical location.[16] For example, the personnel at Wright-Patterson AFB are all part of Detachment 1. Each detachment will typically also have a unit commander separate from the directorate and division structure.
Air Force Office of Scientific Research
The Office of Scientific Research, located in Arlington, Virginia, invests in basic research efforts for the Air Force by funding investigation in areas relevant scientific areas.[1] This work is performed in cooperation with private industry, academia, and other organizations in the Department of Defense and AFRL Directorates. The current Director of AFOSR is Brendan Godfrey.[17]
AFOSR's research is organized into three scientific directorates: the Aerospace, Chemical, and Material Sciences Directorate; the Mathematics, Information, and Life Sciences Directorate; and the Physics and Electronics Directorate.[18] Each directorate funds research activities which it believes will enable the technological superiority of the Air Force.
AFOSR also maintains two foreign technology offices located in London, United Kingdom and Tokyo, Japan. These overseas offices coordinate with the international scientific and engineering community to allow for better collaboration between the community and Air Force personnel.[19]
Air Vehicles Directorate

The Air Vehicles Directorate is located at Wright-Patterson AFB and its vision is on "technology investments that support cost-effective, survivable aerospace vehicles capable of accurate and quick delivery of a variety of future weapons or cargo anywhere in the world."[1] The current Director of the Air Vehicles Directorate is Col John Wissler.[17]
The Air Vehicles Directorate has previously collaborated with NASA in the X-24 project to research concepts associated with lifting body type aircraft.[20] The X-24 was one of a series of experimental aircraft, including the M2-F1, M2-F2, HL-10, and HL-20, by NASA and Air Force programs to develop the lifting body concept into maturity. The tests conducted during these programs led to the choice of an unpowered landing for the Space Shuttle program.[21]
In 2002, the Directorate initiated the X-53 Active Aeroelastic Wing program in cooperation with NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center and Boeing Phantom Works to research ways to make more efficient use of the wing's planform during high-speed maneuvers.[22] The Directorate is also a collaborator with DARPA, and AFRL's Space Vehicles Directorate on the FALCON program, which includes the HTV-3X Blackswift hypersonic flight demonstration vehicle[23] as well as collaboration on the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle.[24]
Directed Energy Directorate

The Directed Energy Directorate "is the Air Force's center of excellence for high power microwave technology and the Department of Defense's center of expertise for laser development, including semiconductor, gas, chemical and solid-state lasers."[1] The current Director of the Directed Energy Directorate is Susan Thornton.[17]
The Starfire Optical Range at Kirtland AFB, North Oscura Peak on White Sands Missile Range, and the Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing observatory (AMOS) are also operated by divisions of the Directed Energy Directorate in addition to their facilities at the Directorate's headquarters at Kirtland AFB.[1] The Starfire Optical Range is used to research various topics of advanced tracking using lasers as well as studies of atmospheric physics which examines atmospheric effects which can distort laser beams.[25] North Oscura Peak is used to research the various technologies necessary to facilitate successful tracking and destruction of an incoming missile via a laser and is used frequently for laser-based missile defense tests.[26] AMOS provides space observation capabilities and computational resources to AFRL, the Department of Defense and other agencies of the US Government.[27]
Directed Energy projects typically fall into two categories: laser and microwave. Laser projects range from completely non-lethal targeting lasers to dazzlers such as the Saber 203 used by US forces during the Somali Civil War and the more recent PHaSR dazzler[28] to powerful missile defense lasers such as the chemical oxygen iodine laser (COIL) used in the YAL-1A project now led by the Missile Defense Agency.[29] A continuation of the Airborne Laser experiment is also being conducted in the form of the Advanced Tactical Laser, which is a Special Forces demonstrator project to mount a COIL system in a tactical AC-130 aircraft.[30] Microwave technologies are being advanced for use against both electronics and personnel. One example of an anti-personnel microwave project is the "less-than-lethal" Active Denial System which uses high powered microwaves to penetrate less than a millimeter into the target's skin where the nerve endings are located.[31]
Going back as far as 1995, there were arguments that laser dazzlers could potentially cause permanent blindness in targets and these same concerns were revived with the announcement of the PHaSR project which is claimed to be a non-blinding laser weapon.[28] Due to concerns that even low-powered lasers could cause blindness, the Human Rights Watch proposed that all tactical laser weapons should be scrapped and research stopped by all interested governments.[32] The Active Denial System has also been the target of Amnesty International as well as, less directly, a United Nations special rapporteur as being a potential weapon of torture.[33]
711th Human Performance Wing
In March 2008, AFRL's Human Effectiveness Directorate located at Wright-Patterson AFB was merged with the Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine and the Human Performance Integration Directorate from the 311th Human Systems Wing both located at Brooks City-Base, Texas to form the 711th Human Performance Wing.[1] In its vision statement, the Directorate includes the goals of "integrating personnel with systems technology," and "protecting the force." Towards fulfilling those goals, the 711th HPW performs research to "define human capabilities, vulnerabilities, and effectiveness." The current Director of the 711th is Thomas Wells.[17] One practical application of its work is ensuring and advancing the safety of ejection systems for pilots[34]. With the increasing number of females in the Air Force ranks, anthropometry is of greater import now than ever, and 711th's WB4 'whole-body scanner' enables swift and accurate acquisition of anthropometric data which may be used to design pilot equipment with a better fit for comfort and safety.[35]
Information Directorate
The mission of the Information Directorate, located at the Rome Research Site in New York, is to lead the discovery, development, and integration of affordable warfighting information technologies for air, space, and cyberspace forces.[1] The current Director of the Information Directorate is Donald Hanson.[17]
The Information Directorate has contributed research to a number of technologies which have been deployed in the field. These projects include collaboration with other agencies in the development of ARPANET, the predecessor of the Internet, as well as technologies used in the Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System which is a key aspect of theater command and control for combat commanders.[36] The Directorate also collaborated with the Department of Justice performing research on voice stress analysis technologies.[37]
Materials and Manufacturing Directorate
The Materials and Manufacturing Directorate, located at Wright-Patterson AFB and Tyndall AFB, Florida, develops materials, processes, and advanced manufacturing technologies for aerospace systems and their components. The Directorate works to improve Air Force capabilities in manufacturing and materials research technologies.[1] The current Director of the Materials and Manufacturing Directorate is David Walker.[17] In 2006, an AFRL project to improve the strength of C-17 landing gear doors using composite materials was completed in cooperation with Boeing.[38] The AFRL has also been conducting research into friction stir welding for use in attaching difficult to weld materials together.[39] In 2008, the Air Force announced that the Directorate had developed a method of using fabric made of fiber optic material in a friend or foe identification system.[40]
Munitions Directorate
The mission of the Munitions Directorate, located at Eglin AFB, Florida, is to "develop, demonstrate and transition science and technology for air-launched munitions for defeating ground fixed, mobile/relocatable, air and space targets to assure pre-eminence of U.S. air and space forces."[1] The current Director of the Munitions Directorate is Col Kirk Kloeppel.[17] Notable projects which have been made public include the GBU-28 "bunker-buster" bomb which debuted during the 1991 Persian Gulf War in Iraq.[41] The Directorate also developed the GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast bomb which was deployed during the 2003 invasion of Iraq for Operation Iraqi Freedom and was the largest non-nuclear air-delivered munitions at that time.[42]
Propulsion Directorate
The mission of the Propulsion Directorate, located at Wright-Patterson AFB and Edwards AFB, is "to create and transition propulsion and power technology for military dominance of air and space."[1] The current Director of the Propulsion Directorate is William Borger.[17] Research areas range from experimental rocket propulsion to developing the first ever lithium-ion main aircraft battery for use in the B-2 stealth bomber.[43] At Edwards AFB, the Directorate's test area is located east of Rogers Lake.
The Propulsion Directorate was formed through the merger of the aerospace propulsion section at Wright Laboratory and the space propulsion section at Phillips Laboratory.[44] Each section, both before and after the merger, has played a significant role in past and present propulsion systems. Prior to the development of Project Apollo by NASA, the Air Force worked on the development and testing of the F-1 rocket engine used to power the Saturn V rocket.[45] The facilities for testing rockets are frequently used for testing new rocket engines including the RS-68 rocket engine developed for use on the Delta IV launch vehicle.[46] The space propulsion area also develops technologies for use in satellites on-orbit to alter their orbits. An AFRL-developed experimental Electric Propulsion Space Experiment (ESEX) arcjet was flown on the ARGOS satellite in 1999 as part of the Air Force Space Test Program.[47]
The Directorate currently manages the X-51A program, which is developing a scramjet demonstration vehicle.[48] In January 2008, the Directorate's experimental pulse detonation engine successfully completed it's first test flight on a significantly modified Scaled Composites Long-EZ aircraft.[49]
Sensors Directorate
The Sensors Directorate's vision is to provide a full range of air and space sensors, networked to the warfighter, providing a complete and timely picture of the battlespace enabling precision targeting of the enemy and protection friendly air and space assets and its core technology areas include: radar, active and passive electro-optical targeting systems, navigation aids, automatic target recognition, sensor fusion, threat warning and threat countermeasures.[1] The current Director of the Sensor Directorate is David Jerome.[17] The Directorate is located at Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio, Hanscom AFB, Massachusetts, and Rome Research Site, New York. The divisions currently located at Hanscom AFB and Rome Research Site are scheduled to move to Wright-Patterson AFB under the Defense Base Realignment and Closure, 2005 Commission.[50] The Directorate has contributed significantly to the Integrated Structure is Sensor (ISIS) project managed by DARPA which is a project to develop a missile tracking airship.[51] In June 2008, the Air Force announced that scientists working for the Sensors Directorate had demonstrated transparent transistors. These could eventually be used to develop technologies such as "video image displays and coatings for windows, visors and windshields; electrical interconnects for future integrated multi-mode, remote sensing, focal plane arrays; high-speed microwave devices and circuits for telecommunications and radar transceivers; and semi-transparent, touch-sensitive screens for emerging multi-touch interface technologies."[52]
Space Vehicles Directorate

The mission of the Space Vehicles Directorate is to develop and transition space technologies for more effective, more affordable warfighter missions.[1] In addition to the Directorate headquarters at Kirtland AFB, New Mexico and an additional research facility at Hanscom AFB, Massachusetts, the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program (HAARP) located near Gakona, Alaska is also jointly operated by the Space Vehicles Directorate as well as DARPA, the Office of Naval Research (ONR), the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) and universities to conduct ionospheric research.[53] The current Director of the Space Vehicles Directorate is Col Robert Green.[17] The Battlespace Environment division currently located at Hanscom AFB is scheduled to move to Kirtland AFB under the Defense Base Realignment and Closure, 2005 Commission.[50]
The IBM RAD6000 radiation hardened single board computer, now produced by BAE Systems, was initially developed in a collaboration with the Space Electronics and Protection Branch and IBM Federal Systems and is now used on nearly 200 satellites and robotic spacecraft, including on the twin Mars Exploration Rovers— Spirit and Opportunity.[54] In November 2005, the AFRL XSS-11 satellite demonstrator received Popular Science's "Best of What's New" award in the Aviation and Space category. [55] The Space Vehicles Directorate is also a leading collaborator in the Department of Defense Operationally Responsive Space Office's Tactical Satellite Program and served as program manager for the development of TacSat-2, TacSat-3, and is current program manager for the development of TacSat-5.[56] They also have contributed experimental sensors to TacSat-4 which is managed by the NRL's Center for Space Technology.[57]
The University Nanosatellite Program, a satellite design and fabrication competition for universities jointly administered by the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), AFOSR, AFRL, and the Space and Missile Systems Center, is also managed by the Space Vehicles Directorate's Spacecraft Technology division.[58] The fourth iteration of the competition was completed in March 2007 with the selection of Cornell University's CUSat as the winner.[59] Previous winners of the competition were University of Texas at Austin's Formation Autonomy Spacecraft with Thrust, Relnav, Attitude, and Crosslink (FASTRAC) for Nanosat-3 [60] and the joint 3 Corner Satellite (3CS) project by the University of Colorado at Boulder, Arizona State University and New Mexico State University for Nanosat-2.[61] As of July 2008[update], only the 3CS spacecraft has launched, however FASTRAC has a launch tentatively scheduled for December 2009.[62]
The Directorate has indirectly faced significant controversy over the HAARP project.[63] While the project claims to be developed only for studying the effects of ionospheric disruption on communications, navigation, and power systems, many suspect it of being developed as a prototype for a "Star Wars" type of weapon system.[64] Still others are more concerned with the environmental impact to migratory birds of beaming thousands of watts of power into the atmosphere.[65] However one thing which all sides can agree on is the shroud of secrecy around the project and the government's attempts to cover up information.[66]
References
![]() This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: http://www.afrl.af.mil
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: http://www.afrl.af.mil
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n US Air Force. "Factsheets : Air Force Research Laboratory". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-06-20.
- ^ Department of Defense Inspector General (2007-09-28). "Contracting Practices at Air Force Laboratory Facilities". Department of Defense. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
- ^ United States Congress (1986-04-08). "S. 2295. Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1986" (PDF). 99th Congress, Second Session. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ Duffner, Robert (2000). Science and technology: the making of the Air Force Research Laboratory (PDF). Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama: Air University Press. pp. pg 9. ISBN 1-58566-085-X. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Duffner 2000: 18
- ^ Duffner 2000: 11
- ^ US Air Force. "Factsheets : Air Force Materiel Command". AFMC. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ Duffner 2000: 12
- ^ United States Congress. "S.1124 National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 1996, Section 277". 104th Congress, Second Session. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ Duffner 2000: 117
- ^ Duffner 2000: 38
- ^ Duffner 2000: 257
- ^ Duffner 2000: 261
- ^ Duffner 2000: 190
- ^ Duffner 2000: 227-251
- ^ Duffner 2000: 262
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j US Air Force. "Air Force Research Laboratory Biographies". AFMC. Retrieved 2008-07-12.
- ^ US Air Force. "AFOSR Fact Sheet". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ US Air Force. "Factsheets : AFOSR : About - Mission". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ Reed, R. Dale (1997). Wingless Flight: The Lifting Body Story. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. pp. pp. 129-143. ISBN 0-16-049390-0.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Reed 1997: 128
- ^ Cole, William. "Let's Twist Again! : Technology that enables wing 'warping' rolled out at Dryden". Boeing Frontiers Online. Boeing. Retrieved 2008-06-29.
- ^ Kleiman, Michael (2006-01-27). "High-speed air vehicles designed for rapid global reach". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
- ^ David, Leonard (2008-11-17). "U.S. Air Force Pushes For Orbital Test Vehicle". Space.com. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ Miller, Paul (2006-06-28). "Starfire Optical Range -- a death ray for science's sake". Engadget. Retrieved 2008-07-20.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org. "Oscura Range". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ Federation of American Scientists. "Air Force Maui Optical Station". Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ a b Knight, Will (2005-11-07). "US military sets laser PHASRs to stun". New Scientist. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org. "Airborne Laser". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- ^ Adams, Eric (2004-06-01). "Advanced Tactical Laser". Popular Science. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- ^ Hooper, Duncan (2007-01-26). "US unveils 'heat gun'". Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- ^ "U.S. Blinding Laser Weapons". Human Rights Watch Arms Project. Human Rights Watch. 1995. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Wright, Steve (2006-10-05). "Targeting the pain business". The Guardian. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ^ US Air Force (1999). "Air Force Research Laboratories Success Stories: A Review of 1997/1998" (PDF). AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Cyberware. "Wright-Patterson to Use the First Whole Body Scanner". Retrieved 2008-07-13.
- ^ US Air Force. "AFRL Information Directorate Overview" (PPT). AFRL. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ Air Force News Service (1997-09-23). "Voice stress analysis evaluation begins". Retrieved 2008-07-06.
- ^ US Air Force. "AFRL Improves Durability For C-17 Main Landing Gear Doors". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ^ US Air Force. "Friction Stir Welding Provides Advantages Over Conventional Fusion Welding Process". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ^ Cooper, Mindy (2008-01-24). "Air Force develops friend vs. foe identification system". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ^ US Air Force. "Factsheets : AFRL Munitions Directorate History". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-10.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org. "GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast Bomb". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ US Air Force (2003). "Air Force Research Laboratories Success Stories: A Review of 2002". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ Duffner 2000: 169
- ^ California Space Authority (2004-01-14). "Huge Rocket Component Test Stand Completed". Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ Skeen, Jim (2001-08-13). "Rocket Lab May Benefit From Renewed Interest In Missiles Edwards Facility Has Been Involved In Most Major Propulsion Projects". Los Angeles Daily News. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ Boeing (1999-01-06). "ARGOS Satellite Serves as Platform for Leading-Edge Technology and Research". Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ Boeing (2007-06-01). "Successful Design Review and Engine Test Bring Boeing X-51A Closer to Flight". Retrieved 2008-06-14.
- ^ Warwick, Graham. "US AFRL proves pulse-detonation engine can power aircraft". Flightglobal. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ a b Principi, Anthony J. (2005-09-08). "2005 Defense Base Closure and Realignment Commission Report: Volume 1" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-07-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Staff Writers (2006-05-22). "AFRL Awards ISIS Contracts To Northrup Grumman". Space Daily. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ^ Lachance, Molly (2008-06-19). "Air Force Scientists Develop Transparent Transistors". Space Mart. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ^ University of Alaska. "HAARP Fact Sheet". Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- ^ Fordahl, Matthew (2004-01-23). "Software on Mars rovers 'space qualified'". Associated Press. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- ^ "Experimental Satellite System 11 (XSS-11)". Popular Science. 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-05-27. Retrieved 2008-07-06.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 2006-12-12 suggested (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Doyne, Col Tom (2007-04-23). "ORS and TacSat Activities Including the Emerging ORS Enterprise" (PDF). 5th AIAA Responsive Space Conference. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Raymond, Col Jay (2005-04-26). "A TacSat Update and the ORS/JWS Standard Bus" (PDF). 3rd AIAA Responsive Space Conference. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ US Air Force. "University Nanosatellite Program". AFRL. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ Staff Writers (2007-04-04). "Cornell University Chosen To Build Nanosat-4 Flight Experiment". Space Daily. Retrieved 2008-07-10.
- ^ Torres, Juliana (2005-01-21). "Students' satellites win right to space flight". The Daily Texan. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
- ^ NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. "Three Corner Satellite". NASA. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (2008-06-26). "FASTRAC Satellites Get Updated Software, New Antennas". University of Texas at Austin. Retrieved 2008-07-15.
- ^ Begich, Nick (1995). Angels Don't Play This HAARP: Advances in Tesla Technology. Earthpulse Press. ISBN 0-96488-120-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Smith, Jerry E. (1998). HAARP: The Ultimate Weapon of The Conspiracy. Adventures Unlimited Press. pp. pp. 21-22. ISBN 0-93281-353-4. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Streep, Abe (2008-06-18). "Scientific Tool or Weapon of Conspiracy?". Popular Science. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- ^ Smith 1998: 16
External links
- Air Force Research Laboratory Homepage (official)


