B.
B or b (spoken: [ beː ]) is the second letter of the classical and modern Latin alphabet . It represents a consonant in German . The letter B has an average frequency of 1.89% in German texts. It is the sixteenth most common letter in German texts .
Pronunciation in German
The grapheme B / b is basically assigned the phoneme / b /, i.e. the voiced bilabial plosive , as in tree, baby, love, seal . In contrast to his counterpart / p /, the latter is a voiced and non- aspirated Lenis . B / b is one of the obstruents that appear opposite each other in German in voiced-voiceless or Lenis-Fortis pairs: b ≠ p .
At the end of the word and syllable and in front of other voiceless obstruents, B / b is pronounced just like its actual Fortis - opposite P / p - i.e. as a voiceless bilabial plosive / p / ( dear, lovely, loves, crawls, pretty ). If voiceless / p / is spoken in related word forms, this is called final hardening : dear [-p], lovely [-pl-], loves [-pt] to love [-b-], crawls [-pt-] to crawl [-b-]; on the other hand, pretty [-pʃ] is without voiced equivalent, so no final hardening.
After a few voiceless obstruents, the pronunciation of b only almost coincides with that of p : lesbian . Here the realized sound lies between a b- and p-sound, is non-aspirated and more or less voiceless. From a phonological point of view, in the cases mentioned, in which the pronunciation deviates from the basic pronunciation (e.g. in the case of the final hardening of the voice), a neutralization takes place, i.e. the opposition voiced-voiceless or Lenis-Fortis is suspended in these positions and has here no longer a function that distinguishes meaning.
In some dialects it is sometimes in the Word inside and the letters as fricative spoken as the voiced labiodental fricative / v / or the voiced fricative bilabiale / β /.

The finger alphabet for the deaf or hard of hearing represents the letter B in the form of an open hand with folded thumbs .
Origin of the letter

|
 |

|
|
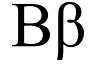
|
|
| Plan of a house (protosinaite) | Phoenician prayer | Ancient Greek Beta | Etruscan B | Greek beta | Latin B |
The Protosinaitic archetype of the letter represents the plan of a house with an exit. The Phoenicians gave the letter the name Bet (house), until the 9th century BC. The letter had become very abstract. Bet already had the sound value [b]. Depending on the writing tool, the letter could be written very square or rounded.
The Greeks took over the Phoenician letter, provided it with an additional curve and called it Beta. They kept the sound value. The Etruscans adopted this letter as "B" without modifying it. However, since the Etruscan language did not contain voiced plosives such as [b], they rejected the letter after a short time.
The early Greek script was written from right to left. When the Greeks changed the direction of writing, they also mirrored the beta. When the Romans created the Latin alphabet , which is also written from left to right, they based themselves on the Greek beta and adopted it without further modifications.
See also
- Β , β (beta), the second letter of the Greek alphabet
- Б , б (Be), the second letter of the Cyrillic alphabet
- В , в (We), the third letter of the Cyrillic alphabet
- Ⲃ , ⲃ (bēta), the second letter of the Coptic alphabet
- ב , the Hebrew letter Beth
- ب , the Arabic letter Bā '
- various UNICODE characters derived from the Latin B , b :
- ♭ , the musical symbol b or Be
- ␢ , a symbol of the spaces (English blank )
- B ...
- with acute: B́
- with a dash : Ƀ , ƀ
- with tick: Ɓ , ɓ (lower case letter also IPA symbol )
- with top bar: Ƃ , ƃ
- with middle tilde : ᵬ
- with palatal hook: ᶀ
- with a dot above: Ḃ , ḃ
- with a dot below: Ḅ , ḅ
- with line below: Ḇ , ḇ
- as small caps: ʙ (also IPA symbol), next to it with a dash : ᴃ
- superscript: ᴮ , ᵇ
- in handwriting: ℬ
- the LB ligature: ℔
- circled B: Ⓑ , ⓑ
- parenthesized lower case b: ⒝
literature
- B (letter). In: Johann Heinrich Zedler : Large complete universal lexicon of all sciences and arts . Volume 3, Leipzig 1733, column 1 f.
Web links
- Evolution of Alphabets (English)
