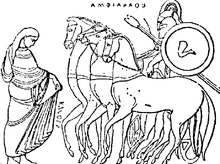
Amphiaraos
Amphiaraos ( ancient Greek Ἀμφιάραος Amphiáraos , also shortened Ἄμφις Ámphis ) is a seer of Zeus and a general from Argos in Greek mythology . He was the son of Oicles , of the house of the Melampids , and of Hypermnestra . He was also referred to as the son of Apollo , which is due to his visionary abilities. He married Eriphyle and with her fathered Amphilochus , Alkmaion , Eurydice , Demonassa and Alkmene .
myth
Hunt for the Calydonian Boar
Since Oineus , the king of Kalydon , one day forgot to include Artemis in his offerings, she sent a mighty boar to devastate the kingdom of the king. Therefore, this hero invited from all over Greece to hunt the animal. Amphiaraos was there too and hit the boar in the eye with his arrow after Atalante had wounded him. Meleagros , the son of Oineus, finally struck him down.
Argonauts legend
Amphiaraos is mentioned as a hero in the saga about the journey of the Argo by both Apollodorus and Pausanias . In the Argonautica of Apollonios of Rhodes , however, he is not listed as a participant.
Seven against Thebes
In Aeschylus ' Seven Against Thebes , Amphiaraos was the husband of Eriphyle, sister of Adrastus , the king of Argos from the house of the Biantides , his brother-in-law. Together with King Iphis , they ruled over the Argive land. There was a dispute between Amphiaraos and Adrastos. Ultimately, however, the two opponents agreed to leave the decision of the Eriphyle in future disputes between her husband and her brother.
In order to reinstate Polynices , his son-in-law, who had been expelled from Thebes by his brother Eteocles , Adrastus decided to launch a campaign against Thebes. Amphiaraos refused to obey the order to participate because he had foreseen the unfortunate outcome of the campaign and his own death. Without the participation of the “Eye of the Army”, as Amphiaraos was called, the other generals also refused to support them. Only when Eriphyle was bribed by Polynices with the necklace of Harmonia (on which, however, there was a curse), she persuaded her husband to participate. Due to the agreement between his brother-in-law, his wife and himself, Amphiaraos now had to join the campaign. Before he left, he asked his sons to kill their mother and to throw war on Thebes when they were adults.
During the attack on Thebes, Amphiaraos commanded part of the army that fought at the Proitic Gate. When Tydeus was fatally wounded by Melanippus , Athena wanted to come to his aid and make him immortal. Since Amphiaraos regarded Tydeus as the originator of the war, he prevented this by killing Melanippus, beheading him and giving his head to Tydeus. This slurped his brain out, whereupon Athena turned away in disgust and Tydeus died.
Another general, Kapaneus , exclaimed during the storm of the wall that even Zeus could not stop him, whereupon Zeus withdrew his benevolence from the attackers. Amphiaraos, the seer of Zeus, recognized this and turned his chariot to flee. Adrastus and his army also fled. Amphiaraos was pursued by the Theban hero Periklymenos and overtaken at a ford of Ismenos . In order to spare his seer an inglorious end on the run, Zeus tore open the earth with lightning. The Erdschlund devoured Amphiaraos including Baton or etalon , his charioteer, carriages and horses. The seer of Zeus was accepted among the gods of the underworld.
cult
The Tanagrians claimed that the place of his disappearance was at Harma (ancient Greek ἅρμα "carriage"). The Thebans gave a place between Potniai and Thebes. Near the place of his disappearance, near Oropos , later rose the Amphiareion , a sanctuary with a famous trauma oracle. Here he was first worshiped as a god. There were also sanctuaries of Amphiaraos in Thebes and Argos. In Lerna and at the Amphiareion there was an amphiaraos spring. Pausanias also reports a depiction of a duel between him and Lykurg, the son of Pronax .
Amphiaraos should in the first Nemean Games victory in the chariot race and in the discus have won.
swell
- Aeschylus , Seven against Thebes 568–608.
- Libraries of Apollodorus 1.68. 70, 103, 111; 3.60-77. 82. 129.
- Diodorus Siculus 4.65.5-9; 4.66.1; 4.68.5
- Herodotus 1.46; 1.49; 1.52; 1.92; 3.91; 8.134.
- Hesiod Eoien , 25.34; 197.6.
- Homer , Odyssey 15,244
- Hyginus Mythographus , Fabulae 73
- Pausanias , travels in Greece 1,8,2; 1.34.1-5; 2.13.7; 2.23.2; 2.37.5; 3.12.5; 3,18,12; 5.17.7-9; 7.17.7; 8,2,4; 8.45.7; 9,8,3; 9.18.1; 9.19.4; 10.10.3.
literature
- Oswald Wolff : Amphiaraos . In: Wilhelm Heinrich Roscher (Hrsg.): Detailed lexicon of Greek and Roman mythology . Volume 1.1, Leipzig 1886, Col. 293-303 ( digitized version ).
- Erich Bethe : Amphiaraos . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume I, 2, Stuttgart 1894, Sp. 1886-1893.
- Pierre Sineux: Amphiaraos. Guerrier, devin et guérisseur. Les Belles Lettres, Paris 2007, ISBN 978-2-251-32441-8 .
Web links
Remarks
- ↑ Erich Bethe : Amphis 1 . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume I, 2, Stuttgart 1894, Sp. 1953.
| predecessor | Office | successor |
|---|---|---|
|
Oikles (Melampide) |
King of Argos 13th century BC BC (mythical chronology) |
Amphilochos (Melampide) |