Asia-Pacific Economic Community
| Asia-Pacific Economic Community APEC |
|
|---|---|
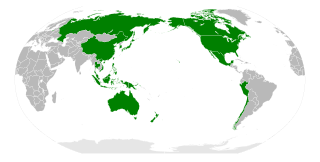 APEC members |
|
| Organization type | Forum |
| Member States | 21st |
| founding |
1989, Canberra |
| www.apec.org | |
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (for English Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation , shortly APEC , also translated as Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation or Asia-Pacific Forum ) is an international organization that has set itself the goal, in the Pacific region a free trade area set up .
Almost half of the world's population lives in the 21 APEC countries . The economic area generates more than half of the world's economic output and is one of the fastest growing economic regions in the world.
history

In 1989 - on the initiative of Australia, Japan and the USA - twelve countries founded APEC. In the first few years, only high-level ministry officials attended the annual meetings; the heads of government of the member states have been meeting since 1993. These meetings are called "Leaders' Meetings" and not the usual "summit" (summit).
At APEC level, numerous political - not just economic - issues have been and are being discussed. B. Future technologies, education , women , youth and the fight against international terrorism .
In 1994 in Bogor , Indonesia , the goal of establishing a free trade area in the Asia-Pacific region for the industrialized nations by 2010 and for the developing countries by 2020 was drawn up. To promote this goal, the member states have drawn up national action plans. The results are reviewed in the form of annual progress reports at the summit meetings.
From 1997 onwards, no new members were accepted for ten years. This period should serve to consolidate the cooperation.
Principles
APEC operates on the basis of non-binding agreements. All decisions of the forum are made by consensus . Since 2002 , bilateral or multilateral agreements with one another have also been permitted. The agreements must conform to the rules of the WTO . Apec members have signed more than 40 such agreements so far.
The APEC budget is relatively small. It amounts to just under 3.5 million US dollars per year, which is raised through membership fees of the APEC states. Japan alone is investing more money (3 to 4 million US dollars annually) in a special liberalization fund of the organization.
The meetings at APEC level are always accompanied by guests and observers. These include representatives from the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC), the Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) and other stakeholders from the public and private sectors. The APEC is also used as an opportunity to discuss the North Korea problem behind closed doors.
Meeting 2018 without a final declaration
The host of the country Papua New Guinea, Peter O'Neill , blamed China and the United States for ensuring that no joint final declaration was reached in 2018. "That's because there are two big giants in the room," he said. One of the disputed points was the question of reforms for the World Trade Organization ( WTO) . Justin Trudeau from Canada spoke more generally of different views on international trade.
Members
| APEC members | Member since |
|---|---|
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1989 |
|
|
1991 |
|
Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China, British Crown Colony until June 1997 |
1991 (1997) |
|
|
1991 |
|
|
1993 |
|
|
1993 |
|
|
1994 |
|
|
1998 |
|
|
1998 |
|
|
1998 |
APEC Leaders' Meetings
| date | Host | place | photo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | November 7, 1989 |
|
Canberra | |
| 2. | 29.-31. July 1990 |
|
Singapore | |
| 3. | 12-14 November 1991 |
|
Seoul | |
| 4th | 10-11 September 1992 |
|
Bangkok | |
| 5. | 19. – 20. November 1993 |
|
Seattle | |
| 6th | November 15, 1994 |
|
Bogor | |
| 7th | November 19, 1995 |
|
Osaka | |
| 8th. | November 25, 1996 |
|
Manila and Subic | |
| 9. | 24.-25. November 1997 |
|
Vancouver | |
| 10. | 17.-18. November 1998 |
|
Kuala Lumpur | |
| 11. | 12-13 September 1999 |
|
Auckland | |
| 12. | 15.-16. November 2000 |
|
Brunei |

|
| 13. | 20-21 October 2001 |
|
Shanghai |

|
| 14th | 26.-17. October 2002 |
|
Los Cabos | |
| 15th | 20-21 October 2003 |
|
Bangkok |

|
| 16. | 20-21 November 2004 |
|
Santiago de Chile |

|
| 17th | 18. – 19. November 2005 |
|
Busan |

|
| 18th | 18. – 19. November 2006 |
|
Hanoi |

|
| 19th | 8th-9th September 2007 |
|
Sydney |

|
| 20th | 22-23 November 2008 |
|
Lima |

|
| 21st | 14.-15. November 2009 |
|
Singapore | |
| 22nd | 13-14 November 2010 |
|
Yokohama |

|
| 23. | 12-13 November 2011 |
|
Honolulu |

|
| 24. | 2-9 September 2012 |
|
Vladivostok |

|
| 25th | 5th-7th October 2013 |
|
Bali |

|
| 26th | 7-12 November 2014 |
|
Beijing |

|
| 27. | 18. – 19. November 2015 |
|
Manila |

|
| 28. | 19. – 20. November 2016 |
|
Lima |

|
| 29 | 10-11 November 2017 |
|
Đà Nẵng |

|
| 30th | 17.-18. November 2018 |
|
Port Moresby |

|
literature
- Patrick Ziltener (2005): "Pacific Drift - The APEC between Bi- and Multilateralism", in: Blätter für deutsche und internationale Politik , 12, pp. 1465–1474.
Web links
- Official website of the organization
- Database of literature on the social, political and economic situation in the countries of the APEC
- Documentation of some protests against APEC
- Contribution to Deutsche Welle about the APEC summit 2003 in Bangkok
- Australia's hosting site for the 19th September 2007 Summit
Individual evidence
- ↑ Source , WirtschaftsWoche , November 18, 2018
- ↑ Due to the complex political relations with the People's Republic of China , the Republic of China does not appear on Taiwan in the APEC under its official name, but as "Chinese Taipei". In addition, it is not represented by its President , but usually by a representative from the environment of the Ministry of Economic Affairs or the President.
- ↑ 2017 Leaders' Declaration. Accessed February 26, 2018 (English).