Iron (III) nitrate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
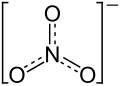
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Iron (III) nitrate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Fe (NO 3 ) 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
violet to white-gray, dissolvable mass |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 241,86 g · mol -1 (anhydrous) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.68 g cm −3 (nonahydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
47 ° C (nonahydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very good in water (1500 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Iron (III) nitrate Fe (NO 3 ) 3 , EC number : 233-899-5, UN number : 1466) is a salt of iron and nitric acid that crystallizes as hexahydrate or nonahydrate .
presentation
It can be produced by converting metallic iron in medium-concentration nitric acid with the formation of nitrous gases :
properties
Iron (III) nitrate forms, depending on the water content and impurities, almost colorless, gray-white or light purple or light yellow to brownish, somewhat deliquescent crystals. Stronger colors are also caused by decomposition. Aqueous solutions are yellowish-brown in color and react acidic through hydrolysis .
use
Iron (III) nitrate is used for tanning . In the textile industry it is used as a stain for cotton fabrics and for dyeing silk black by depositing iron (III) hydroxide . It has also been used as a corrosion inhibitor for a long time . More recently, it has been used, not always successfully, to reduce the hydrogen sulfide concentration in pressurized sewage pipes. Two principles work here:
- toxic hydrogen sulfide is precipitated as iron (III) sulfide .
- the reduction of sulphate to sulphide , instead the nitrate is reduced to ammonia.
In addition, the ammonia formed has a neutralizing and buffering effect .
For the production of iron (III) oxide (Fe 2 O 3 ) as a color pigment , iron (III) nitrate is calcined at a little over 500 ° C until it is completely decomposed.
Iron (III) nitrate is used as a catalyst and as a starting material for the production of catalysts.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry for CAS no. 10421-48-4 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 29, 2011(JavaScript required) .



