Flag of japan
| Nisshōki | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vexillological symbol : |
|
| Aspect ratio: | 2: 3 |
| Officially accepted: | Officially introduced: August 5, 1854 Declared a national flag: August 13, 1999 |
The flag of Japan ( Japanese 日 章 旗 Nisshōki 'sun coat of arms flag ' or 日 の 丸 Hi no Maru 'sun disk') shows a large vermilion-red circle arranged exactly in the middle as a sun symbol on a white background .
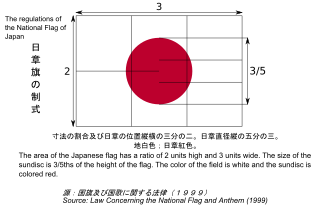
construction
The aspect ratio of the national flag is 2: 3, the diameter of the sun disk is 3/5 of the short side of the rectangle of the flag. Correct measurements would be, for example, a flag that is 1.50 m wide and 1 m high with a sun disk 60 cm in diameter.
history
The Hinomaru flag with the sun disk, also called Nisshoki, was introduced on August 5, 1854. Already at the time of the Meiji Restoration in 1868 it was considered the national flag. Although the sun disk design was officially introduced for flags at sea in 1870 , it was not formally declared a national flag until August 13, 1999. Up to this point in time there was no legally determined state flag, even if Hinomaru was widely regarded as a synonym of Japan both domestically and abroad.
In 1999 the aspect ratio was changed from 7:10 to 2: 3. In addition, according to the regulation from 1870, the sun disk was slightly offset by 1/100 towards the mast. In today's version, the disc in the center is shifted towards the Liek. The symbolism of the solar disk pervades the entire history of Japan.
It was said to be the emblem of Mommu, the 42nd Japanese emperor. The oldest surviving flag is kept in the Umpoji Temple in Yamanashi . It is believed that it originated long before the 16th century and was passed on from dynasty to dynasty. Other Japanese myths attribute the Hinomaru symbolism to an event in the 13th century. According to legend, a Buddhist priest had given the emperor a sun disk flag to honor Amaterasu , sun goddess and ancestor of the Shinto faith .
During the time of the Meiji Restoration, in which the empire was renewed, the now iconic Hinomaru sun disk flag and the Kyokujitsuki ( Japanese旭日 旗, German "flag of the rising sun") were spread.
Other Japanese flags were developed from a similar aesthetic point of view in order to consolidate the idea of a united Japanese empire. The standard of the Japanese emperor is a classic example of this. It also shows a central golden disc on a red background, which is decorated with chrysanthemums , the symbol of the Japanese emperor since the 12th century.
Propaganda posters, school books and films depicted the flag as a source of national pride to reinforce the citizens' patriotic sense of identity. According to an official order, the flag had to be hoisted in homes on national holidays as well as at celebrations and other occasions specified by the government.
More flags of Japan
The version with the 16 red rays ( Kyokujitsuki ) was used by the Japanese armed forces until the end of the Second World War. It has been reused for the Japanese Navy since 1954 . In the surrounding Asian countries, which were occupied by Japan, this flag still evokes negative associations. All the more so since this flag is still used today by right-wing conservative groups in Japan.
The standard of Emperor Naruhito shows a gold, 16-petalled chrysanthemum flower (in stylized form), which is in the center of a red flag. The aspect ratio is 2: 3.
9:11 ? Flag of the Ground Self Defense Forces

2: 3 ? Flag of the Marine Self-Defense Forces

See also
Web links
- Flags of the World - Japan (English)
- Japan Fact Sheet: National Flag and Anthem (English; PDF; 410 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Janese Silvey: Soccer team's use of Rising Sun flag causes stir . In: Columbia Daily Tribune . April 19, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2017.
- ↑ Naoto Okamura: Japan fans warned about rising sun flag . In: Reuters , August 8, 2008. Retrieved April 5, 2012.
- ↑ Japan fans warned about rising sun flag . In: Japan Probe , August 8, 2008. Archived from the original on August 31, 2011 Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. . Retrieved April 5, 2012.
- ↑ World: Asia-Pacific Reprise for Japan's anthem , BBC News. August 15, 1999.