Penicillamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 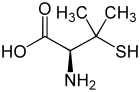
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| L -penicillamine (left) or D -penicillamine (right) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Penicillamine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 11 NO 2 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 149.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
202-206 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water, poorly soluble in ethanol 96% |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Penicillamine is a non-proteinogenic α- amino acid . There are two enantiomers of penicillamine : D- penicillamine and L- penicillamine . The D -enantiomer ( D -amino acid according to D, L-nomenclature , often called DPA for short) or ( S ) -enantiomer (according to CIP nomenclature ) is used as a drug in Wilson's disease . In addition, D- penicillamine can be used as a chelating agent for heavy metal poisoning with lead , cadmium or mercury or for rheumatism . The L variant, on the other hand, is poisonous because the body cannot distinguish this variant of penicillamine from other proteinogenic amino acids.
Occurrence
D -penicillamine is a precursor of penicillin . In molds that can produce penicillin naturally, it is therefore an intermediate product of natural metabolism.
Extraction and presentation
The starting material for D- penicillamine synthetically produced from penicillin is the amino acid valine . Alternatively, D- penicillamine is produced in a thirteen-step synthesis chain from isobutyraldehyde, ammonia and sulfur , with the Asinger reaction as the starting reaction.
Analytics
The enantiomeric purity can be determined by measuring the rotation value or by chiral thin-layer chromatography .
Medical importance
D- penicillamine can be used as a medicinal substance at
- Wilson's disease / hepatolenticular degeneration : D -penicillamine easily forms chelate complexes due to its molecular structure . The thiol group has a high affinity for copper, which means that excess copper caused by illness can be bound to the molecule and excreted from the body in the urine .
- Heavy metal poisoning: Heavy metals can bind irreversibly to enzymes and inhibit their function or deactivate them completely. The chelating property of D- penicillamine is also used here . The molecule binds free metal ions present in the body. These can then be eliminated.
- Cystine stones : Cystine stones form when excessive cysteine and homocysteine aggregate to form a disulfide bridge . The thiol group of D-penicillamine is able to split these disulfide bonds and thus dissolve the urinary stones.
- Rheumatoid arthritis : With an unknown mechanism of action, it influences collagen formation and leads to a reduction in the rheumatoid factor
- Scleroderma: prevents or partially improves the induration of the skin and the involvement of other organs
Adverse effects of penicillamine (choice, uncommon to common):
- Teratogenicity : an effective case childbearing women contraception to look for.
- Skin conditions (common, 1 to 10%)
- Kidney damage (common)
- Bone marrow damage (common)
- Myasthenic syndrome (uncommon, 0.1 to 1%)
Interactions with other drugs
If gold preparations are used at the same time in the therapy of rheumatoid arthritis, the gold is bound in the complex and is therefore ineffective; a combination with azathioprine is also unsuitable as this leads to increased bone marrow toxicity. Joint use with chloroquine is also contraindicated.
toxicity
The LD 50 value for the oral administration of the racemate from D - and L -penicillamine in the model organism rat is 365 mg / kg. For the pure D- penicillamine, however, there are no signs of toxicity even at a dose of 1200 mg / kg.
Trade names
Artamin (A), Metalcaptase (D), Trolovol
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet PENICILLAMINE CRS (PDF) at EDQM , accessed on February 16, 2009.
- ^ The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals . 14th edition, 2006, p. 1223, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b Data sheet D-Penicillamine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 18, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Wolfgang M. Weigert, Heribert Offermanns and Paul Scherberich: D -Penicillamine - Production and Properties. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 14, 1975, pp. 330-336, doi : 10.1002 / anie.197503301 . PMID 808979 .
- ^ E. Busker, K. Günther, J. Martens : Application of Chromatographic Chiral Stationary Phases to Pharmaceutical Analysis: Enantiomeric Purity of D-Penicillamine , J. Chromatogr. 1985, 350, 179-185. doi: 10.1016 / S0021-9673 (01) 93517-49 .
- ↑ a b Thomas Karow, Ruth Lang-Roth: General and special pharmacology and toxicology lecture-oriented presentation and clinical guidelines for study and practice 2013; [+ Marking of the examination facts of the "hammer exam" until 04/2012, + therapy recommendations from German and international specialist societies, + extensive dosages] . [Self-published], Pulheim 2013.
- ^ Harrison's internal medicine, 18th edition, German edition, p. 2989.
- ^ IA Jaffe, K. Altman, P. Merryman: The antipyridoxine effect of penicillamine in man. In: The Journal of clinical investigation. Volume 43, October 1964, pp. 1869-1873, doi: 10.1172 / JCI105060 . PMID 14236210 . PMC 289631 (free full text).