Methiocarb
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Methiocarb | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 15 NO 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 225.31 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
119 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3.8 10 −7 h Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
27 mg l −1 in water (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Methiocarb ( mercaptodimethur ) is a chemical compound that belongs to the thioethers and the carbamates . Methiocarb was introduced by Bayer in 1962 as an insecticide and acaricide and is also used as a bird repellent .
effect
Methiocarb acts by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase as neurotoxin . It is also toxic to humans and can cause vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath, and pulmonary edema . In 2001 it was allowed to be labeled as less toxic in product names . It is very toxic to aquatic life.
Methiocarb also acts on the nervous system of snails, which initially become hyperactive but then lose muscle tone and die on the spot. Methiocarb is a widely used molluscicide for this reason . The Stiftung Warentest advises against the use of slug pellets with this active ingredient if children and pets are on the treated areas.
Dismantling
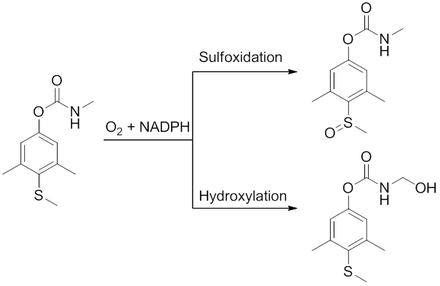
Methiocarb is mainly metabolized in organisms by sulfoxidation , and more rarely also by hydroxylation at the N -methyl group.
regulation
Europe
In the European Union, this active ingredient had been approved for plant protection products since 2007. The latest approval expired on September 30, 2017. Only applications as repellants were allowed. The authorization for use as a molluscicide was withdrawn on February 26, 2014 for the protection of birds, mammals and non-target arthropods. Since then, only applications as repellants for seed treatment have been permitted. Methiocarb is approved in 23 EU countries at national level. The permitted daily dose , the acute reference dose and the acceptable user exposure are 0.013 milligrams per kilogram of body weight and day.
Methiocarb was approved in Germany in numerous insect sprays for home and allotment gardeners, always in combination with thiacloprid . The approval expired on October 3, 2019. The use-by period runs until April 3, 2020. To prevent bird damage, the Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety has now issued an emergency approval for Korit with the active ingredient Ziram for the seed dressing of maize , which is valid from December 15, 2019 to April 12, 2020 . Methiocarb was the only active ingredient in slug pellets. The application is no longer permitted since September 19, 2014.
In Switzerland, only use as a seed dressing is permitted. Preparations containing methiocarb were permitted in Austria as insecticide spray, slug pellets ( Mesurol ) and seed dressing, but are no longer on the market.
Web links
- Methiocarb data sheet (PDF, 497.3 kB, English) of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry for CAS no. 2032-65-7 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 7, 2011(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Daunderer - Clinical Toxicology - 115th Erg.-Lfg. 3/97
- ↑ Entry on mercaptodimethur in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Datasheet Methiocarb analytical standard from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 6, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on Methiocarb. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 14, 2014.
- ↑ a b Stiftung Warentest: Fighting snails: Murder at dawn . In: test 6/2001 (accessed on February 4, 2013)
- ↑ Glen, D .; Orsman, I .: Comparison of molluscicides based on metaldehyde, methiocarb or aluminum sulphate . In: Crop Protection . tape 5 , 1986, pp. 371 , doi : 10.1016 / 0261-2194 (86) 90067-0 .
- ^ Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR), Monograph for Methiocarb , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ Regulation (EU) No. 187/2014 (PDF) of the Commission of February 26, 2014.
- ↑ a b Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Methiocarb (aka mercaptodimethur) in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.
- ↑ EU approval for the active ingredient methiocarb in plant protection products not renewed . Retrieved December 6, 2019.
- ↑ Klaus Strotmann: Ban on Mesurol: Finally clarity about the consumption periods. In: agrarheute.com . October 23, 2019, accessed January 17, 2020 .
- ↑ Klaus Strotmann: After the Mesurol ban: Emergency approval for Korit bird feeding stain. In: agrarheute.com . December 5, 2019, accessed January 17, 2020 .
- ↑ BVL - Revoked and dormant approvals . Retrieved June 22, 2015.
- ↑ Chemical control of snails