PKP Intercity
| PKP Intercity
|
|
|---|---|
| legal form | Spółka akcyjna |
| founding | September 1, 2001 |
| Seat | Warsaw , Poland |
| management |
|
| Number of employees | 7 851 (2018) |
| Branch | traffic |
| Website | www.intercity.pl |
PKP Intercity ( PKPIC ) is a Polish , the long-distance passenger specialized transport companies based in Warsaw . In the form of Twoje Line Kolejowe and InterCity, the company offers inexpensive express trains as well as high-quality long-distance transport ( Express InterCity , EuroCity and Express InterCity Premium ). Also sleeping - and couchette cars can be found in the product portfolio again.
In 2014, PKP IC carried nine percent of the total number of passengers, making it third among the railway companies; the share of passenger kilometers was the largest at 39%.
history
PKP Intercity was founded in 2001 as a subsidiary of PKP . A 50-year concession made it possible to start voivodeship and cross-border passenger traffic on September 1, 2001. The subsidiary employed around 1,500 people in its early days. On April 28, 2005, the majority stake in the sleeping and dining car operator WARS was taken over.
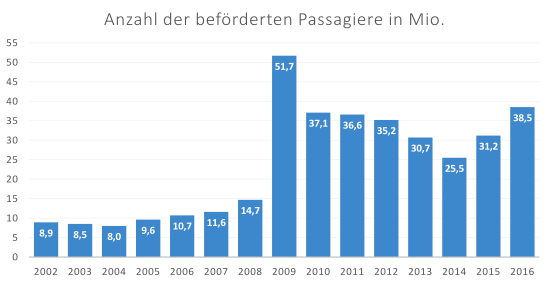
As part of a reform, PKP Intercity became a public company in early 2008. In addition, in December 2008, the company inherited the long-distance transport division of the broken PKP Przewozy Regionalne. The joint stock company received part of the fleet and took over 4070 employees and 1850 others from the logistics company PKP Cargo . This resulted in an increase in the number of passengers carried from 14.7 million (2008) to 51.7 million (2009). Since the reform there has been a systematic decrease in passenger numbers up to and including 2014, whereas the previous four years showed an upward trend. In 2015, PKP IC recorded growth again. After the takeover, the company slipped into the red.
Due to enormous train delays during the severe winter in December 2010, the company came under fire. This also resulted in personnel consequences with the dismissal of Transport Minister Juliusz Engelhardt, the managing director of the PKP group Andrzej Wach and the then chairman of PKP Intercity Grzegorz Mędza. On February 21, 2011, an agreement was reached with the Ministry of Infrastructure, which provides for subsidizing national transport for the next ten years. In detail, the state is to pay 4.5 billion zloty for 299 million passenger kilometers.
Since its inception, PKP Intercity has been exposed to new competing products. In the low cost price segment, Przewozy Regionalne's Interregio is in direct competition with the TLK . With the expansion of the motorway and expressway network, the rivalry with long-distance bus companies such as Polski Bus increased . All this moved the company to change its strongly degressive price system.
Long-distance passenger transport
In the initial phase, the company operated the Express, InterCity, EuroCity and EuroNight train categories. In 2002 the night train brand Nocny Express was added. InterRegion followed two years later for the express trains. On April 4, 2005, both categories were combined under the name Tanie Line Kolejowe (TLK). With reservation requirements and better rolling stock, a product competing with the Przewozy Regionalne trains should establish itself. In the same year, the Express InterCity was created from the merger of Express and InterCity. In December 2014, the Express InterCity Premium and InterCity categories were added.
Express InterCity Premium
The Express InterCity Premium brand has existed since December 14, 2014. It is served exclusively by high-speed trains of the ED250 series ; these connect the most important cities with Warsaw, Gdynia , Gdansk , Katowice , Krakow and Wroclaw . The trains are air-conditioned, allow bicycles to be transported and have a bistro area. Passengers can enjoy free little things. Internet is to be offered in the future. In contrast to the other types of train, there is no provision for ticket sales on the train.
Express InterCity
The Express InterCity is assembled from the latest rolling stock and runs at a top speed of up to 160 km / h. A WARS-operated dining or bar car is scheduled to be found on all Express InterCity trains. Travelers can also use free WiFi . In some trains there are also so-called business compartments, which are designed for the transport of wheelchair users and bicycles. Child-friendly coaches with toys also run.
InterCity
The InterCity brand came with the 2014/15 timetable change and includes new or modernized rolling stock that was partially financed by the European Union. The planned routes are Przemyśl - Stettin and Wroclaw - Gdynia . The trains are equipped with ergonomic seats, air conditioning and telephone signal amplifiers and only run bistro cars. The price range is identical to the TLK trains.
Since the end of 2015, the range has been supplemented by 20 electric multiple units each from the ED160 and ED161 series .
In contrast to the EIC and EIP, this train category is not self-financed, but subsidized by orders from the Ministry of Infrastructure.
Twoje line Kolejowe
The train category TLK is qualitatively the lowest operated by PKP Intercity. Consequently, the price level falls under the EIP / EIC train types. The 2014/15 timetable provided for 266 trains of this brand, which served around 350 train stations. Since December 2014 only a so-called “snack caddy” has been carried instead of the bar and dining car.
First established in April 2005, initially twelve daily connections were operated with Tanie Line Kolejowe ( German cheap rail routes ). At the end of 2009, after the takeover of all express trains, the number rose from 24 to 377. On January 1, 2011, the name was changed to Twoje Line Kolejowe ( German your railway lines ). In the long term, this brand is to be completely replaced by the Intercity category. These trains are also subsidized by the Ministry of Infrastructure.
International connections
The company also operates international train connections with EuroCity and EuroNight as well as cross-border express trains. The EuroCity trains correspond to the Express InterCity standard.
Intercity bus
PKP Intercity also offers a network of bus connections under the Intercity Bus brand . They are used for route modernization work as substitute transport for people, or supplement the range of tourist areas. At the end of 2014, all train traffic between Warsaw and Białystok was compensated for with the bus connections due to fundamental renovation work.
Fleet


After the re-establishment of PKP Intercity, their 1,300 passenger coaches were provided by the parent company. These include passenger coaches (UIC-X and UIC-Z) as well as luggage, dining, couchette and sleeping cars. The latter was transferred in full to PKP Intercity. Since PKP Intercity did not have any locomotives or railcars at that time, they were lent by PKP Cargo as required . The company gradually expanded its fleet of vehicles. Between 2001 and 2003, 17 brand new type 154Aa passenger coaches and seven type 152Aa coaches were added.
Newly purchased rolling stock made it possible for the international train Jan Kiepura to be categorized as EuroNight again . The maximum speed in German territory could be increased to 200 km / h. PKP also bought ten 305Ad sleeping cars. and had four passenger coaches converted from 152A to 152Az ( sleeperette )
In 2008, some of the locomotives were taken over by the freight transport division PKP Cargo . On April 8, 2008, PKP Intercity signed a contract with H. Cegielski - Poznań for the delivery of 17 passenger coaches (HCP Z1) for services in the EIC and EC train categories. Due to delays, the scope of delivery was reduced to 14 pieces. In the same year, an order was placed with Siemens Mobility for the delivery of ten multi-system locomotives of the Siemens ES64U4 series , which were given the series designation EU44 Husarz .
Together with the takeover of express train services on December 1, 2008, PKP Intercity came into possession of locomotives of the EU07 , EP07 , SU45 series , ED74 Bydgostia electric multiple units and 1830 passenger cars. After Poland joined the European Union, the structural funds offered the opportunity to partially finance new acquisitions. For the period from 2009 to 2012, plans were made to purchase 20 high-speed trains, 36 multiple units with a maximum speed of 160 km / h and a comprehensive modernization program for 360 passenger coaches.
On May 30, 2011, PKP Intercity signed a contract with Alstom for the delivery of 20 seven-car high-speed trains of the ED250 series . The contract also provided for the construction of a maintenance hall in Warsaw. Alstom undertook to maintain these trains on a regular basis for a period of 17 years. The total cost was PLN 2,110 million, of which PLN 317 and PLN 28 million were borne by the POIiŚ structural fund . The European Commission rejected a 50 percent grant . The tilting technology common for the Pendolino was not ordered, although the railway line between Gdansk and Warsaw is designed for it. As a justification, the company gave insufficient travel time savings in view of the additional costs.
In 2011, the company ZNTK Oleśnica carried out a complex modernization of the EU07 locomotive on behalf of PKP Intercity. Asynchronous motors made it possible to increase the top speed from 125 km / h to 160 km / h. In June 2013, the same manufacturer received the order to convert two further EU07 locomotives to the EU07A platform .
On July 23, 2012 a contract was signed for the modernization of 68 passenger coaches intended for the Przemyśl - Wrocław - Szczecin route. The following companies won partial lots: H. Cegielski - Poznań (20 cars), a consortium consisting of Pesa and ZNTK "Mińsk Mazowiecki" (38 cars) and Newag (10 cars). In August of the same year, Pesa and ZNTK “Mińsk Mazowiecki” received the order to modernize 115 additional passenger coaches, which was expanded by another 35 a month later. A total of 218 passenger coaches were ordered for modernization. The total value is 594 million zlotys and also includes ten vehicles for maintenance. Of this, 320 million zlotys are borne by the EU . On October 18, 2012 PKP Intercity ordered 25 brand-new Z1-type wagons from H. Cegielski - Poznań for the service between Wrocław and Gdynia . The order value is 164 million zloty, of which 84 million zloty is partially financed by a fund of the European Union .
In September 2013, PKP Intercity commissioned Newag to modernize 20 diesel locomotives of the SM42 series . They are intended for traffic on non-electrified railway lines and for shunting trips. The total order value is 77 million zlotys. The EU pays 44 million zlotys of this.
On November 18, 2013, the transport company signed a contract for the delivery of 20 eight-part ED160 FLIRT 3 multiple units by the consortium of Stadler Rail and Newag . On May 23, 2014, the delivery of 20 eight-part electric multiple units of the ED161 Dart series was agreed with Pesa . The order volume amounts to PLN 1,157 million (of which EUR 658 million is borne by the EU) and PLN 1,009 million (of which EUR 574 million is borne by the EU).
In December 2013, the average age of electric vehicles was estimated at 30 years and non-electric vehicles at 28 years.
In July 2014, an order was placed with Pesa for the delivery of ten new class 111dB Gama (SU160) diesel locomotives. The value of the contract is 166 million zloty, of which the European Union partially financed 94 million zloty.
On January 16, 2015, PKP Intercity ordered five special vehicles from Corail, which are capable of driving both on tracks and on the road.
On May 15, 2015, H. Cegielski - Poznań agreed to deliver 20 brand-new Z1 passenger coaches. They are intended for the EIC train category and cost 148 million zloty. The EU funding pot POIiŚ will cover 60 million zloty of this.
listing
Electric locomotives
| model series | number | Top speed |
Manufacturer | modernized by | receipt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU07 | 86 | 125 km / h | Pafawag / HCP | ||
| EU07A | 3 | 160 km / h | HCP | ZNTK Oleśnica | |
| EP07 | 150 | 125 km / h | Pafawag / HCP | ZNTK | |
| EP08 | 9 | 140 km / h | Pafawag | ||
| EP09 | 46 | 160 km / h | Pafawag | ZNLE / Newag Gliwice | |
| EU44 Husarz | 10 | 230 km / h | Siemens |
Diesel locomotives
| model series | Type | number | Top speed |
Manufacturer | modernized by | receipt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM42 | 6D | 30th | 90 km / h | Fablok | ||
| SM42 | 18D | 10 | 90 km / h | Fablok | Newag | |
| SU42 | 6Dl | 10 | 90 km / h | Fablok | Newag | |
| SU160 | 111Db Gama | 10 | 140 km / h | Pesa |
Electric multiple units
| model series | number | Number of car parts |
number of seats |
|
Top speed |
Manufacturer | receipt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd class | 1st class |
|
|||||||
| ED74 Bydgostia | 14th | 4th | 161 + 8 | 33 | 2 | No | 160 km / h | Pesa | |
| ED250 Pendolino | 20th | 7th | 355 | 45 | 2 | Yes | 250 km / h | Alstom | |
| ED160 FLIRT 3 | 20th | 8th | 294 + 6 | 60 | 2 | Yes | 160 km / h | Stadler Rail | |
| ED161 darts | 20th | 8th | 292 | 60 | 2 | Yes | 160 km / h | Pesa | |

Passenger coaches
As of December 31, 2013, the company owned 2,681 passenger coaches; 60.9% were 2nd class cars and 22.2% were 1st class cars. 492 of them were air-conditioned; 64.33% allowed a top speed of 160 km / h and 5.95% of 200 km / h. The median age was 28 years. In June 2014, the company owned 1,500 operational cars, 518 of which were air-conditioned.
leasing
As a result of cooperation, PKP Intercity uses locomotives from foreign transport companies in some cases.
In the past, when there were bottlenecks, electric and diesel locomotives were rented.
The company is also testing new locomotives. In the past, for example, the Siemens Vectron (2012) or the 111Ed Gama from Pesa were used.
Others

In 2007, the company's own magazine W Podróży was first published. The first VIP lounge opened in the Warszawa Centralna station , which was later expanded to include Kraków Główny and Wrocław Główny . At the end of 2014 it was decided not to pursue this offer any more.
In 2009, in Warsaw Centralna began selling tickets via ticket machines.
Since the beginning of 2012, passengers have been able to track delays and seat occupancy of individual trains via the InfoPasażer service.
In January 2014, a contract was signed with T-Mobile Polska to set up the Internet and a multimedia offering in part of the vehicle fleet.
From November 16 to 20, 2014, the changeover to a dynamic system resulted in outages, which restricted ticket sales. From December 2014, tickets can also be purchased with a smartphone using the Sky Cash system. The collaboration with Google was announced in early 2015; since then, the train connections have also appeared on Google Maps . In February 2015, a new sales channel was tested as a pilot project with 37 post offices over a period of three months.
PKP IC advertises on television, radio, newspapers and the Internet. The company has also had an official Facebook profile since 2011 .
Some locomotives are also used for advertising purposes:
- In the course of the European Football Championship 2012 , PKP IC covered ten locomotives of the Siemens ES64U4 and EP09 series with films from the participating countries and the four Polish venues.
- As part of a collaboration with the organizer of the Open'er Festival , two Siemens ES64U4 locomotives were given the logo of the event in June 2013 .
- Between October 2013 and January 2014 PKP Intercity applied for modernized rolling stock to a locomotive.
The company made it possible to view rolling stock that had been modernized or new several times at large train stations.
In May 2015, the former managing director of the PKP group Jakub Karnowski announced that the aim was to privatize PKP Intercity by 2017 or 2018.
CEO
| Period | executive Director |
|---|---|
| 2001 - February 2005 | Andrzej Żurkowski |
| February 2005 - June 2006 | Jacek Prześluga |
| June 2006 - January 9th 2009 | Czesław Warsewicz |
| January 9, 2009 - April 7, 2010 | Krzysztof Celiński |
| April 7, 2010 - February 2, 2011 | Grzegorz Mędza |
| February 2, 2011 - March 23, 2011 | Lucyna Krawczyk |
| March 23, 2011 - January 22, 2014 | Janusz Malinowski |
| January 22, 2014 - January 16, 2015 | Marcin Celejewski |
| January 16, 2015 - March 9, 2016 | Jacek Leonkiewicz |
| since March 10, 2016 | Marek Chraniuk |
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Dane o Spółce. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved November 17, 2014 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Nowy zarząd PKP Intercity. In: logistyka.wnp.pl. March 10, 2016, accessed March 10, 2016 (Polish).
- ↑ Dane o Spółce. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved December 21, 2016 (Polish).
- ↑ Wykaz Aktuell uzgodnionych z Prezesem Urzędu Transportu Kolejowego identyfikatorów literowych VKM. (No longer available online.) In: Urząd Transportu Kolejowego. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016 ; Retrieved June 14, 2015 (Polish). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c PKP IC: 5.2 mln pasażerów mniej w roku 2014. Grudzień bez rewelacji. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 30, 2015, accessed June 14, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ A b Marek Rabsztyn. 75 lat PKP. Od Drogi Żelaznej Warszawsko-Wiedeńskiej do PKP SA “Technika Transportu Szynowego”. 10/2001, p. 14. ISSN 1232-3829 . (Polish)
- ↑ a b c d In: Karol Trammer. Skok na pospieszne. "Z Biegiem Szyn". 3/2008, pp. 6-7. Warszawa. ISSN 1896-4079 . (Polish)
- ↑ Przewozy dalekobieżne na przestrzeni ostatnich lat. In: inforail.pl. February 1, 2011, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Polska Agencja Prasowa: PKP Intercity zamierzają zahamować spadek liczby pasażerów. In: pb.pl. February 2, 2005, accessed June 14, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Kolej traci pasażerów! Ponad 16 mln w Przewozach Regionalnych, ponad 4.5 mln w PKP Intercity. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. February 3, 2014, accessed February 3, 2014 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2004. In: pkpsa.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2005. In: pkpsa.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2007. In: pkpsa.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2009. In: pkpsa.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2011. In: pkpsa.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b c d e Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2013. In: pkpsa.pl. December 22, 2014, pp. 63–80 , accessed June 14, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Czym żyła polska kolej w 2010 r.? In: kurierkolejowy.eu. January 1, 2011, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Kto będzie szefem PKP Intercity? Lucyna Krawczyk pełni obowiązki prezesa. In: biznes.newsweek.pl. February 3, 2011, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Odpowiedź na interpelację nr 31609 w sprawie dotacji na przewozy międzywojewódzkie i międzynarodowe realizowane przez spółkę PKP Intercity SA. In: orka.sejm.gov.pl. April 7, 2015, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity przewiozło w 2015 ponad 31 mln pasażerów. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 20, 2016, Retrieved January 20, 2016 (Polish).
- ↑ UTK: Kolej miała o 4,3% pasażerów więcej w 2016 r., Wyniki poprawiły PR i PKP IC. In: Onet.pl . January 28, 2017. Retrieved January 28, 2017 (Polish).
- ↑ Grupa PKP - Raport roczny 2015. (PDF) In: pkpsa.pl. P. 27 , accessed on November 25, 2016 (Polish).
- ↑ Podróże po Polsce nareszcie tanie. Konkurencja czyni cuda. In: wyborcza.biz. May 2, 2012, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Dziobaki poszły w read. In: polityka.pl. December 9, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Ostatni dzień Eurolotu. Q400 będą miały przerwę. In: pasazer.com. March 13, 2015, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Historia firmy. In: pasazer.com. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Andrzej Żurkowski. Nowa jakość w przewozach kwalifikowanych. "Technika Transportu Szynowego". 10/2001, pp. 27-28. ISSN 1232-3829 . (Polish)
- ↑ a b Karol Trammer. Nowa oferta - Tanie Line Kolejowe. "Technika Transportu Szynowego". 4/2005, p. 12. ISSN 1232-3829 . (Polish)
- ↑ Tanie znaczy lepsze - czym są Tanie line Kolejowe? In: wiadomosci24.pl. December 25, 2007, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Intercity zamienia pospieszne na TLK. In: waluty.onet.pl. October 20, 2009, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Pendolino już na torach. Wszedł w życie nowy rozkład jazdy. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. December 14, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b c InterCity Kolejowe. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Szczegóły techniczne Alstom Pendolino ETR610. In: inforail.pl. January 9, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Express InterCity Premium (Specyfikacja i usługi). In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 16, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Wi-Fi już we wszystkich krajowych pociągach EIC ... poza Pendolino. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 7, 2015, accessed June 16, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ Express InterCity Premium (Oferta). In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 16, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Express InterCity. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 16, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ Gastronomia (WARS). In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b MIR: Category pociągów InterCity bez wpływu na ceny biletów i umowę PSC. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. November 21, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Informacja prasowa PKP InterCity. In: intercity.pl. December 12, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Tanie line Kolejowe w nowym rozkładzie jazdy. In: inforail.pl. November 22, 2009, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b TLK bez wagonów barowych. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. March 30, 2005, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ 4 kwietnia ruszają Tanie line Kolejowe. In: pb.pl. December 4, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ Twoje Line Kolejowe. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b EuroCity, EuroNight. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ AKTUALNOŚCI: ZMIANA ORGANIZACJI RUCHU NA LINII WARSZAWA - BIAŁYSTOK. In: rozklad-pkp.pl. October 6, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Rusza wakacyjna oferta PKP Intercity Bus. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. June 25, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Od dziś zamknięcie Rail Baltiki. Jak poradzić sobie z utrudnieniami? In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. October 12, 2014, accessed June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ In Andrzej Etmanowicz. Pierwsze wagony bezprzedziałowe 1 klasy standardu Z1 na PKP type 154A / 154Aa. "Świat Kolei". 10/2008, pp. 22-27. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ In Andrzej Etmanowicz. Pierwsze wagony bezprzedziałowe 1 klasy standardu Z1 na PKP type 152A / 152Aa. "Świat Kolei". 7/2008, pp. 22-27. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ a b In: Andrzej Etmanowicz. Wagony sypialne PKP standardu Z1 type 305Ad. "Świat Kolei". 5/2008, pp. 12-16. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ In Andrzej Etmanowicz. Modele wagonów PKP z miejscami do leżenia typu 134Ab firmy ACME “Świat Kolei”. 11/2012, p. 57. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ In Andrzej Etmanowicz. Wagony "sliparetki" type 152Az. "Świat Kolei". 3/2008, pp. 16-21. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ Porozumienie PKP Intercity z Fabryką Pojazdów Szynowych. In: biznes.pl. October 5, 2010, archived from the original on July 14, 2014 ; Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Po szynach . "Biuletyn internetowy PKP Intercity - IC news". 3/2012, p. 10. Warszawa: PKP Intercity SA Centrala Spółki, Biuro Komunikacji i Promocji. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved June 15, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ In: Marek Graff, Krzysztof Rutkowski. Wielosystemowe lokomotywy Siemens dla PKP IC. "Świat Kolei". 9/2008, p. 4. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ GRUPA PKP . In: intercity.pl. P. 41 , accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity kupują Pendolino. In: inforail.pl. May 31, 2011, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b c d e f g LISTA PROJEKTÓW INDYWIDUALNYCH DLA PROGRAMU OPERACYJNEGO INFRASTRUKTURA I ŚRODOWISKO 2007-2013. In: cupt.gov.pl. Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Wszystkie grzechy Pendolino? Replica PKP IC. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. November 28, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Asynchroniczna EU07. In: inforail.pl. June 21, 2011, Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Usługi w zakresie napraw i konserwacji lokomotyw 2013 / S 108-185459. In: ted.europa.eu. June 4, 2013, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ IC modernizują 68 wagonów za 180 mln zł. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. July 23, 2012, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity podpisały kontrakt na modernizację 115 wagonów. In: pb.pl. August 14, 2013, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Wszystkie umowy na modernizację wagonów PKP Intercity podpisane! In: inforail.pl. September 30, 2013, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Odnowa taboru PKP Intercity SA dla relacji Przemyśl - Szczecin - Etap II. In: cupt.gov.pl. Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Fabryka pojazdów Szynowych wychodzi na PROSTA. In: inforail.pl. October 22, 2012, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Newag zmodernizuje spalinowe lokomotywy Intercity. Pojadą w góry i nad morze. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. September 25, 2013, Retrieved October 2, 2013 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Elektryczny pociąg FLIRT³ dla PKP Intercity, przeznaczony do ruchu dalekobieżnego. (No longer available online.) In: stadlerrail.com. Archived from the original on July 18, 2015 ; Retrieved June 12, 2015 (Polish). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Darty dla PKP IC mają zapewnić comfort i bezpieczeństwo. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. May 30, 2014, accessed May 31, 2014 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity GAMA Diesel Contract Signed. In: railvolution.net. September 10, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 .
- ↑ Umowa na dostawę pojazdów szynowo-Drogowych dla PKP Intercity podpisana. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 22, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Zamówienie publiczne - 51053-2015. In: ted.europa.eu. February 9, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b c d e f g PKP Intercity. In: Jacek Chiżyński: Atlas przewoźników kolejowych Polski 2011. , Rybnik: Eurosprinter, 2011, pp. 60–63. ISBN 978-83-931006-5-1 . (Polish)
- ↑ a b Intercity jednak zamawia kolejne EU07A. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. August 20, 2012, accessed August 20, 2012 (Polish).
- ↑ 2013 SPRAWOZDANIE ZARZĄDU Z DZIAŁALNOŚCI GRUPY KAPITAŁOWEJ NEWAG. (No longer available online.) In: newag.pl. March 14, 2014, p. 18 , archived from the original on March 25, 2014 ; Retrieved June 12, 2015 (Polish). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ SM42-18D Newagu dla PKP Intercity: Dane techniczne. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. June 13, 2014, accessed June 13, 2014 (Polish).
- ↑ Trzy kolejne SM42 PKP IC zmodernizowane. In: inforail.pl. July 31, 2014, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Zmodernizowane SM42 - lokomotywy drugiej generacji. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. May 21, 2015, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Pierwsza dwuagregatowa SU42 już w Gdyni. In: inforail.pl. August 18, 2014, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP IC testuje już nowe Gamy. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. May 13, 2015, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity kupują Pendolino. In: inforail.pl. May 31, 2011, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Express InterCity Premium. In: intercity.pl. Retrieved April 8, 2016 (Polish).
- ↑ Wszystko co Musisz wiedzieć o Pendolino. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. December 13, 2014, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Za dwa lata Pendolino będzie na siebie zarabiać? In: inforail.pl. March 22, 2015, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Wszystkie Flirty3 dla PKP Intercity powstaną w Siedlcach. In: inforail.pl. April 27, 2015, accessed June 12, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Jedna trzecia wagonów 7PKP Intercity z klimatyzacją. In: inforail.pl. June 27, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Obsługa relacji Zagranicznych polskimi lokomotywami. In: inforail.pl. December 11, 2007, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ^ Seweryn Dębski. Nowości z Olszynki. "Świat Kolei". 6/2010, p. 3. ISSN 1234-5962 . (Polish)
- ↑ PKP Intercity wyleasingowało dwie lokomotywy Eurosprinter. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. March 9, 2011, Retrieved December 23, 2012 (Polish).
- ↑ Już trzy "okularniki" w PKP IC. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. July 7, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity wynajęło Vectrony DB Schenker. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. February 9, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity wynajęło TRAXX-a or PKP Cargo. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 4, 2011, accessed May 8, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity brakuje 180 wagonów. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. May 12, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Intercity wypożyczyło SM42 or Newagu. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. July 4, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Vectron już po testach w PKP Intercity. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. September 26, 2012, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Gama Marathon Passenger Debut. In: railvolution.net. March 2, 2013, accessed June 17, 2015 .
- ↑ PKP Intercity kończy ze Strefami VIP. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. November 14, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ InfoPasażer
- ↑ W końcu jest internet w PKP Intercity. Pierwszy pociąg na torach. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. July 1, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ W Intercity w końcu więcej niż Internet. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. April 13, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ PKP Informatyka: Awaria sprzedaży biletów uwidoczniła braki. Konieczne zmiany. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. November 24, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Bilety na pociągi PKP Intercity już w SkyCash. In: bankier.pl. December 9, 2014, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Pociągi PKP Intercity już na mapach Google. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 20, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Bilety na pociągi IC w placówkach Poczty Polskiej. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. February 4, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Startuje kampania PKP za 10 mln zł. Zobacz film reklamowy. In: bankier.pl. February 10, 2015, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Zobacz wszystkie lokomotywy Intercity na Euro. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. April 29, 2012, Retrieved December 24, 2012 (Polish).
- ↑ Husarze znów kolorowe. Tym razem z okazji Open'era. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. June 14, 2013, Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Specjalne malowanie EP09 PKP Intercity. In: kurierkolejowy.eu. October 25, 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Jacek Goździewicz, Jan Raczyński. TRAKO 2013. “Technika Transportu Szynowego”. 12/2013, pp. 24-26. ISSN 1232-3829 . (Polish)
- ↑ Jacek Goździewicz, Jan Raczyński. TRAKO 2007. “Technika Transportu Szynowego”. 11/2007, pp. 18-23. ISSN 1232-3829 . (Polish)
- ↑ Jakub Karnowski: Za 2-3 lata PKP Intercity powinno trafić na giełdę. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. May 4, 2015, Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b Bardziej pasażer niż menadżer. In: zbs.net.pl. June 2005, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Warsaw: Rozstrzygnięcie konkursu na Prezesa Zarządu PKP Intercity. In: inforail.pl. December 1, 2006, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ a b PKP Intercity z nowym Prezesem. In: inforail.pl. April 13, 2010, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Zmiany w Intercity. In: inforail.pl. May 31, 2011, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Janusz Malinowski prezesem PKP Intercity. In: inforail.pl. March 23, 2011, accessed June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Prezes PKP Intercity odwołany. Never chodzi o zimę, ale o "utratę zaufania". In: gazeta.pl. Retrieved June 17, 2015 (Polish).
- ↑ Leonkiewicz nowym prezesem PKP Intercity. In: rynek-kolejowy.pl. January 16, 2011, accessed January 16, 2015 (Polish).