Reichsgau
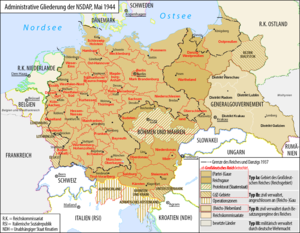
Reichsgaue were state administrative districts and self-governing bodies in parts of the German Empire in the era of National Socialism 1939-1945.
Definition
Reichsgaue were under the direction of a Reichsstatthalters who was mostly in personal union Gauleiter for the (party) district of the NSDAP . They had a right derived from the Reich, in agreement with the Reich Minister of the Interior, to independently legislate by way of ordinances. It is the beginning of a reorganization of the Reich Central Authority, initially outside the boundaries of the Reich territory from 1937 .
Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia)
According to the law on the division of the Sudeten German territories , the Reichsgau Sudetenland (initially as Sudetengau ) was established on April 15, 1939 . The affected areas were combined into three administrative districts and certain areas were also incorporated into other rural and urban districts.
Integrated Eastern Territories (Poland)
The German Reichsgaue existed on previously Polish territory
- Danzig-West Prussia (initially West Prussia) and
- Wartheland (initially Posen).
The Führer decree on the structure and administration of the Eastern Territories regulated the formation of the two new Reichsgaue from October 26, 1939 in "appropriate application" of the Sudetengau Act. They were also divided into urban and rural districts, each grouped into three administrative districts.
In the case of the Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, part of the German Reich was included in a Reichsgau for the first (and last) time with the administrative region of West Prussia within the borders of 1937 .
Alpine and Danube Reichsgaue (Austria)
- Carinthia
- Lower Danube (initially: Lower Austria)
- Upper Danube (initially: Upper Austria)
- Salzburg
- Styria
- Reichsgau Tirol-Vorarlberg
- Vienna
The Ostmarkgesetz had ordered the formation of seven Reichsgauen as " legal successors of the former Austrian states " (§ 14 Paragraph 2) and their division into urban and rural districts as early as 1939. Because of the lower population density, the division into administrative districts had been abandoned. The Reichsgau Greater Vienna comprised only one municipality, namely the city of Vienna .
Since the division of Austria , whose competencies were divided between the Reichsgau and Reichsgau levels, dragged on for a long time, the Reichsgaue was not established until the beginning of 1940.
Westmark (Palatinate, Saarland, Lorraine)
The NSDAP Gau Westmark , formed in 1940, was to become the "Reichsgau Westmark", comprising the Saarland , the Bavarian Palatinate - at that time combined in the NSDAP as the Gau Saarpfalz - and the Lorraine department of Moselle , which was conquered during the French campaign and which was to be incorporated into the Reich as Lorraine . The plan was not implemented during World War II . Admittedly, on October 18, 1940, Hitler signed a decree of October 12th. J., who created this Reichsgau on paper, as well as a "Reichsgau Oberrhein"; there were even implementing regulations of November 2, 1940. In order to avoid a desire for revenge and protests in France, the publication of the decree on the annexation of Lorraine was banned at the same time. Outwardly it remained with the old name and the associated designation "CdZ" ( head of civil administration ). Göring got through that he was allowed to co-rule because of his planning of the war economy. Rather, it remained so until 1945 that the Reichsstatthalter in the Westmark in Saarbrücken (formerly: Reichskommissar für die Rückgliederung des Saarlandes / Reichskommissar für die Saarpfalz) administered the Saarland and the Bavarian administrative district of the Palatinate as well as the duties of the head of civil administration for Lorraine perceived.
This area of the Westmark , which comprised the old Reich territory and with the Lorraine part also French state territory , was thus administered uniformly, but was still formally divided into the actual Reich territory (Saarland / Land Bavaria) and the CdZ area Lorraine.
Upper Rhine (Baden, Alsace)
Likewise, the Reichsgau Upper Rhine was planned as a merger of the Gaus Baden or the Republic of Baden with Alsace , but this did not formally come about until 1945. Baden and Alsace were jointly administered from Strasbourg . The city of Kehl fell to Strasbourg, the Mayor of Kehl became an alderman in Strasbourg, while the Lord Mayor of Strasbourg also became Mayor of Kehl. For the area of the NSDAP the name of the Gaus was "Baden-Alsace".
Flanders and Wallonia (Belgium)
Shortly before the end of the Second World War, after Belgium had already been liberated, administrations for the future districts of Flanders and Wallonia (→ Wallonia region ) were created in the German Reich by collaborators who had fled .
Due to the advance and not least the liberation by the Allies , the responsible Gauleiter were forced to perform their administrative tasks from Germany: The Reichsgau Flanders (without Voeren , but included Comines-Warneton ) was proclaimed on December 15, 1944, the Gauleiter in German exile was Jef Van de Wiele . The Reichsgau Wallonia was established on December 8, 1944, the Gauleiter in exile was Léon Degrelle .

See also
Web links
- Legal basis of the Reichsgaue
- Collegium Carolinum / Jörg Osterloh: National Socialist Persecution of Jews in the Reichsgau Sudetenland 1938–1945 ( Memento from July 18, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) (Book previews: [1] , [2] )
- Reichsgaue in Austria
Remarks
- ^ Law on the structure of the Sudeten German territories of March 25, 1939
- ^ Decree of the Führer and Reich Chancellor on the organization and administration of the Eastern Territories of October 8, 1939
- ^ Law on the structure of the administration in the Ostmark ("Ostmarkgesetz") of April 14, 1939
- ↑ Section 14 (1) of the Ostmarkgesetz still stipulated that the Reichsgaue had to be set up by September 30, 1939.
- ^ Eberhard Jäckel: France in Hitler's Europe . Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Stuttgart 1963, p. 83 f. (with indication of the archival sources).
- ↑ In detail on Westmark, also as an ideological construct by scientists from Western research : Annexion et nazification en Europe: Actes du colloque de METZ, 7–8 November 2003 ( Memento of 7 October 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF, French; 6 , 7 MB). In addition to the NS administrative unit ( Party Gau of the NSDAP) , the Westmark should then also include Luxembourg and East Belgium as Reichsgau .
- ↑ Le petit journal de guerre de Marguerite Liechty: Wintzenheim, de décembre 1944 à février 1945 ( Memento of October 23, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (French)
- ^ Territorial changes in Germany and German administered areas 1874–1945
- ↑ Notes on the formation of Belgium ( Memento of July 29, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ World Statesmen.org - Belgium (Eng.)
