Black-ear jewelry hummingbird
| Black-ear jewelry hummingbird | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Black-eared hummingbird ( Heliothryx aurita phainolaemus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Heliothryx auritus | ||||||||||||
| ( Gmelin, JF , 1788) |
The Black ear jewelry Hummingbird ( Heliothryx auritus ) or Schwarzohrelfe is a species of bird in the family of hummingbirds (Trochilidae) in Colombia , Venezuela , Guyana , Suriname , French Guiana , Brazil , Ecuador , Peru and Bolivia happens. The IUCN assesses the population as Least Concern .
features
The black-ear jewelry hummingbird reaches a body length of about 10.5 to 13.7 cm, with a weight of 4.0 to 6.3 g. The male has a short, straight, sharp-tipped black bill. The top of the head glistens green. There is a black line under the eye, the ear covers glitter purple. The rest of the top is green and the bottom is white. With the rounded tail, the three outer control feathers are white, the two central ones are dark blue. The female resembles the male, but the glittering purple ear covers are missing. Gray spots on the throat and chest. The tail is slightly longer than that of the male. The outer control springs are white with a black band at the base of the springs. Young birds are similar to females, but the head and neck feathers have cinnamon-colored fringes.
Behavior and nutrition
The black-eared hummingbird gets its nectar from flowering undergrowth, tendrils, cacti, epiphytes z. B. of species from the family of the red family , the diamond family , the ginger family , the passion flower family and the leguminous plants . He also gets his nectar by picking flowers. He hunts insects in flight. In Terra Firme forests he searches for food in all strata . This extends from the undergrowth to the treetops and into the interior of forests.
Reproduction
Black-eared hummingbirds' nests exist year-round, but most appear to be between July and March. He was observed building nests in Manaus in July and with nestlings from August to September. In eastern Brazil, the range of H. a.auriculatus , the breeding season seems to last from October to March. The nest is a fluffy cup that is attached to vertical branches. This can be at heights between 3 and 30 meters above the ground. The nests are approx. 40 mm high. The outer radius is approx. 55 mm, the inner radius approx. 35 mm. The eggs weigh about 0.7 g and are about 16 × 10 mm in size. The incubation period is 15 to 16 days and incubation is carried out exclusively by the female. The chicks are black with faint grayish stripes on the back. The nestlings fledge after 23 to 26 days. Presumably, a strategy against nest predators is that the female imitates a dead leaf that falls on the ground while leaving and while the nest is being built. It then stops sliding down the undergrowth about 2 meters above the ground. The first brood occurs in the second year of life of the hummingbird.
Vocalizations
The black-ear jewelry hummingbird emits light tsit and richer chip sounds, which it repeats at intervals.
distribution and habitat
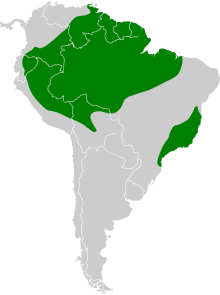
The black-eared hummingbird prefers moist lowland forests, forest edges and secondary vegetation at altitudes of up to 800 meters. Most often it can be found at altitudes of up to 400 meters.
migration
The black-eared hummingbird is a resident bird . Irregular reports of occurrences in southern Brazil could indicate migration.
Subspecies
There are three known subspecies:
- Heliothryx auritus auritus ( Gmelin, JF , 1788) occurs in southeast Colombia and eastern Ecuador via Venezuela, the Guyanas and northern Brazil.
- Heliothryx auritus phainolaemus Gould , 1855 is widespread in north-central Brazil south of the Amazon . The male of this subspecies has a green chin and a green throat. The female is spotlessly white on the underside.
- Heliothryx auritus auriculatus ( Nordmann , 1835) occurs in eastern Peru to central Bolivia and central and eastern Brazil. The male of this subspecies has a green chin and green sides on the throat.
Etymology and history of research
The first description of the Black ear jewelry hummingbirds carried out in 1788 by Johann Friedrich Gmelin under the scientific name Trochilus auritus . The type specimen came from the area around Cayenne . It was not until 1831 that Friedrich Boie introduced the genus Heliothryx for several hummingbird species a. a. the black-ear jewelry hummingbird. This name is derived from the Greek words "hēlios, ἡλιος " for "sun" and "thrix, trikhos, θριξ, τριχος " for "hair". The species name »auritus« is derived from the Latin »auris« for »ear«. "Auriculatus" has the same ancestry and means "eared, having ears". "Phainolaemus" is a Greek word formation from "phaeinos, phainō φαεινος, φαινω " for "brilliant, shining, shining" and "laimos, λαιμος " for "throat".
literature
- Karl-Ludwig Schuchmann , Guy Maxwell Kirwan , Peter Boesman in: Josep del Hoyo , Andrew Elliott, Jordi Sargatal , David Andrew Christie, Eduardo de Juana: JBlack-eared Fairy (Heliothryx auritus) In: Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive . Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
- James A. Jobling: Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names . Christopher Helm, London 2010, ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4 .
- Johann Friedrich Gmelin: Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, Cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, Locis . tape 1 , no. 1 . Georg Emanuel Beer, Leipzig 1788 ( biodiversitylibrary.org ).
- John Gould: On two new species of Humming Birds . In: Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London . tape 23 , no. 289 , 1855, pp. 86-87 ( biodiversitylibrary.org ).
- Alexander von Nordmann in Georg Adolf Erman: Chapter I. Birds, II. Mammals, III. Amphibians, IV.Fishes in voyage around the earth through North Asia and the two oceans, in the years 1826, 1829 and 1830 . Natural history atlas. G. Reimer, Berlin 1835, p. 1–26 ( books.google.de ).
- Friedrich Boie: Comments on species and some ornithological families and clans . In: Isis von Oken . tape 24 , 1831, pp. 538-548 ( biodiversitylibrary.org ).
Web links
- Heliothryx auritus inthe IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019.1. Listed by: BirdLife International, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- BirdLife International: Species Factsheet - Black-eared Fairy ( Heliothryx auritus ) . Retrieved May 26, 2019.
- Videos, photos and sound recordings of Black-eared Fairy (Heliothryx auritus) in the Internet Bird Collection
- Black-eared hummingbird ( Heliothryx auritus ) at Avibase; accessed on May 26, 2019.
- Heliothryx auritus in the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Retrieved on 2019-05-26.
- xeno-canto: Sound recordings - Black-eared jewelry hummingbird ( Heliothryx auritus )
- Black-eared Fairy (Heliothryx auritus) in the Encyclopedia of Life . Retrieved May 26, 2019.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Karl-Ludwig Schuchmann u. a.
- ^ IOC World Bird List Hummingbirds
- ↑ a b Johann Friedrich Gmelin (1788), p. 493.
- ^ John Gould (1855), p. 87.
- ↑ Alexander von Nordmann (1835), p. 5, plate 2 fig. 1 & 2.
- ^ Friedrich Boie, p. 547.
- ↑ James A. Jobling, p. 188.
- ↑ a b James A. Jobling, p. 62.
- ↑ James A. Jobling, p. 301.
Remarks
- ↑ Boie assigned the amethyst -eared hummingbird ( Colibri serrirostris ) ( Vieillot , 1816) (Syn: Trochilus petasophorus ( Wied-Neuwied , 1832)) and the green-masked hummingbird ( Augastes scutatus ) ( Temminck , 1824) to the genus .