Storm Daisy
| Storm Daisy 2010 | |
|---|---|
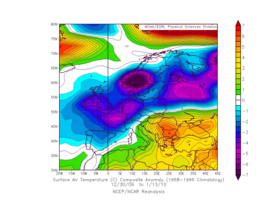
| Temperature anomalies Dec 30, 2009–13. Jan. 2010 | |
| storm | Snow storm , cold spell |
| weather condition | Mediterranean / Vb-low with ingress of polar cold air |
| Data | |
| education | January 5th |
| The End | 11th January |
| Annuality of snowfalls | ≈25 ( northern Spain , 6-7 January. But 2 months later surpassed ) |
| Annuality of the cold | ≈30 ( United Kingdom , but exceeded the year after ) |
| consequences | |
| affected areas | West and North Central Europe : Spain , France , Belgium , Netherlands , Luxembourg , United Kingdom , Switzerland , Germany , Denmark , Poland |
| Victim | > 100 cold deaths |
| Damage amount | 1.245 billion € total damage (of which 750 million € insurance damage) |
The storm Daisy is the name of a low pressure system , the wide in the period from 8 to 11 January 2010 parts of Central Europe recorded. It led to severe impairment from snowstorms in large areas of Europe. Connected were low temperatures in Western Europe, which claimed over 100 lives.
weather condition
Daisy was a typical Mediterranean low, where a relatively warm, but at the same time moist air flow from the Mediterranean area meets a cold air flow from a high pressure area from the Scandinavian or Eastern European region. It formed on the 5th over the Iberian Peninsula , moved with the classic Va-orbit on the 9th over northern Italy and then north-eastwards in a typical Vb direction. From the 7th on, there was a strong pressure gradient to the North Atlantic / Scandinavian Hoch Bob - combined with an ingress of arctic cold air over the British Isles down to −20 ° C - and on the 8th also one over the Black Sea region - where scirocco-like currents of African air in Romania set record values up to +20 ° C. As a result, a strong snowstorm developed over Central Europe first from the west, then from the south-east, with wind speeds well over 100 km / h. The low moved over the Carpathian Mountains and disintegrated 11th to 12th d. M. in the northern Black Sea region.
Assumed amounts of snow in the range of 40 cm / 24 h, as they had not occurred in northern Germany since 1986/87 or the disaster winter 1978/79, did not occur in the area, but in Boizenburg an der Elbe on January 10, 2010 a total snow depth of 46 centimeters measured and thus the highest snow cover since 1979. In the area of the Austrian Southeast Alps and Carpathians , the amount of snow was less than feared. Nevertheless, there were local snow depths of over one meter in northern Germany.
Estimation of the annuality
Snowfall occurred in Spain, as it had not for 25 years ( January 5, 1985 ). Nevertheless, this event was already exceeded two months later by the Mediterranean depression Andrea , which caused snow chaos in the entire northern Mediterranean area, so that an annual rate of 25, as stated after the event, needs to be reconsidered.
The British Isles experienced a cold spell as a result of the ingress of polar cold air as it had not for 30 years ( 1981/1982 ). However, this was exceeded by far the following winter with a devastating cold spell in November / December .
consequences
Northern Spain experienced heavy snowfalls with heavy local flooding , even on Mallorca snow fell and Vesuvius near Naples was covered in deep snow.
Serious adverse effects from snow drifts and wind breaks were recorded throughout France . In southern France , 7,000 households were without electricity after a snow load failure. Flight operations came to a standstill in some places, in Lyon 800 passengers had to sleep on camp beds at the airport on January 9, in Roissy and Orly up to half of all flights had to be canceled by the 13th. In northern France there were severe traffic delays with numerous serious car accidents over several days.
In Holland on the 9th 100,000 people were cut off from the electricity supply.
England had over 100 deaths from cold. Most of the major airports ( London-Gatwick and City , Birmingham ) had to be closed or most of the flights had to be canceled ( Heathrow ).
In Germany, the north was mainly affected, numerous motorists and two regional trains at Anklam and Greifswald were snowed in and had to be rescued, but southwest Germany also recorded almost 1,000 weather-related traffic accidents with around 100 injuries. In Schleswig-Holstein and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania , a number of smaller localities have been cut off from the outside world (e.g. on the island of Fehmarn ). There were port areas such. B. in Flensburg flooded and on the Baltic Sea between the seaside resorts of Dahme and Kellenhusen near Dahmeshöved the dike threatened to break.
In Poland at times over 80,000 people were without electricity after a snow break.
Damage analysis
According to Munich Re , the storm and the accompanying cold spell caused total economic damage of EUR 1.245 billion, of which EUR 750 million was covered by insurance. After the cold spell on the British Isles in early winter 2010, the Daisy event is the second most expensive insured event for winter damage in the period 1980–2011.
Web links
- Case study Christian Csekits, Andreas Frank, Herbert Gmoser, Gerhard Hohenwarter, Andreas Jäger, Thomas Krennert, Erich Steiner, Thomas Turecek, Christian Zwatz, Veronika Zwatz-Meise: 6th - 11th January 2010 - Why the big snow didn't come. Snow chaos in Europe from 6th to 11th January 2010: Effects of the low pressure areas "Barbara" and "Daisy". ZAMG , January 14, 2010, accessed on March 10, 2010 .
- Storm and snow depth Daisy , meteomedia, 01/2010
- [1] , Wetteronline, snow depths January 10, 2010
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Snow chaos in Spain. (No longer available online.) In: Ö1 Abendjournal. ORF , January 11, 2010, formerly in the original ; accessed on January 14, 2010 (link to audio file, info radio). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Chaos again due to snowfall in Great Britain . In: Salzburger Nachrichten . January 13, 2010, Chronicle ( article archive ).
- ↑ Forecast 20100105 . Institute for Meteorology, FU Berlin
- ↑ Forecast 20100109 . Institute for Meteorology, FU Berlin
- ↑ Forecast 20100107 . Institute for Meteorology, FU Berlin
- ↑ Forecast 20100108 . Institute for Meteorology, FU Berlin
- ↑ Forecast 20100111 . Institute for Meteorology, FU Berlin
- ↑ The ZAMG analyzed that the warm air had penetrated much further north due to the large pressure difference and had cleared out the cold air. APA, cit. n. Salzburg news . January 11, 2010, Austria, p. 8 (article in article archive ).
- ↑ a b c d e When winter came . In: Salzburger Nachrichten . January 11, 2010, Chronicle, p. 20 ( article archive ).
- ↑ a b c Hundreds of drivers freed from the snow. In: Panorama / Miscellaneous. Tages-Anzeiger , January 10, 2010, accessed January 14, 2010 .
- ↑ a b c Winter chaos caused by storm "Daisy" . In: Salzburger Nachrichten . January 9, 2010, Chronicle ( article archive ).
- ↑ Stern.de: Daisy causes school dropout . January 10, 2010
- ↑ Focus.Online
- ↑ Danger on the dike averted; shz January 11, 2010
- ↑ Reuters Germany Information Service
- ↑ The most expensive cold spells for insurers . In: Insurance Journal Austria. 3rd February 2012