Cause of death
The cause of death is the cause of the occurrence of dying and death . Depending on the perspective, the term can be defined differently. Causes of death in a broader sense include events and circumstances that can result in death. In the field of medicine, specific illnesses or external acts of violence are named as causes of death.
The term type of death refers to the distinction between the causes of death in three categories: natural , not natural, or unexplained .
Determination of the cause of death
The determination of death in humans is a matter for doctors. The technical term for this is morgue , this is carried out in Germany by a licensed physician. In the death certificate (death certificate, corpse certificate), the cause of death is indicated as far as possible.
If no natural cause of death is determined (i.e. unnatural or unclear cause), the public prosecutor decides on how to proceed ( death investigation procedure ). Usually an autopsy by a forensic doctor follows . The determination of the exact cause of death by the autopsy also enables an important quality control with regard to the previous diagnosis and therapy .
Particularly in the case of unexpected deaths, it should be investigated which illness or violence caused the death.
Within the process of dying, another complication can ultimately lead to death without, from a medical point of view, triggering the dying process, in which more and more organ systems irreversibly cease to function. For example, if someone with fatal cancer last died of pneumonia, the cancer is considered to be the (causative) cause of death. In people with multiple illnesses ( multimorbidity ), it is often not easy to determine the decisive cause of death and the sequence of conditions that led to it. This can be of decisive legal importance in the case of insurance cases, violent deaths or medical malpractice, but also in the case of so-called "late death" after an accident. The event that ultimately led to death could have been weeks or years ago. Example: traumatic brain damage → dementia and bed restraint → pulmonary embolism → late death; Conclusion: unnatural death from brain trauma .
statistics
The cause of death statistics are based on the medical death certificates. There, even if several illnesses leading to death are present, a single entry must be ticked as the cause of death.
The cause of death statistics of the states differ greatly, depending on the respective average income. The global cause of death statistics are very different from the statistics of a country like Germany. The most common causes of death in Central Europe are circulatory diseases and cancer . Infectious diseases dominate in developing countries (often due to malnutrition).
Worldwide
Around 50–60 million people die on earth every year (as of 2020).
According to estimates by the World Health Organization , the top twenty causes of death worldwide in 2016 were:
| Cause of death | Annual deaths (in thousands) |
|---|---|
| Coronary heart disease | 9,433 |
| stroke | 5,781 |
| COPD | 3,041 |
| Lower respiratory diseases ( pneumonia ) | 2,957 |
| Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias | 1,992 |
| Tracheal , bronchial , lung cancer | 1,708 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1,599 |
| traffic accident | 1,402 |
| Diarrheal diseases ( cholera , typhus , dysentery ) | 1,383 |
| tuberculosis | 1,293 |
| Cirrhosis of the liver | 1,254 |
| Kidney disease | 1,180 |
| Complications of premature birth | 1,013 |
| HIV / AIDS | 1.012 |
| Hypertonic heart disease | 898 |
| Liver cancer | 830 |
| Anal cancer | 794 |
| Self harm | 793 |
| Stomach cancer | 760 |
| Death in childbirth | 679 |
| other | 17,071 |
| All in all | 56,874 |
The frequencies of the causes of death are subject to changes over time. In 1996, worm diseases ranked tenth with 135,000 victims. In 2000, around 2.2 million people died of diarrhea. Of diabetes mellitus died in 2000 less than 1 million. The HIV / AIDS epidemic peaked in 2005 with 1.8 million deaths. In 2018 approximately 770,000 people died of HIV / AIDS.
The most common causes of death at the beginning of the 21st century are coronary heart disease and stroke.
Jean Ziegler , the UN special rapporteur on the right to food from 2000 to 2008, estimated in 2007 that hunger or the consequences of malnutrition or malnutrition were the causes of death in around 30–40 million people , see also World Hunger .
About two thirds of all deaths are caused by old age diseases. In developed countries - including Germany - this ratio is even more extreme and can reach 90 percent.
In 2007, the annual number of deaths from smoking was estimated at 5.4 million.
In 2016, alcohol consumption resulted in approximately 3 million deaths worldwide.
Germany

Between 1990 and 2016, between 818,000 and 925,000 people died annually in Germany , see birth balance # Germany . 910,902 people died in 2016.
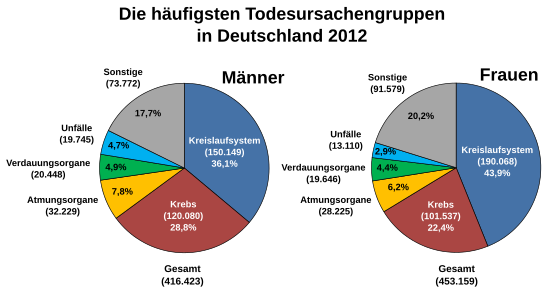
The most common natural causes of death (as of 2015):
- Cardiovascular diseases ( heart attack , stroke ) with almost half of all victims
- Cancer ( lung cancer , colon cancer , prostate cancer , breast cancer )
- Liver disease , especially alcoholic cirrhosis
- Lung diseases ( bronchial asthma ; chronic bronchitis and emphysema , see COPD )
- Infections
The most common unnatural causes of death:
- Falls: almost 13,000 people
- Suicide : over 11,000 people, 74% of them men and 26% women
- Traffic accidents : around 4,000 people
- Other accidents : work accidents, domestic accidents, sports accidents
- Injuries
- Poisoning
The order of the most common causes of death differs further according to gender and age group, which can be considered separately (e.g. due to age-related diseases ).
Switzerland
In 2015, 67,606 people died in Switzerland, 6 percent more than in the previous year. The spring flu wave , the July heat wave and the aging population all contributed to this. The mortality rate and the potential years of life lost increased accordingly, and life expectancy at birth temporarily decreased. The most common causes of death are accidents and suicide between the ages of 15 and 40, cancer between the ages of 40 and 80 and cardiovascular diseases in those over 80. This emerges from the statistics on causes of death from the Federal Statistical Office . Overall, cancer was the leading cause of premature death in 2016. In 2017 1043 people have suicide committed and other 1,009 people to assisted suicide committed.
Miscarriages and stillbirths
The statistics usually relate to live births, so miscarriages and stillbirths are not recorded. Infections, malformations, insufficient care or abortions of unborn babies are therefore not listed as causes of death in the official statistics.
In Austria between 1970 and 2010 there were 3,597,777 live births, 19,110 stillbirths (0.5%). The infant mortality rate in 2010 was 3.9 ‰.
Drugs cause death
The more common cause of death is not illegal, but legal drugs . In Germany, the number of drug deaths from illegal drugs has fallen from around 2000 to around 1300 (in 2018) since the beginning of the millennium.
The number of deaths as a result of alcohol abuse was given in the reports of the drug commissioner of the federal government 2002 to 2008 with "over 40,000 people". Since the report from 2009 (up to and including 2012), more recent calculations have given significantly higher numbers, according to which “over 73,000 people die as a result of their alcohol abuse”. The most common alcohol-related cause of death is alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver . Men are three times more likely to die from alcohol abuse than women.
As a result of tobacco smoking , 110,000 to 140,000 people die annually in Germany (5.4 million worldwide per year). In addition, 3300 deaths from passive smoking are assumed.
In the wake of the US drug crisis in 2016, overdoses overtook heart disease as the leading cause of death among those under 55.
Cause of death war service
During the Second World War, up to half of a cohort of German men perished in individual cohorts. In the post-war population, the number of surviving men tends to die earlier than would be expected in a population unaffected by war. Injuries, psychological stress, malnutrition or health hazards from combat operations shorten the life expectancy of survivors. However, since these men reach 50 and more years of life and only then die increasingly, this change in the health situation of those affected by the war does not have an impact immediately after the end of the war.
In a study of the Germans who survived both world wars, it was found that the male adolescents at the end of the war later had a significantly higher mortality in the middle age groups. This is not evident in German women. Something similar can be observed, but not to the same extent, in the other warring countries of both world wars. This is explained by the fact that the blood vessel structures are impaired by malnutrition, but this only has an effect in the age groups in which cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death. This affects young people most at the end of the war, as undernourishment in the last years of growth cannot be compensated for later, as is the case with smaller children. That this only affects men is explained by the fact that women can store more fat.
Unnatural causes of death
The list below contains examples of unnatural causes of death.
Accidents:
- Traffic accidents : cars , trains , planes , pedestrians and cyclists
- Domestic accidents
- Sports accidents : riding accidents , mountain accidents
- Fall, e.g. B. Slipping while walking (see also falling in old age )
- Electricity accidents (accidents involving electricity)
- Burn injuries
- Drown
- Freeze to death
- Firearm accidents
- Animal bite ( dog bite , etc.)
- lightning strike
Intentional Killing:
Others:
- Poisoning
- Radioactivity (artificial and naturally occurring, e.g. radon )
- Side effects of drugs, e.g. B. by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or with existing penicillin allergy
- Incidents of surgery or anesthesia , malpractice
See also
literature
- Sherwin B. Nuland : How We Die. An end with dignity? Kindler Verlag , Munich 1996, ISBN 3-426-77237-X (English: How We Die . Translated by Enrico Heinemann and Reinhard Tiffert).
Web links
- Steffen Kröhnert, Rainer Münz: Mortality and Causes of Death. In: Online Handbook Demography. Berlin Institute for Population and Development, August 2008, archived from the original on January 13, 2011 ; Retrieved November 25, 2017 .
- Federal Statistical Office (Destatis): causes of death .
- Federal Statistical Office (Destatis): Publications in the field of causes of death . Retrieved October 4, 2017
- Deaths from selected causes of death 1901 - 1938. Lebendiges Museum Online , archived from the original on January 25, 2010 ; Retrieved November 25, 2017 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c The top 10 causes of death , WHO, May 24, 2018, accessed May 26, 2020.
- ↑ Demographic Overview - World , International Data Base, United States Census Bureau, accessed May 23, 2020.
- ↑ Summary tables of mortality estimates by cause, age and sex, globally and by region, 2000–2016 (XLS format), Cause-specific mortality , Disease burden and mortality estimates, WHO, accessed on May 24, 2020.
- ↑ Estimates of global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV, 1980–2015: the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 , Lancet HIV, August 2016, 3 (8): e361 – e387. DOI : 10.1016 / S2352-3018 (16) 30087-X, published online July 19, 2016, accessed May 26, 2020.
- ↑ Global HIV & AIDS statistics - 2019 fact sheet , UNAIDS , accessed May 26, 2020.
- ↑ A child who dies of starvation is murdered. World Food Program (WFP) , archived from the original on January 17, 2009 ; Retrieved October 22, 2008 .
- ^ A b de Gray Aubrey DNJ : Life Span Extension Research and Public Debate: Societal Considerations . (PDF) In: Studies in Ethics, Law, and Technology . 1, No. 1, Article 5, 2007. doi : 10.2202 / 1941-6008.1011 . Retrieved August 7, 2011.
- ↑ One billion deaths from smokers this century , welt.de, July 2, 2007, accessed on May 26, 2020.
- ↑ Global status report on alcohol and health 2018. (PDF; 7.4 MB) World Health Organization, accessed on January 8, 2020 (English).
- ↑ Causes of death in Germany in 2015. Accessed on November 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Federal Statistical Office: Number of deaths according to selected causes of death in 2015. Accessed on November 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Federal Statistical Office: Number of deaths according to selected causes of death in 2015. Accessed on November 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Cause of death statistics 2015 In: bfs.admin.ch , November 14, 2017, accessed on December 12, 2017.
- ↑ Cancer. In: bfs.admin.ch. Retrieved May 3, 2020 .
- ↑ Cause of death statistics 2017: Cardiovascular diseases and cancer are still the most common causes of death in Switzerland. In: bfs.admin.ch. December 16, 2019, accessed December 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Cause of death statistics - What most Swiss people die from. In: srf.ch . December 16, 2019, accessed December 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Live / still births after the reporting year. Statistics Austria , accessed on February 28, 2012 (SDB online database: select the tab "Databases → Statistics → Population → Births → Born" at the top left; years 1970–2010).
- ↑ Deaths and infant mortality since 1946. Statistics Austria , May 19, 2011, accessed on February 28, 2012 .
- ↑ Drugs and Addiction Report 2002 (PDF; 983 kB) of the Drugs Commissioner of the Federal Government
- ↑ Drugs and Addiction Report 2019 , Publications of the Drug Commissioners, accessed on May 28, 2020.
- ↑ a b c The individual reports can be found in the overview of publications ( Memento of the original from January 27, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. can be obtained from the drug commissioner of the federal government.
- ↑ a b Drug and Addiction Report 2012 (PDF; 2.5 MB) of the Federal Government's Drugs Commissioner
- ↑ Josh Katz and Abby Goodnough, "The Opioid Crisis Is Getting Worse - Particularly for Black Americans," New York Times, December 22, 2017
- ↑ Marc Luy : Why women live longer . Findings from a comparison of the monastery and general population. In: Materials on Population Science . No. 106 . Federal Institute for Population Research , 2002, ISSN 0178-918X , DNB 965668789 , LCCN 2003-362130 , p. 13 f . ( PDF; 1.5 MB [accessed on December 6, 2015] plus diploma thesis 1998). PDF; 1.5 MB ( Memento of the original dated December 6, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Marc Luy: Insa Cassens, Marc Luy , Rembrandt Scholz (ed.): The population in East and West Germany. Demographic, social and economic developments since the fall of the Wall . VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften , Wiesbaden 2009, ISBN 978-3-8350-7022-6 , The gender-specific mortality differences in West and East Germany with special consideration of the war-related long-term effects on cohort mortality, p. 169–198 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).