Thorium nitrate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
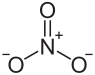
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thorium nitrate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Th (NO 3 ) 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
hygroscopic white platelets |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 480.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.78 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Easily soluble in water and ethanol |
|||||||||||||||
| Hazard and safety information | ||||||||||||||||
 Radioactive |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Thorium nitrate (Th (NO 3 ) 4 ) is a colorless, readily soluble in water and ethanol -soluble chemical compound , the thorium salt of nitric acid . The nitrate is an important intermediate in the preparation of thorium (IV) oxide and thorium metal and is also in the generation of gas mantles used.
properties
Chemical reaction
Thorium nitrate itself is not flammable, but - like other nitrates - oxidizes . Mixtures with flammable substances can therefore react violently or explosively when ignited . The resulting gases contain nitrogen compounds that are harmful to health.
Aqueous solutions are acidic because hydrolysis produces nitric acid . The solutions slowly decompose with the separation of so-called basic thorium nitrates.
Health effects
Thorium nitrate itself is slightly toxic, but the released alpha radiation can be harmful in large quantities. The emission of beta and gamma radiation is rather low. The dust can irritate the eyes, nose, throat and skin. In the event of contact with the eyes, they should be rinsed thoroughly with running water.
Oral administration in high doses to mice caused fatal gastrointestinal disorders such as gastric ulcer and intestinal bleeding . If swallowed, it is recommended to drink plenty. In any case, a doctor should be consulted immediately. The substance can cause nausea, drowsiness, vomiting, abdominal cramps, bloody diarrhea, seizures and circulatory collapse .
radioactivity
Thorium nitrate has a specific activity of 3.93 kBq / g.
use
Up until a few years ago, the most important thing was the use of incandescent mantles , which improved the light output of gas lamps . In the meantime, however, the substance has been successfully replaced by non-radioactive materials.
It was also used for the production of electrodes for welding ( tungsten inert gas welding (TIG)). Likewise, cathodes for magnetron and traveling wave tubes were made using thorium nitrate, as these were able to emit free electrons even at low temperatures and also had a longer service life.
As part of Thorium-X
Thorium nitrate is a component of Thorium-X , a mixture of different radioactive isotopes, which was used in the past, among other things, for the production of the toothpaste Doramad , which was considered particularly healthy at the time , but which was withdrawn from the market after the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki because of the since then obvious harmfulness of radioactivity has been. There were also ointments, bath additives and tinctures , mainly against eczema, under the name Thorium-X . This use had e.g. Sometimes serious long-term consequences.
Thorium-X has been widely researched, including its (presumed positive) effects on the immune system and on mycoses .
In the 1960s, Thorium-X was also used against ankylosing spondylitis .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds, pp. 4-95.
- ↑ a b ibilabs.com: MSDS Thorium Nitrate ( Memento from February 13, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Thorium nitrate hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ The hazards emanating from radioactivity do not belong to the properties to be classified according to the GHS labeling.
- ↑ a b c Environmental Quality and Safety, Supplement , Vol. 1, 1975, p. 1.
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on thorium nitrate in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b S. J. Patrick: Some effects of the administration of thorium nitrate to mice . In: Canadian Journal of Research . tape 26 e, no. 6 , 1948, pp. 303-316 , doi : 10.1139 / cjr48e-019 .
- ↑ Entry on thorium tetranitrate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 12, 2014.
- ↑ James B. Hedrick: Thorium (PDF; 36 kB).
- ^ Victor H Witten, Milton S Ross, Eleanor Oshry, Arthur B Hyman, Vera Holmstrom: Studies of Thorium X Applied to Human Skin. In: Journal of Investigative Dermatology . 17, 1951, pp. 311-322, doi: 10.1038 / jid.1951.100 .
- ↑ J. Natkunarajah, S. Cliff: Thorium X treatment: multiple basal cell carcinomas within a port-wine stain. In: Clinical and Experimental Dermatology . 34, 2009, pp. E189 – e191, doi: 10.1111 / j.1365-2230.2008.03012.x .
- ↑ Ludvig Hectoen, HJ Corper: The Influence of Thorium X on Antibody Formation . In: Journal of Infectious Diseases . tape 26 , no. 4 , 1920, p. 331-335 , JSTOR : 30082119 .
- ↑ Bernard Green: mycosis fungoides - Treated with thorium X . In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine . tape 40 , no. 9 , 1947, pp. 503 , PMID 19993605 , PMC 2183582 (free full text).
literature
- Mathias S. Wickleder, Blandine Fourest, Peter K. Dorhout: Thorium. In: Lester R. Morss, Norman M. Edelstein, Jean Fuger (Eds.): The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements. Springer, Dordrecht 2006, ISBN 1-4020-3555-1 , pp. 52-160, doi : 10.1007 / 1-4020-3598-5_3 .
Web links
- Information (PDF, en; 17 kB) from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration




