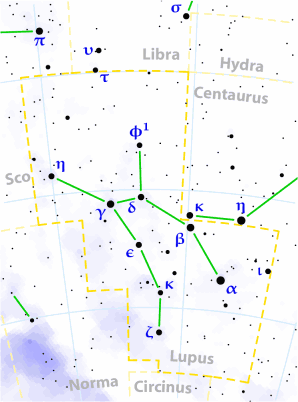
Wolf (constellation)
|
Constellation wolf |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Lupus |
| Latin genitive | Lupi |
| Abbreviation | Lup |
| Right ascension | 14 h 17 m 48 s to 16 h 08 m 37 s |
| declination | −55 ° 34 ′ 48 ″ to −29 ° 50 ′ 16 ″ |
| surface | 333,683 deg² rank 46 |
| Completely visible | 34.7 ° N to 90 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | not visible |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 3 |
| Brightest star (size) | Alpha Lupi (2.30) |
| Meteor streams | |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
The wolf ( Latin lupus ) is a constellation in the southern sky .
description
The wolf lies between the distinctive constellations Scorpio and Centaur . Three of its stars are brighter than the 3rd magnitude . The Milky Way runs through the southern part , so it contains a number of foggy objects. Because of its southern location, only the northern part of the wolf can be seen from southern Europe and southern central Europe.
history
The wolf is one of the classic 48 constellations of antiquity described by Ptolemy . It was completely visible from southern Europe 2,000 years ago. As a result of the precessional movement of the earth's axis, its position has shifted south over time.
In 1006 an extremely bright supernova lit up in the wolf , which is now referred to as SN 1006 .
mythology
The Sumerians , Assyrians and Babylonians also called the constellation wolf ( Sumerian UR.DIM) and was considered to be the embodiment of the god Kusu , who in turn was counted among the 12 celestial objects of Enki .
The ancient Greeks called him Θηρίον Thēríon (an unspecified raging animal). The centaur sacrificed the animal on an altar.
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | F. | Names or other designations | size | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Men , Kakkab | 2.30 m | 500 | B1 III | |
| β | 2.68 m | 500 | B2 IV | ||
| γ | 2.80 m | 400 | B2 IV | ||
| δ | 3.22 m | 600 | B2 IV | ||
| ε | 3.37 m | 400 | B3 IV | ||
| ζ | 3.41 m | 120 | G8 + F8 | ||
| η | 3.42 m | 600 | B2 IV | ||
| ι | 3.55 m | 400 | B3 IV | ||
| φ 1 | 3.57 m | 200 | K5 III | ||
| κ | 3.7 m | 200 | B9 + A2 | ||
| π | 3.91 m | 400 | B5 + B5 | ||
| χ | 5 | 3.97 m | |||
| ρ | 4.05 m | ||||
| λ | 4.07 m | ||||
| θ | 4.22 m | ||||
| μ | 4.27 m | 251 | B8 + B8 + A0 + F5 | ||
| ο | 4.32 m | ||||
| τ 2 | 4.33 m | ||||
| ω | 4.34 m | ||||
| f | 2 | 4.35 m | |||
| σ | 4.44 m | ||||
| φ 2 | 4.54 m | ||||
| d | 4.55 m | 800 | B3 + B8 | ||
| τ 1 | 4.56 m | ||||
| k | 4.60 m | ||||
| G | 4.64 m | ||||
| ψ 1 | 3 | 4.66 m | |||
| ψ 2 | 4th | 4.75 m | |||
| e | 4.83 m | ||||
| i | 1 | 4.91 m | |||
| ν 1 | 4.99 m | ||||
| ξ 1 | 4th | 5.14 m | |||
| b | 5.22 m | ||||
| H | 5.23 m | ||||
| υ | 5.36 m | ||||
| c | 5.38 m | ||||
| a | 5.39 m | ||||
| ξ 2 | 5.59 m | ||||
| ν 2 | 5.65 m |
β Lupi is a bluish shining star of spectral class B2 IV, 500 light-years away .
Double stars
| system | Sizes | distance |
|---|---|---|
| ζ | 3.41 / 6.7 m | 71 " |
| η | 3.42 / 7.8 m | 15 " |
| κ | 3.88 / 5.7 m | 27 " |
| ξ | 5.2 / 5.6 m | 10.7 " |
| π | 4.6 / 4.7 m | 1.6 " |
| μ | 5.0 / 5.1 / 7.2 / 7.1 m | 1.0 / 23.6 / 242 " |
κ Lupi is a binary star system 200 light years away. The two components belong to the spectral classes B9 and A2. Due to the angular distance of 27 arc seconds , they can be resolved into single stars even with a smaller telescope .
The ξ Lupi system is 250 light years away. It consists of two whitish shining stars of the spectral classes A0 and A2.
μ Lupi is a quadruple star 250 light years away . Two stars are already visible in the binoculars. A telescope with an opening of at least 20 cm is required to observe all four components .
Variable stars
| star | size | period | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| α | 2.30 ± 0.03 m | 6.23 hours | Beta Cephei star |
| EX | 8 m to 14 m | T-tauri star | |
| GQ |
α Lupi, the brightest star in the wolf, is a star of spectral class B1 III, 548 light years away . It has 10 times the mass and 10 times the diameter of our sun . Its brightness changes over a period of 6 hours and 14 minutes by the small amount of 0.03 size classes. It is a variable star of the Beta-Cephei type .
NGC objects
| NGC | other | size | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5749 | 8.8 m | Open star cluster | ||
| 5822 | 6.5 m | Open star cluster | ||
| 5824 | 9.0 m | Globular clusters | ||
| 5882 | 10.5 m | Planetary nebula | ||
| 5927 | 8.0 m | Globular clusters | ||
| 5986 | 7.1 m | Globular clusters |
In the wolf there are the open star clusters NGC 5749 and NGC 5822 .
NGC 5822 is about 2500 light years away and consists of about 100 stars. With a diameter of 40 arc minutes , it takes up a larger area in the sky than the full moon. In the prism binoculars it appears as an extended foggy spot.
The globular clusters NGC 5824 , NGC 5927 and NGC 5986 can also be seen with binoculars.
NGC 5986 is approximately 35,000 light years away. With a telescope with an opening of 15 cm or more, the edge area can be broken down into individual stars.
The open star cluster NGC 5822 has an extension of only 6 arc seconds.
The Retinal Nebula is a planetary nebula 1900 light years away.