Transylvania: Difference between revisions
Hubacelgrand (talk | contribs) m Transylvania is itself part of the Western world, thank you |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
The German name ''Siebenbürgen'' means "seven fortresses", after the seven ([[ethnic German]]) [[Transylvanian Saxons]]' cities in the region ([[Braşov|Kronstadt]], [[Sighisoara|Schäßburg]], [[Mediaş|Mediasch]], [[Sibiu|Hermannstadt]], [[Sebeş|Mühlbach]], [[Bistriţa|Bistritz]] and [[Cluj-Napoca|Klausenburg]]). The Hungarian name ''Erdély'' is derived from ''Erdő-elve'' meaning ''"beyond the forest"'' in Hungarian (a meaning first referred to in its Medieval Latin version in a 12th century document - ''[[Gesta Hungarorum]]''). |
The German name ''Siebenbürgen'' means "seven fortresses", after the seven ([[ethnic German]]) [[Transylvanian Saxons]]' cities in the region ([[Braşov|Kronstadt]], [[Sighisoara|Schäßburg]], [[Mediaş|Mediasch]], [[Sibiu|Hermannstadt]], [[Sebeş|Mühlbach]], [[Bistriţa|Bistritz]] and [[Cluj-Napoca|Klausenburg]]). The Hungarian name ''Erdély'' is derived from ''Erdő-elve'' meaning ''"beyond the forest"'' in Hungarian (a meaning first referred to in its Medieval Latin version in a 12th century document - ''[[Gesta Hungarorum]]''). |
||
The origin of the [[Romanian language|Romanian]] name ''Ardeal'' is controversial. ''Ardeal'' - as ''Ardeliu'' - was first referred to in a document in [[1432]]. It may be a borrowing from the [[Khazar]] “Ardil-land” (Hebrew „Eretz Ardil”, „ארדיל”), first mentioned in [[960]]. It could be likewise borrowed from the Celtic "Arduenna" (forest), reflected in other names such as [[Arda]], [[Ardal]], [[Ardistan]], [[Ardiche]], [[Ardennes]], [[Ardelt]], [[Ardilla]] or from the |
The origin of the [[Romanian language|Romanian]] name ''Ardeal'' is controversial. ''Ardeal'' - as ''Ardeliu'' - was first referred to in a document in [[1432]]. It may be a borrowing from the [[Khazar]] “Ardil-land” (Hebrew „Eretz Ardil”, „ארדיל”), first mentioned in [[960]]. It could be likewise borrowed from the Celtic "Arduenna" (forest), reflected in other names such as [[Arda]], [[Ardal]], [[Ardistan]], [[Ardiche]], [[Ardennes]], [[Ardelt]], [[Ardilla]] or from the [[Sanskrit]] ''Har-Deal''. Lastly, it may be a borrowing of the [[Hungarian language|Hungarian]] name ''Erdély'', as is the [[Romani language|Romani]] name ''Ardyalo'' - in old Hungarian, ''Erdély'' was pronounced as ''Erdél''. The initial [[Hungarian language|Hungarian]] ''e-'' occasionally changes to ''a'' in Romanian (cf. Hung. ''egres'' "gooseberry" and ''Egyed'', which became ''agriş'' and ''[[Adjud]]'' in [[Romanian language|Romanian]]). See also [[List of European regions with alternative names#T|other languages]]. |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
Revision as of 22:02, 7 October 2007
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2007) |
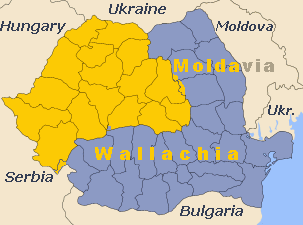
Transylvania (Romanian: Ardeal or [Transilvania] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help); Hungarian: Erdély; German: ; Bulgarian: Трансилвания; Serbian: Трансилванија / [Transilvanija] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) or Ердељ / [Erdelj] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help); Latin: Transsilvania) is a historical region in central and western Romania.
In its early history, the territory of present-day Transylvania belonged to Dacia, the Roman Empire, the Hun Empire and the Gepid Kingdom[1]. As a political entity, Transylvania is mentioned from the 11th century (after the Hungarian conquest) as a voivodship, part of the Kingdom of Hungary. It then successively became an autonomous principality under Ottoman suzerainty in 1571, a part of the Habsburg Monarchy in 1711 (Austria-Hungary after 1867), and a part of the Kingdom of Romania after World War I.
Transylvania's main city, Cluj-Napoca, is today considered to be the region's capital, although Transylvania was also ruled from Alba Iulia during its vassalage to the Ottoman Empire, and from Sibiu, where the Habsburg governor was located from 1711 until 1848. The seat of the Transylvanian Diet was itself moved to Sibiu for some time in the 19th century.
Etymology
Transylvania was first referred to in a Medieval Latin document in 1075 as Ultra silvam, meaning "beyond the forest" (ultra meaning "beyond, on the other side" and the accusative case of sylva (sylvam) meaning "wood or forest"). That name was later changed to "Transylvania" (trans also meaning "across, over, beyond").
The German name Siebenbürgen means "seven fortresses", after the seven (ethnic German) Transylvanian Saxons' cities in the region (Kronstadt, Schäßburg, Mediasch, Hermannstadt, Mühlbach, Bistritz and Klausenburg). The Hungarian name Erdély is derived from Erdő-elve meaning "beyond the forest" in Hungarian (a meaning first referred to in its Medieval Latin version in a 12th century document - Gesta Hungarorum).
The origin of the Romanian name Ardeal is controversial. Ardeal - as Ardeliu - was first referred to in a document in 1432. It may be a borrowing from the Khazar “Ardil-land” (Hebrew „Eretz Ardil”, „ארדיל”), first mentioned in 960. It could be likewise borrowed from the Celtic "Arduenna" (forest), reflected in other names such as Arda, Ardal, Ardistan, Ardiche, Ardennes, Ardelt, Ardilla or from the Sanskrit Har-Deal. Lastly, it may be a borrowing of the Hungarian name Erdély, as is the Romani name Ardyalo - in old Hungarian, Erdély was pronounced as Erdél. The initial Hungarian e- occasionally changes to a in Romanian (cf. Hung. egres "gooseberry" and Egyed, which became agriş and Adjud in Romanian). See also other languages.
History
Ancient History: Dacia and the Roman Empire
The kingdom of Dacia was in existence at least as early as the beginning of the 2nd century BC and it reached its maximum extent under Burebista. The area now constituting Transylvania was the political center of Dacia where several important fortified cities, among them Sarmizegetusa, near today's Hunedoara were built.
In 101-102 and 105-106, Trajan, the Roman emperor, fought a military campaign against the Dacians, known as the Dacian Wars. He managed to vanquish them and after the suicide of Decebalus parts of Dacia were incorporated into the Roman province Dacia Trajana. The Romans built mines, access roads and forts to protect them. Colonists from other Roman provinces were brought in to settle the land and cities like Apulum (now Alba Iulia) and Napoca (now Cluj-Napoca) appeared. The Dacians rebelled frequently and due to increasing pressure from them and the Visigoths in 271, the Emperor Aurelian abandoned Dacia Trajana.
The Middle Ages
The former Dacia Trajana province was controlled by the Visigoths and Carpians until they were in turn displaced and subdued by the Huns in 376, under the leadership of Attila. After the disintegration of Attila's empire, the rules of Gepids of Avars succeeded. The region was also influenced during this period by massive Slavic migration. At the beginning of the 9th century, Transylvania, along with eastern Pannonia, was incorporated into the First Bulgarian Empire followed by Magyar tribes linking it to the Principality of Hungary.
The Kingdom of Hungary
The early 11th century was marked by the conflict between King Stephen I of Hungary and his maternal uncle Gyula, the ruler of Transylvania. After the defeat of the latter, Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Transylvanian Roman Catholic bishopric and the comitatus system were organised. By the 12th century the Szeklers were established in eastern and southeastern Transylvania as border guards and in the 12th and 13th centuries, the areas in the south and northeast were settled by German colonists called Transylvanian Saxons. In 1241-1242, during the Mongol invasion, Transylvania was devastated and a large portion of the population perished. In 1285, there was another Mongol invasion in Transylvania, led by Nogai Khan.
Transylvania was organized according to the system of Estates, which were privileged groups (universitates) with power and influence in socio-economic and political life, being nonetheless organized according to certain ethnic criteria as well. The first Estate was the lay and ecclesiastic aristocracy, ethnically heterogeneous, but undergoing a process of homogenization around its Hungarian nucleus. The other Estates were Saxons, Szeklers and Romanians (or Vlachs - Universitas Valachorum), all with an ethnic and ethno-linguistic basis (Universis nobilibus, Saxonibus, Syculis et Olachis). The general assembly (congregatio generalis) of the four Estates had mainly supra-legislative powers in Transylvania, but it sometimes took measures regarding order in the country, relationships between the privileged, military issues, etc.

After the Decree of Turda (1366), which openly called for "to expel or to exterminate in this country malefactors belonging to any nation, especially Romanians" in Transylvania, the only possibility for Romanians to retain or access nobility was through conversion to Roman Catholicism. Some Orthodox Romanian nobles converted, being integrated in the Hungarian nobility, but the most of them declined, thus losing their status and privileges.
In some border regions (Maramureş, Ţara Haţegului) the Orthodox Romanian ruling class of nobilis kenezius (classed as lower nobility in the Kingdom as a whole) had the same rights as the Hungarian nobilis conditionarius. Nevertheless, because of the gradual loss of a nobility of its own, Romanians were no longer able to keep their Universitas Valachorum.
After the suppression of the Budai Nagy Antal-revolt in 1437, the political system was based on Unio Trium Nationum (The Union of the Three Nations). According to the Union, which was explicitly directed against serfs and other peasants, society was ruled by three privileged Estates or nations (Nationes), the nobility (mostly Magyars), the Szekelys, and the Saxon burghers.
A key figure to emerge in Transylvania in the first half of the 15th century was John Hunyadi. His subsequent military exploits against the Ottoman Empire brought him further status as the governor of Hungary in 1446 and papal recognition as the Prince of Transylvania in 1448. John Hunyadi was also the father of Matthias Corvinus of Hungary.
Independent principality


The 16th century was marked by the struggle between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg Empire. After Sultan Suleiman I overran central Hungary and established there the Turkish rule (see Ottoman Hungary), Transylvania became a semi-independent region where Austrian and Turkish influences vied for supremacy for nearly two centuries.
Due to the fact that Transylvania was now beyond the reach of Catholic religious authority, Protestant preaching such as Lutheranism and Calvinism were able to flourish. In 1568 the Edict of Turda proclaimed four religious expressions -Catholic, Lutheranism, Calvinism and Unitarianism - as "accepted" (receptae), while Orthodoxy, which was the confession of the Romanian population, was proclaimed as "tolerated" (tolerata). The Edict of Turda is considered by mostly Hungarian historians as the first legal guarantee of religious freedom in Christian Europe.
The Báthory family came to power in 1571 and ruled Transylvania as princes under the Ottomans, and briefly under Habsburg suzerainty, until 1600. The latter period of their rule saw a four-sided conflict in Transylvania involving the Transylvanians, the Austrians, the Ottomans, and the Wallachian voivod Michael the Brave. The latter gained control of Transylvania in 1599 after the Battle of Şelimbăr and succeeded in uniting the three principalities of Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania (the three main parts of present-day Romania). The union did not last long, however, as Michael was assassinated by mercenaries under the command of the Habsburg general Giorgio Basta in August 1601. Basta swore allegiance to the Habsburg Emperor, Rudolph II and by 1604 reclaimed the principality for Catholicism through the Counter Reformation.

The Calvinist magnate of Bihar county Stephen Bocskai managed to obtain, through the Peace of Vienna (June 23, 1606), religious liberty and political autonomy, the restoration of all confiscated estates, the repeal of all "unrighteous" judgments, and a complete retroactive amnesty for all Hungarians in Royal Hungary, as well as his own recognition as independent sovereign prince of an enlarged Transylvania. Under Bocskai's successors Transylvania passed through a period of flourishment both for the religious movements and for the arts and culture. It was one of the few European countries where Roman Catholics, Calvinists, Lutherans, and Unitarians lived in mutual tolerance, but Orthodox Romanians were denied equal rights.
Habsburg Empire

After the defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683, the Habsburgs gradually began to impose their rule on the formerly autonomous Transylvania. Apart from strengthening the central government and administration, the Habsburgs also promoted the Roman Catholic Church, both as a uniting force and also as an instrument to reduce the influence of the Protestant nobility. In addition, they tried to persuade Romanian Orthodox clergymen to join the Greek (Byzantine Rite) Catholic Church in union with Rome. As a response to this policy, several peaceful movements of the Romanian Orthodox population advocated for freedom of worship for all the Transylvanian population, most notably being the movements led by Visarion Sarai, Nicolae Oprea Miclăuş and Sofronie of Cioara.
From 1711 onward, the princes of Transylvania were replaced with Austrian governors and in 1765 Transylvania was declared a grand principality.
The revolutionary year 1848 was marked by a great struggle between the Hungarians, the Romanians and the Habsburg Empire. Warfare erupted in November with both Romanian and Saxon troops, under Austrian command, battling the Hungarians led by the Polish general Józef Bem. He carried out a sweeping offensive through Transylvania, and Avram Iancu managed to retreat to the harsh terrain of the Apuseni Mountains, mounting a guerrilla campaign on Bem's forces. After the intervention by the armies of Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, Bem's army was defeated decisively at the Battle of Temesvár (Timişoara) on 9 August 1849.
Having quashed the revolution, Austria imposed a repressive regime on Hungary, ruled Transylvania directly through a military governor and granted citizenship to the Romanians. However, in the Ausgleich of 1867, which established the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the special status of Transylvania ended and it was reincorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary. The new unity of Austria-Hungary created a process of Magyarization affecting Transylvania's Romanians and German Saxons.
Austria-Hungary
The 300-year long separate status of Transylvania came to an end after the Compromise from 1867. On 20 June 1867, the Diet was dissolved by royal decree, and an ordinance abrogated the legislative acts of the Sibiu provincial assembly. The department of the interior inherited the responsibilities of the Transylvanian Gubernium, and the government reserved the right to name Transylvania's royal magistrates as well the Saxon bailiff of the Universitas Saxorum. Hungarian legislation also came to supersede the Austrian code of civil procedure, penal law, commercial law, and regulations for bills of exchange.
Romania

Since the Austro-Hungarian empire had begun to disintegrate after the end of the First World War, the nationalities living inside proclaimed their independence from the empire. The 1228-member National Assembly of Romanians of Transylvania and Hungary, headed by leaders of Transylvania's Romanian National Party and Social Democratic Party, passed a resolution calling for unification of all Romanians in a single state on 1 December in Alba Iulia. This was approved by the National Council of the Germans from Transylvania and the Council of the Danube Swabians from the Banat, on 15 December in Mediaş. In response, the Hungarian General Assembly of Cluj reaffirmed the loyalty of Hungarians from Transylvania to Hungary on December 22, 1918. (See also: Union of Transylvania with Romania)
The Treaty of Versailles placed Transylvania under the sovereignty of Romania, an ally of the Triple Entente, and after the defeat in 1919 of Béla Kun's Hungarian Soviet Republic by the Romanian army, the Treaties of St. Germain (1919) and Trianon (signed in June 1920) further elaborated the status of Transylvania and defined the new border between the states of Hungary and Romania. King Ferdinand I of Romania and Queen Maria of Romania were crowned at Alba Iulia in 1922 as King of all Romania.
In August 1940, the second Vienna Award gave the northern half of Transylvania to Hungary but after the Treaty of Paris (1947) at the end of the Second World War the territory was returned to Romania. The post-WWII borders with Hungary, agreed on at the Treaty of Paris were identical with those set out in 1920.
Historical coat of arms of Transylvania
The Diet of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations in Transylvania's coat of arms. It depicts:
- A black turul on a blue background, representing the medieval nobility, which was primarily Magyar.
- The Sun and the Moon representing the Székelys.
- Seven red towers on a yellow background representing the seven fortified cities of the Transylvanian Saxons
(The red dividing band was originally not part of the coat of arms.)
-
Coat of Arms of 1659
-
Landesfarben of Transylvania in Austria-Hungary, reflecting the tinctures of the coat-of-arms
-
As part of the coat of arms of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920
-
As in the coat of arms of Romania at present
Geography and ethnography

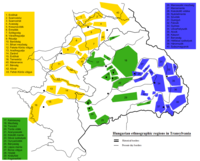
The Transylvanian plateau, 300 to 500 metres (1,000-1,600 feet) high, is drained by the Mureş, Someş, Criş, and Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. Other areas to the west and north, which also united with Romania in 1918 (inside the border established by peace treaties in 1919-20), are since that time widely considered part of Transylvania.
See also Administrative divisions of the Kingdom of Hungary. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the Treaty of Trianon, although geographically the two are not identical.
Administrative divisions

The historical region covers 16 present-day counties (Romanian: judeţ) which include nearly 103 600 km² of central and northwest Romania. The 16 counties are:
- Alba
- Arad
- Bihor
- Bistriţa-Năsăud
- Braşov
- Caraş-Severin
- Cluj
- Covasna
- Harghita
- Hunedoara
- Maramureş
- Mureş
- Sălaj
- Satu Mare
- Sibiu
- Timiş
The most populous cities are:
- Cluj-Napoca (318,027)
- Timişoara (317,651)
- Braşov (283,901)
- Oradea (206,527)
- Arad (172,824)
- Sibiu (155,045)
- Târgu Mureş (149,577)
- Baia Mare (137,976)
- Satu Mare (115,630)
Population
According to the 2002 census, Transylvania has a population of 7,221,733, with a large Romanian majority (74.69%). In addition, there are also sizeable Hungarian (19.60%), Roma (3.39%), German (0.73%) and Serb (0.1%) communities. [2] [3] Fourteen of the 16 counties have Romanian majorities, and two (Covasna and Harghita) are mostly Hungarian.
The percentage of Romanians has increased since the union of Transylvania with Romania (1918). This is due to three processes: emigration of minority populations (1,000,000 Germans, Hungarians and Jews have left the country since WWII[citation needed]), assimilation, and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people have moved from the Regat to Transylvania, and 250,000 from Transylvania to the Regat, most notably to Bucharest).[4] The assimilation process slowed down during the first stages of the communist era (see Hungarian Autonomous Province) and then accelerated under the Ceauşescu regime.
Culture
For people connected to Transylvania's cultural life, see: List of Transylvanians.
Economy
Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably lignite, iron, lead, manganese, gold, copper, natural gas, salt, and sulfur.
There are large iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries. Stock raising, agriculture, wine production, and fruit growing are important occupations. Timber is another valuable resource.
Transylvania accounts for around 35% of Romania's GDP, and has a GDP per capita (PPP) of around $11,500, around 10% higher than the Romanian average.
Tourist attractions
- The medieval cities of Alba Iulia, Cluj-Napoca, Sibiu (European Capital Of Culture-2007) , and Sighişoara
- The city of Braşov and the nearby Poiana Braşov ski resort
- The city of Hunedoara with the 14th century Hunyadi Castle
- The citadel and the Sezession city centre of Oradea
- The Wooden Churches of the Maramureş region
- The Saxon fortified churches
- The Székely Land - mountains, spas, mofette, Hungarian traditions and folk culture
- The Dacian Fortresses of the Orăştie Mountains, including Sarmizegetusa
- The cafe culture [3], street theatre and cosmopolitan society of Sibiu
-
Arad cultural center
-
Arad Evangelical church
-
Black Church in Braşov
-
Braşov Council Square (Piaţa Sfatului)
-
The Theatre in Oradea
-
The town hall in Oradea
-
Dacia Hotel in Satu Mare
-
View of Sibiu
-
Sighişoara clock tower
-
View of Sighişoara
-
Orthodox Cathedral in Timişoara
-
The Catholic Cathedral in Timişoara
Transylvania in fiction
In much of the Western world, Transylvania is famously the home of Count Dracula from Bram Stoker's Dracula.
References
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
- ^ Béla Köpeczi (editor). "History of Transylvania". Atlantic Research and Publications, Inc. Retrieved 2007-01-29.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ 2002 Census official results:[1]
- ^ Ethnocultural Diversity Resource Centre database:[2]
- ^ Varga, E. Árpád, Hungarians in Transylvania between 1870 and 1995, Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999 , p. 27.
Further reading
- Patrick Leigh Fermor, Between The Woods And The Water (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ISBN 1-59017-166-7). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986.
- Zoltán Farkas and Judit Sós, Transylvania Guidebook
External links
- RTI Radio - Radio Transsylvania International
- Hungarian Human Rights Foundation — Human Rights group dedicated to preserving the rights of Transylvania's Hungarians
- Tolerant Transylvania - Why Transylvania will not become another Kosovo, Katherine Lovatt, in Central Europe Review, Vol 1, No 14 27 September 1999.
- The History Of Transylvania And The Transylvanian Saxons by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany
- Template:Hu icon Transylvanian Webcatalogue
- Template:De icon Historical Literature about Transilvania and Neighbouring Territories by Klaus Popa, Germany
- Transylvania, its Products and its People, by Charles Boner, 1865
- Template:Hu icon Transylvanian Family History Database














