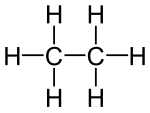
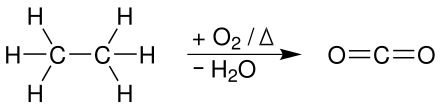Ethane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless gas |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 30.07 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−183.3 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−88.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3.8 M Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Dipole moment |
0 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 10,000 ml m −3 or 12,500 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−84.0 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Ethane (standard language ethane ) is a chemical compound that belongs to the alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons ). It has the molecular formula C 2 H 6 and is a colorless and odorless gas that is mainly used for heating and combustion purposes. The ethyl residue (-C 2 H 5 ) is derived from this . Along with methane, ethane is a main component of natural gas .
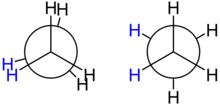
Conformation
Ethane has two conformations , they differ in their energy, which in this case is called the torsional energy , by about 12.6 kilojoules per mole . It is highest in the ecliptic conformation and is therefore unstable. It is lowest in the staggered conformation, which is therefore energetically preferred. The energy of all other conformations lies between these two extremes.
The torsional energy of the ethane molecule is small compared to the thermal energy at room temperature, so that it is in constant rotation around the CC axis. However, it "locks" in the staggered conformation at regular intervals, so that around 99 percent of all molecules are close to the energy minimum. The transition between two adjacent staggered conformations takes an average of 10 −11 seconds (see also the conformation of ethane ).
properties
Ethane is a colorless and odorless gas ; it melts at −182.76 ° C and boils at −88.6 ° C. It is only sparingly soluble in water: 61 mg / l at 20 ° C. 583 J / mol are required for melting and 10 kJ / mol for boiling.
Solid ethane exists in several modifications . When ethane is cooled under normal pressure, a cubic, crystallizing shape is initially created, in which the molecules can rotate around their longitudinal axis, which is why it is a plastic crystal . With a slight further cooling, a metastable modification occurs at around 89.9 K, which crystallizes in the monoclinic system.
The critical temperature is 32.18 ° C, the critical pressure 48.714 bar and the critical density 0.2045 g / cm³.
structure
- Bond lengths : C − C bond 154 pm, C − H bond 109 pm
- Bond angle : C − H − C: 109.5 °, H − C − H 109.5 ° ( tetrahedral angle )
Occurrence and representation
| planet | Ethane content |
|---|---|
| Jupiter | 5.8 ± 1.5 ppm |
| Saturn | 7 ± 1.5 ppm |
| Neptune | ≈ 1.5 ppm |
Not inconsiderable amounts of ethane can be found in natural gas and swamp gas , but only traces are found in the atmosphere. The relatively large amounts of methane and ethane on earth are mainly due to their forms of life and the decomposition of organic matter. But they also arise without the presence of life forms in the presence of hydrogen and carbon, since they are very simple compounds.
Traces of ethane can be found on the planets Jupiter , Saturn and Neptune . Ethane is also found on some comets, for example small amounts of ethane were found in the coma of Comet Hale-Bopp . The ethane deposits in space are small and much smaller than those of methane . Ethane can also be found on some moons: Traces of ethane can be found on Saturn's moon Enceladus , on July 30, 2008 it was announced that Lake Ontario Lacus on Titan is mainly filled with ethane. Ethaneis can also be found on the dwarf planet Pluto .
It can be produced on a laboratory scale by Kolbe electrolysis of acetic acid or potassium acetate .
hazards
When inhaled, ethane causes increased breathing and heart rates. Furthermore, inhalation in large quantities leads to numbness in the limbs, insomnia, mental confusion, loss of coordination and memory as well as hyperventilation. When ingested, it causes nausea and vomiting. Because ethane is usually stored in liquid form at low temperatures, escaping ethane can cause frostbite. Ethane is extremely flammable.
It forms explosive mixtures between 2.7 and 15.5 percent air volume, with the most ignitable mixture containing 6.5 percent by volume of ethane. The flash point is −135 ° C, the ignition temperature is 515 ° C.
use
Ethane is burned with the natural gas for heating purposes in combustion systems; it has a calorific value of 64 MJ / m³ (47 MJ / kg). It also serves as a raw material for the synthesis of ethene , acetic acid and other chemical compounds. Ethane is also used as a refrigerant (R 170) in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Reactions
Ethane burns to water and carbon dioxide when oxygen is added :
In order for the complete oxidation to carbon dioxide to take place, ideal reaction conditions are required (main criterion: sufficient oxygen).
Ethane is split into hydrogen and ethene :
A very high temperature (> 700 ° C) is necessary for the reaction to take place.
Web links
- Safety data sheet ( Memento of February 1, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 39 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on ethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Gases, pp. 6-188.
- ↑ Entry on ethane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 74-84-0 or ethane ), accessed on September 15, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-22.
- ↑ GJH van Nes & A Vos (1978): Single-Crystal Structures and Electron Density Distributions of Ethane, Ethylene and Acetylene. I. Single-Crystal X-ray Structure Determinations of Two Modifications of Ethane. Acta Cryst. , Sect. B, vol 34, pp. 1947-1956 ( doi : 10.1107 / S0567740878007037 ).
- ↑ JL Duncan, DC McKean and AJ Bruce: Infrared spectroscopic studies of partially deuterated ethanes and the r 0 , r z , and r e structures . In: Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy . tape 74 , no. 3 . Elsevier Inc., March 1979, p. 361-374 , doi : 10.1016 / 0022-2852 (79) 90160-7 .
- ↑ DLR: Saturn's moon Titan - streams and lakes made of liquid hydrocarbons