Anisaldehyde
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
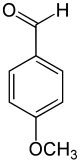
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Anisaldehyde | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish liquid with a characteristic odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 136.15 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.12 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
0-2 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
247-249 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1 hPa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (2 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5731 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Anisaldehyde is an aromatic compound , is structurally derived from benzaldehyde or anisole and belongs to the group of methoxybenzaldehydes .
Occurrence
In nature, aniseed aldehyde occurs in anise , fennel and other essential oils. It is synthesized in plants via the shikimic acid route .
Extraction and presentation
Anisaldehyde can be obtained by oxidation (e.g. by nitric acid or chromic acid ) of anethole or 4-methoxytoluene or from anisole by a Vilsmeier reaction .
properties
By reaction of anisaldehyde with oxidizing agents (. Eg Fehling - or silver mirror sample ) can be anisic acid ( p -Methoxybenzoesäure) represent.
use
Anisaldehyde is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of drugs, fragrances and other chemicals.
Anisaldehyde is used in thin-layer chromatography in the form of a spray reagent for the detection of various classes of natural substances (especially terpene derivatives ). For this, 0.5 mL anisaldehyde is mixed with 10 mL glacial acetic acid , 85 mL methanol and 5 mL conc. Sulfuric acid mixed in the order given. After this solution has been sprayed onto the TLC plate and the plate is subsequently heated to approx. 110 ° C. for 5 to 10 minutes, the corresponding zones change color characteristic in daylight. This reagent is listed under the name anisaldehyde reagent R in the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.). The reagent is stable for a limited time only. If it turns red-violet, it should be discarded.
safety instructions
The vapors of anisaldehyde can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 116 ° C, ignition temperature 220 ° C).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on ANISALDEHYDE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 25, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry for CAS no. 123-11-5 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 7, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ^ A b Egon Stahl, Werner Schild: Isolation and characterization of natural substances . 1st edition. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart / New York 1986, ISBN 3-437-30511-5 , p. 173 .
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia . 4.00 edition. tape 1 . Deutscher Apotheker Verlag / Govi-Verlag - Pharmazeutischer Verlag GmbH, Stuttgart / Eschborn 2002, ISBN 3-7692-2947-9 , p. 384 .