Kleinbahn Niebüll – Dagebüll
| Niebüll – Dagebüll | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route number (DB) : | 9100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course book section (DB) : | 136 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 13.7 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ); until 1926: 1000 mm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kleinbahn Niebüll – Dagebüll is a synonym for the Niebüll – Dagebüll railway line. This designation was also the main part of the name of previous operating companies.
Although the line is no longer a small train , it is still commonly referred to as that. The operation of the railway line has been the responsibility of the Norddeutsche Eisenbahngesellschaft Niebüll mbH (neg) as a railway infrastructure company since 2004 .
route
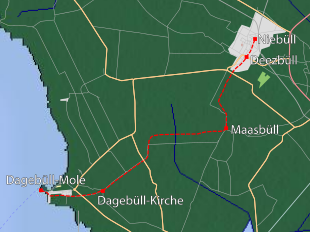
The Niebüll neg – Dagebüll railway is now 13.7 kilometers long. It is located in North Frisia and connects the city of Niebüll with the Dagebüll ferry port on the North Sea . The route number is 9100.
The railway line runs mostly through flat, agricultural marshland and partly follows alongside and alongside the historical dike lines of the former Wadden Sea area of Dagebüller Bucht . In addition to the location of the numerous previous train stations along the route, this is the reason for several tight curves such as the Blocksberger curve northeast of the station of the same name.
Between the Dagebüller harbor and pier stations, the route leads through a dike passage that can be closed by flood gates .
List of train stations and stops
Train stations and stops are:
- 0.0 Niebüll neg (formerly also Niebüll Kleinbahnhof or Niebüll NVAG)
- 1.1 Mittel-Niebüll (closed in 1926)
- Niebüll-Süd (closed after 1926)
- Deezbüll funnel (abandoned in 1926)
- 1.9 Deezbull
- Deezbüll-Burg (closed after 1926)
- Moorhouses (abandoned after 1926)
- 4.5 Maasbüll
- 9.1 Blocksberg (closed for passenger traffic after 1992)
- 11.3 Dagebüll Church
- 13.6 Dagebüll Hafen (closed for passenger traffic around 1990, can be used as the terminus of the route in the event of storm surge and closed dyke gates )
- Dagebüll Mole
history
Kleinbahn Niebüll-Dagebüll oHG
On July 13, 1895, the line was opened as a narrow-gauge line in meter gauge according to a plan by Emil Kuhrt . A route between Lindholm and Dagebüll was also discussed. The line was built and operated by Kleinbahn Niebüll-Dagebüll oHG , in which the communities of Niebüll and Wyk auf Föhr and the province of Schleswig-Holstein were involved. The company was later converted into the Niebüll-Wyk Kleinbahn-Zweckverband . The track initially led to the Dagebüll Hafen station, which is located on the inland dike . Outside the dike, the onward transport to the ship took place on a 600 mm track. In 1911, the 1000 mm track was extended to the Dagebüller pier by the newly built staircase , and the 600 mm track was dismantled. The local train station was only used during severe floods when ships were still in service. The route length was 13.78 kilometers.
On May 1, 1926, the change of gauge to standard gauge was completed. The reason for the gauging was the threat of competition from the Hindenburgdamm, which is under construction, to Sylt . In order to cope with the financial burdens, the circle of investors was expanded to include the German Reich and the Free State of Prussia , which then founded the Kleinbahn Niebüll – Dagebüll AG on November 15, 1927 . The gauge change led to an upswing in traffic, which continued even after the Second World War . The track length shrank slightly to 13.7 kilometers as a result of the gauging and re-routing.
Nordfriesische Verkehrsbetriebe AG - NVAG
On December 21, 1964, Nordfriesische Verkehrsbetriebe AG (NVAG) was founded as the legal successor. In 1982, the state of Schleswig-Holstein as well as the district of North Friesland and the city of Wyk auf Föhr were almost 75 percent involved. The NVAG was also involved in bus transport and local rail and road freight transport .
Since 1971 the ferries from Dagebüll have been able to travel independently of the tide , so that the NVAG's timetable has also been simplified. In the 1970s, there was a risk of the line being closed due to falling income. Therefore it was completely renovated from 1981 to 1984. In 1995 the state of Schleswig-Holstein sold its NVAG shares to Wyker Dampfschiffs-Reederei . In 1999, general cargo traffic on the railway to Dagebüll ended.
To reactivate the route from Niebüll to Tønder , Denmark , NVAG ran trial operations in the summer season for two years from 2000 before regular passenger services were ordered. In 2003, NVAG had to file for bankruptcy due to over-ambitious projects in northern German freight transport .
North German Railway Company Niebüll GmbH - neg
On January 1, 2004, the Norddeutsche Eisenbahngesellschaft Niebüll GmbH , neg for short, a 100 percent subsidiary of the Chemins de Fer Luxembourgeois (state-owned Luxembourg railroad), took over rail operations. At the same time, the bus division of NVAG was continued by the newly founded Niebüller Verkehrsbetriebe (NVB), a subsidiary of Connex , now Veolia .
On December 7, 2006, neg received a GVFG grant of 6.37 million euros for necessary renovation measures along the Niebüll – Tønder and Niebüll – Dagebüll routes . The work was completed before the start of the 2007 Easter tour. In addition to ensuring operational safety for the next 20 years, the maximum permissible speed on sections between Niebüll and Dagebüll has been increased to up to 80 km / h. This means that the trains arrive in Dagebüll six minutes earlier, which makes it possible to have the railcar commute every hour .
Operations
history
Up to 1926 there were a maximum of five steam locomotives (per year) , ten passenger cars , one baggage car, 23 freight cars and a lever draisine .
After the conversion to the standard gauge, there were a total of three steam locomotives, two diesel locomotives (including DL2, which arose from a DB class 211 locomotive and is still in operation) and six railcars. T1 was a benzene railcars , while it is a T2 at Esslinger motor coaches and T3 a MaK - railcars acted. T4 was delivered to NVAG in 1996. It comes from the Jenbacher works and is derived from the railcars of the ÖBB 5047 series , but also has a generator for supplying the through carriages. A class 629 railcar , which was taken over by the Frankfurt-Königsteiner Eisenbahn in 2008 , was also procured, as was another in 2015, which was converted from two former class 628 CFL railcars into a class 629 railcar. In addition, there was a maximum of six passenger cars, one baggage car, seven boxcars (G-cars, some still in use today), a railroad master's car, a lever trolley and a steering wheel. In 2008 and 2012 a heating car was purchased for the through-car operation .
In the 1930s, there were trains with over ten express coaches and other baggage cars during the holiday season. This was a large number for a small train. Before and after public holidays, the length of the trains could still be five passenger cars (including two through cars) and some G-cars for general cargo traffic around 2000.
present
The current operation is characterized by through coaches , which are exchanged in summer and over Christmas with three to four IC trains on the Hamburg - Westerland march railway in the Niebüller train station, in order to use neg vehicles by means of a sawing drive (a journey with a change of direction to get on a change to the Niebüll neg train station. From this station, the scheduled journey time is 15 to 19 minutes to Dagebüll Mole. In addition to the T4 railcar, the towing vehicle of the through car train can also be one of the two railcars of the 629 series . All other neg trains run without through cars.
In the summer months 2008 and 2009 the neg resorted to the operation of the steam locomotive 52 8079 to increase the tourist attractiveness of the weekend trips . In 2010 the plan steam took place for the first time with the locomotive 78 468 of the "Lengerich Railway Tradition". In 2011 this locomotive also ran in front of several scheduled trains on three summer weekends; The occasional use of a DB class 220 diesel locomotive was planned for 2012 . In the following years there were trips on the Angelner steam train .
The trains run to the pier. From there it is only a short walk to the ferries to Föhr and Amrum. In the event of a storm surge and closed dykes , the Dagebüll Hafen station, which was closed as a regular stop in 1992 and is now only used as an operating point, is used instead of Dagebüll Mole.
For operational reasons, buses are occasionally used. Their travel time is 20 minutes; However, instead of stopping at the subway stations, it is only stopped once in Deezbüll, as the stations are some distance from the road to Dagebüll. Since December 14, 2014, the Niebüll – Dagebüll connection has had the line number “ RB 65”. The core feature of the company is the connection security. For example, the neg train waits at the expense of the timetable for delayed trains at the DB station or delayed ferries at the pier in Dagebüll.
The Schleswig-Holstein Passenger Advisory Board honored neg together with the Wyker Dampfschiffs-Reederei Föhr-Amrum with the 2017 public transport award for its commitment to the tourist connection of the North Frisian Islands.
The neg is planning the electrification of the route and therefore put these services out to tender at the beginning of 2020. Electrical operation is scheduled to start in 2024, after the state of Schleswig-Holstein would already have to take over a financial share in July 2020 after a refusal of funding in 2019.
Through car operation
meaning
Since its construction, the route has primarily served to transport tourists and residents to and from the North Sea islands of Föhr and Amrum . Inland traffic on the railway line remained low and is almost of no importance today. At times, the other branches of the Kleinbahn and its successor companies were more important than the railway operations.
Others
- The choice of Niebüll as the starting point of the route in competition with Lindholm, which was more important at the time, led to an upswing in the city. It became the capital of what was then the district of Südtondern .
- The operation with through coaches is maintained, while otherwise there is no longer any intra-German through coach traffic - except for some night trains.
- The Dagebüll Hafen station is located near the building yard of the Husum water and economic authority, from which the Halligbahn Dagebüll – Oland – Langeneß leads to the Halligen in the Wadden Sea with a Lorendamm for material transport.
- The route is part of the ProTrain railway simulation Hamburg (more precisely: Hamburg-Altona –Westerland). Among other things, through car operation can be simulated there.
literature
- Heinz-H. Schöning: From Niebüll to the Wadden Sea . Schweers + Wall, Aachen 1986, ISBN 3-921679-47-8 .
- Erich Staisch (Ed.): The train to the north . Ernst Kabel, Hamburg 1994, ISBN 3-8225-0298-7 .
- Gerd Wolff: German small and private railways, part 1 Schleswig-Holstein Hamburg . Zeunert, Gifhorn 1972.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ General. Norddeutsche Eisenbahn Niebüll GmbH, accessed on April 14, 2020 .
- ↑ vehicles. In: neg-niebuell.de. Norddeutsche Eisenbahn Niebüll GmbH, accessed on August 1, 2020 .
- ↑ history. In: neg-niebuell.de. Norddeutsche Eisenbahn Niebüll GmbH, accessed on August 1, 2020 .
- ^ Website of the Rendsburger Eisenbahnfreunde ( Memento from February 16, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ LOK Report - Schleswig-Holstein: Passenger Advisory Board awards the 2017 Public Transport Prize to the Wyker Dampfschiffs Reederei and the North German Railway Company . ( lok-report.de [accessed on February 26, 2018]).
- ↑ Hands-free, competitive award of surveying services (engineering services) for the electrification of the Niebüll – Dagebüll railway line. neg-Norddeutsche Eisenbahn Niebüll GmbH, February 28, 2020, accessed on August 1, 2020 .
- ↑ Arndt Prentzel: A train ride is dirty. In: taz.de. July 3, 2019, accessed August 1, 2020 .
- ↑ From 2024: Trains between Niebüll and Dagebüll should run on wind power. In: Nordfriesland Tageblatt. July 31, 2020, accessed August 1, 2020 .