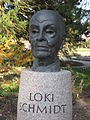Loki Schmidt garden
The Loki-Schmidt-Garten is a public park at the Biozentrum of the University of Hamburg in Hamburg-Osdorf at the Klein Flottbek S-Bahn station . Until 2012 it was called the New Botanical Garden . The greenhouses of the former Botanical Gardens on the site of Planten un Blomen at Dammtor also belong to it .
history

The Botanical Garden in Hamburg was founded in 1821 by Johann Georg Christian Lehmann . The first technical manager (inspector) was Johann Heinrich Ohlendorff . Originally 2.5 hectares in size, it has been expanded several times. Ohlendorff's successor was Eduard Otto (1812–1885). From 1845 to 1852 he took over the management of the garden for Lehmann and was appointed garden inspector. After the death of Johann Georg Christian Lehmann in 1860, Eduard Otto took over the management again. In July 1863 Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach was appointed director. In 1857 the Senate of Hamburg converted the garden into a state institute; since the University of Hamburg was founded in 1919, it has been part of its Botanical Institute. Until the 1970s, the garden was located exclusively in the Hamburg ramparts on the site of today's Planten un Blomen park . It was used by scientists Amalie Dietrich , Otto Wilhelm Sonder and Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach , among others .
The air raids on Hamburg in World War II destroyed large parts of the open fields and the greenhouses. The reconstruction of the Botanical Garden was largely shaped by the three International Horticultural Exhibitions (IGA) in 1953, 1963 and 1973.
Initially, the IGA 1953 focused on eliminating the war damage and restoring an attractive garden. As part of the IGA 1963 , the architect Bernhard Hermkes and the horticultural engineer Johannes Apel built the 2,500 m² tropical greenhouses and Karl Plomin redesigned the entire Old Botanical Garden .
With the IGA 1973 the relocation of the botanical garden was planned at the same time, it was decided in 1970 by the Hamburg city council . The construction of the New Botanical Garden began in 1971, after almost eight years of construction, the approximately 25 hectare open space was opened on July 5, 1979. The tropical greenhouses remained at the old location. In 1986 the remains of the Old Botanical Garden were converted into a public park. The building of the Botanical Institute there was later occupied by the Bucerius Law School and two additional new buildings were added.
On 23 October 2012, the New Botanical Garden was in honor of Hannelore "Loki" Schmidt in Loki Schmidt garden renamed.
Structure and scope
The Botanical Garden primarily provides a scientific collection for the teaching and research tasks of the Biological Institute and supplies the Biozentrum with the plant material necessary for its work, but is at the same time a public green area and is intended to meet the public's need for information on botanical issues . Since around 1980 it has been integrated into various species protection projects and maintains some so-called protection and conservation collections. Both the outdoor area and the tropical greenhouses are accessible free of charge during opening times.
Outdoor area
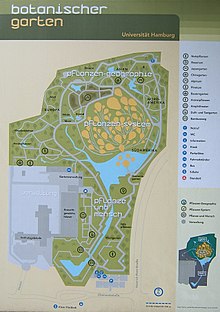
The outdoor area deals with various aspects of the biology , ecology , distribution and relationship of plants, but also with questions of their use and processing. It is divided into three thematic areas: plant systematics , plant geography, and plants and humans .
The 7,000 m² plant system area is the heart of the garden. Here an attempt is made to arrange 75 plant beds with representatives of individual orders in such a way that the family relationships and assumed origins are shown. The garden is based on a system developed by Armen L. Takhtajan and largely used until 2009 . It is called the "phylogenetic clock" and is designed according to the aid of the molecular clock . The concept of displaying plants according to lines of development can also be found in the rose garden, in which the wild forms are at the top of a hill and current cultivated forms are at its foot.
The area of plant geography presents different natural regions. The attempt is made to achieve this with plants that also grow outdoors in the Hamburg climate. The maintenance of some areas that represent areas that differ greatly from this climate, such as mountains , moors or dune landscapes, however, requires considerable effort. Particularly noteworthy in this area are the depiction of southeastern North America through a grove of bald cypress trees , the Chinese garden and the Japanese garden designed by Yoshikuni Araki .
In the area of plants and humans , the interlinking of human life with botany should be shown. There are extensive collections of useful and ornamental plants as well as those of poisonous plants . Cultural-historical aspects are also presented in the form of different themed gardens (e.g. Low German cottage garden , Bible garden , typical allotment garden ). The 3,000 m² desert garden, opened in 2005, offers a part designed to be close to nature and a part dedicated to typical oasis farming. It should particularly depict aspects of desertification and desertification .
The Propagator in the open area serve up to small show and event spaces the research activities of the Biozentrum and one of its central institutions.
Paths through the Loki Schmidt garden
The main path frames a body of water. Counterclockwise, the areas of useful plants, poisonous plants, desert, rose and rock gardens are affected. Further north follow trees and other plants from South and North America. The path runs in the northern arch through Japanese and Chinese gardens. Forests of Europe follow in a southerly direction. Towards the end it branches off to the Loki Schmidt House Museum and the entrance.
Tropical greenhouses in Planten un Blomen
The tropical greenhouses are located in Planten un Blomen at Dammtor . The greenhouses are supposed to cultivate plants that are native to foreign climates. They are divided into different structurally separate areas, each with its own climatic conditions: tropical house , cycad house , subtropical house , fern house and cactus house . Each greenhouse presents either the plant communities of a certain climatic zone or a certain group of plants. The cycad house displays a rare collection of these very slow growing plants, some of which are over 100 years old and were among the first examples of bread palm ferns introduced into Europe .
Cooperations
The Green School is a joint institution of the State Institute for Teacher Training and School Development and the University of Hamburg, Department of Biology . This publishes indoor plants and test plants for cell theory, but also carnivorous plants (carnivores), succulents , plants for leaf evolution, tree slices, scented geraniums, driven onions and tropical useful plants if necessary .
A support association , the Society of Friends of the Botanical Garden Hamburg eV , regularly offers expert guided tours with changing themes through the outdoor area and through the tropical greenhouses. In addition, plant consultations and seminars are organized and some special areas are supervised in the outdoor area.
museum
With support from the Zeit Foundation , the Loki-Schmidt-Haus was created as a museum for useful plants at the University of Hamburg and the successor to the collections of the Botanical Institute. The collection kept in the museum includes plants used by humans as well as their raw products and processing stages. One of the main focuses are crops from overseas . Today the museum's collection comprises around 50,000 objects, including the Carpological Collection, the teaching collection for teaching purposes and collections of medicinal plants, mushrooms and woods. The puristically designed building with the characteristic cobalt blue tile cladding encloses around 460 m² of exhibition space.
Works of art
In 1982 the bronze sculpture “Adam plunders his paradise” by Waldemar Otto was placed in front of the entrance to the outdoor area. Originally, an Eva figure was to be added, whose hand can still be seen today in the golden apple tree. But after public protests about the design and cost of the figures, it was finally abandoned. After a while, strangers painted “Adam” underpants, which were initially removed several times, but eventually remained.
Loki Schmidt was erected a monument in the botanical garden during his lifetime.
Connection to the public transport network
The Loki-Schmidt-Garten is opposite the Klein-Flottbek S-Bahn station with the S1 and S11 lines. The M21 and M15 buses have their terminus here.
Photos and map
Coordinates: 53 ° 33 ′ 44 ″ N , 9 ° 51 ′ 40 ″ E
The "desert garden", a gift from the United Arab Emirates to Hamburg
Order by subject:
The plants of the BibleAdam loots his paradise from Waldemar Otto in front of the main entrance
Loki Schmidt bust by Manfred Sihle-Wissel
literature
- Carsten Schirarend: Hamburg Botanical Garden, tropical greenhouses (Flyer) . University of Hamburg, Biozentrum Klein Flottbek, Hamburg 2008.
- Carsten Schirarend: Hamburg Botanical Garden, the outdoor area . University of Hamburg, Biozentrum Klein Flottbek, Hamburg 2005.
- Ralf Lange : Architecture in Hamburg . Junius Verlag , Hamburg 2008, ISBN 978-3-88506-586-9 , p. 72, 285 .
- Axel Iwohn, Martina Nath-Esser, Claudia Wollkopf: Hamburg Grün - The gardens and parks of the city . L&H Verlag, Hamburg 1998, ISBN 3-928119-39-7 , p. 64-73, 265-271 .
- Martin Haller : Reflections on the future of the zoological garden, the botanical garden and the former burial grounds in front of the Dammthor Hamburg , Strumper & Co, Hamburg, 1909, ( SUB Hamburg )
- Alfred Voigt: The botanical institutes of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg . Leopold Voss, Hamburg 1901 ( digitized ).
- Friedrich Ahlborn : The tasks and the organization of the botanical garden in Hamburg . In: Negotiations of the Natural Science Association . in Hamburg 1893. L. Friederichsen & Co, 1894, p. 16 ff . ( Digitized version ).
- Nekrolog: Edmund Goeze: Garden Inspector Eduard Otto , in: Hamburger Garten- und Blumenzeitung , 41st year, 1885, p. 472ff.
- Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach: VII. The scientific institutes and associations . In: Hamburg in natural history and medicine . Dedicated as a festive gift to the members and participants of the 49th Assembly of German Naturalists and Physicians. L. Friederichsen & Co, Hamburg 1876, The Botanical Garden, p. 193 ff . ( online ).
- On the history of the Hamburg botanical garden; act-like representation . From the creation of the garden to the time when it became a state institute. In: Eduard Otto (Ed.): Hamburger garden and flower newspaper . No. 14 . Robert Kittler, Hamburg 1858, p. 529–538 ( biodiversitylibrary.org - the text comes mainly from Johann Georg Christian Lehmann).
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Loki Schmidt garden. University of Hamburg, December 19, 2017, accessed on February 9, 2018 .
- ↑ In 1810 Johannes Flügge founded the first botanical garden in Hamburg as a public limited company. It was completely destroyed during the occupation of Hamburg by Napoleonic troops in 1813.
- ↑ Klein-Flottbek. Loki Schmidt Garden - New Botanical Garden on hamburg.de
- ↑ Loki Schmidt Garden - Botanical Garden of the University of Hamburg (ed.): Biozentrum Klein Flottbek and Botanical Garden. Loki Schmidt garden. Leaflet from 5/2015.
- ↑ Tropical greenhouses (Dammtor). University of Hamburg, December 1, 2017, accessed on February 9, 2018 .
- ↑ Loki Schmidt House. In: Biozentrum Klein Flottbek. University of Hamburg, January 9, 2018, accessed on February 9, 2018 .
Web links
- Biozentrum Klein Flottbek
- Society of Friends of the Botanical Garden Hamburg eV
- Description on the website of the Biozentrum of the University of Hamburg