Seto Inland Sea
The Seto Inland Sea or the Seto Inland Sea ( Japanese 瀬 戸 内海 Seto-naikai ) is an inland sea that separates the Japanese islands of Honshū , Shikoku and Kyūshū . Within the Seto Inland Sea there are many small islands, the largest of which is Awaji-shima in the east.
geography
expansion
Seto Inland Sea between Kyūshū, Honshū and Shikoku |
The implementing regulation for the Ryōkai-hō ( 領海 領海 ' Territorial Waters Act ') defines in Article 1 the limits of the sea as follows:
- the line from the lighthouse at Cape Kii-Hi-no-misaki ( 33 ° 52 ′ 55 ″ N , 135 ° 3 ′ 40 ″ E ) to the lighthouse at Cape Kamoda-misaki ( 33 ° 50 ′ 3 ″ N , 134 ° 44 ′ 58 ″ O ), d. H. the narrowest point of the Kii Canal as the southeastern boundary ;
- the line from the lighthouse at Cape Sada-misaki ( 33 ° 20 ′ 35 ″ N , 132 ° 0 ′ 54 ″ E ) to the lighthouse at Cape Seki-zaki ( 33 ° 16 ′ 0 ″ N , 131 ° 54 ′ 8 ″ E ) , d. H. the Hōyo Strait as the south-western boundary as the northern end of the Bungo Canal ( 豊- 水道Bungo-suidō );
- the line from Daidabana rock on Takenokojima Island ( 33 ° 57 ′ 2 ″ N , 130 ° 52 ′ 18 ″ E ) [on which there is also a lighthouse] to the lighthouse at the breakwater of Dōkai Bay of Wakamatsu ( 33 ° 56 ′ 28 " N , 130 ° 51 '2" O ), i.e. H. the north-western limit of the Kammon Strait to the Sea of Japan .
The environmental law Setonai-hō ( 瀬 戸 内 法 ) describes in article 2 paragraph 1 an almost identical expansion. However, Article 1 of its implementing regulation gives it a greater extension:
- the line from Cape Kōmo-saki ( 32 ° 54 ′ 27 ″ N , 132 ° 28 ′ 20 ″ E ) to Cape Tsurumi-saki ( 32 ° 55 ′ 55 ″ N , 132 ° 5 ′ 0 ″ E ), d. H. the south-western boundary of the Bungo Canal,
- the line from the lighthouse Kottoi ( 34 ° 19 '9 " N , 130 ° 53' 30" O ) to the Cape Tōrise-saki ( 34 ° 20 '28 " N , 130 ° 50' 47" O ) on the island Tsunoshima and then to the lighthouse at Cape Myōken-zaki ( 33 ° 56 ′ 13 ″ N , 130 ° 41 ′ 0 ″ E ), d. H. the northwest boundary goes far to the north and also includes the entire west coast of Yamaguchi Prefecture .
According to the narrower definition, the sea has an area of 19,700 km², according to the other one of 21,827 km². The maximum water depth is 105 m.
Regions
The Seto Inland Sea is divided into the following marine regions:
- Kii Canal between Honshū and Shikoku
- Osaka Bay between Honshū and Awaji-shima
- Harima-nada ( 播 磨 灘 ) between Awaji-shima and Shōdoshima
- Bisan Strait ( 備 讃 瀬 戸 Bisan-seto ) between the prefectures of Okayama and Kagawa prefecture
- Bingo-nada ( 備 後 灘 ) north between the Kasaoka and Geiyo Islands
- Hiuchi-nada ( 燧 灘 ) south of it between the Shōnai and Takanawa peninsula
- Aki-nada ( 安 芸 灘 ) between the Geiyo and Bōyo Islands
- Hiroshima Bay north of Aki-nada between the Geiyo Islands and Hiroshima
- Iyo-nada ( 伊 予 灘 ) south of Aki-nada between the Yashiro Island (Suō-ōshima) of the Bōyo Islands and the Kunisaki Peninsula
- Suō-nada ( 周 防 灘 ) north of it to Kammon Street
For the larger definition, there are also:
- Bungo Canal between Iyo-nada and Hyūga-nada, d. H. here the open sea of the Pacific
- Hibiki-nada ( 響 灘 ) north of the Kammon Strait, between the western coast of Honshū and Genkai-nada, d. H. the coastal waters of the Sea of Japan off Kyūshū
coast
The following prefectures border the Seto Inland Sea (counter- clockwise ):
- on Honshū Wakayama , Osaka , Hyōgo , Okayama , Hiroshima and Yamaguchi ,
- on Kyūshū Fukuoka and Ōita and
- on Shikoku Ehime , Kagawa and Tokushima .
The region around the Inland Sea is also called the Setouchi region. Important coastal cities in the region are Kobe , Ube , Hiroshima , Iwakuni , Kurashiki and Matsuyama .
Islands
According to the official definition, which requires an island to have a land area of at least 100 m in circumference during floods , there are 727 islands in the inland sea (in the narrower sense of the Ryōkai-hō implementing regulation ). 681 have a designation ending in -shima / -jima ( 島 ) 'island'. Since Osaka prefecture has no island at all, these islands are distributed among the other ten prefectures on the Seto Inland Sea, as shown in the following table. The percentage indicates what proportion the islands in the Seto Inland Sea have in relation to all islands in the respective prefecture .
| prefecture | Islands | |
|---|---|---|
| officially | by name | |
| Hiroshima | 142 (100%) | 153 |
| Ehime | 133 (49%) | 136 |
| Yamaguchi | 127 (51%) | 105 |
| Kagawa | 112 (100%) | 111 |
| Okayama | 87 (100%) | 75 |
| Hyogo | 57 (52%) | 44 |
| Wakayama | 41 (16%) | 22nd |
| Tokushima | 24 (27%) | 26th |
| Fukuoka | 6 (10%) | 7th |
| Ōita | 3 (3%) | 2 |
| total | 727 (11%) | 681 |
| 5 islands extend over two prefectures | ||
Taking into account further, z. B. differently named or unnamed islands are given as a maximum number of about 3000 pieces.
The ten largest islands are:
- Awaji-shima (592.55 km²)
- Shōdoshima (153.25 km²)
- Yashirojima (128.48 km²)
- Kurahashijima (69.46 km²)
- Ōmishima (64.58 km²)
- Ōshima (41.87 km²)
- Ōsakikamijima (38.27 km²)
- Innoshima (35.03 km²)
- Ikuchijima (31.21 km²)
- Itsukushima (Miyajima) (30.33 km²)
nature
Much of the lake belongs to the 1934 as one of the first national parks of Japan established Setonaikai National Park . It has a temperate climate with relatively low seasonal fluctuations and little rainfall. In Japan this area is therefore also called "The Land of Fine Weather" ( Japanese 晴 れ の 国 hare no kuni ). Most of the islands in the Inland Sea are covered with pine trees. The lake is known for regular algae blooms ( 赤潮 akashio ), a sudden mass increase in algae in a body of water. Another natural spectacle are the Naruto whirlpools , which are created due to the different water depths of the inland sea and the Pacific Ocean. Furthermore, one of the last remaining Japanese tidal flats exists in the inland sea , which has not yet been destroyed due to dikes.
The region around the Inland Sea is industrialized. Raw materials can be delivered by ship. The mild climate is favorable for fishing and agriculture.
bridges
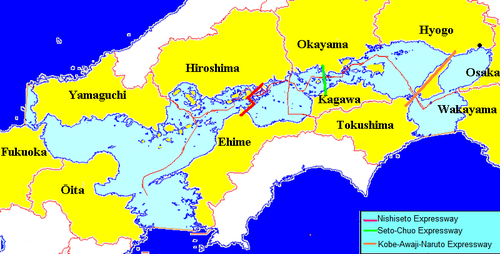
The islands of Honshū and Shikoku are connected by three bridge systems.
Kobe-Awaji-Naruto Highway
The easternmost link completed after breaking ground in 1976 in 1998, leads from Akashi ( prefecture Hyogo ) on the Akashi Kaikyō Bridge , the longest suspension bridge in the world, the island of Awaji Island , from there via the Naruto Bridge to Ōge-jima ( Naruto , Tokushima Prefecture ) across the 1.3 km wide Naruto Street and finally over the Muya Bridge to Shikoku. Originally, a train connection was also planned, but this was ultimately dispensed with.
Seto Chūō Highway
Erected in just ten years, Seto-Ōhashi has linked Okayama Prefecture with Kagawa Prefecture since 1988 . It consists of a total of six two-story bridges, each of the lower floors being used by Japan Railways . The Shinkansen does not run to or on Shikoku.
Nishiseto Highway / Shimanami Highway
The first of the three crossings of the inland sea, started in 1975, but the last to be completed in 1999, the Nishiseto motorway connects Onomichi in Hiroshima Prefecture via a total of ten bridges and several smaller islands, on which around 100,000 people live together, with Imabari in the prefecture Ehime . The bridges are: Shin Onomichi Bridge , Innoshima Bridge , Ikuchi Bridge , Tatara Bridge , Ōmishima Bridge , the two Ōshima bridges and the three Kurushima-Kaikyō bridges .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ 領海 及 び 接 続 水域 に 関 す る 法律 施行 令 in the amendment of December 28, 2001, coordinates from the text of the regulation
- ↑ 瀬 戸 内海 環境 保全 特別 措置 法 in the amendment of August 30, 2011
- ↑ 瀬 戸 内海 環境 保全 特別 措置 法 施行 令 in the amendment of March 25, 2009, coordinates added
- ↑ 日本 の 閉鎖 性 海域 . (No longer available online.) 国際 エ メ ッ ク ス セ ン タ ー March 25, 2009, archived from the original on September 1, 2011 ; Retrieved October 20, 2013 (Japanese). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b 瀬 戸 内海 に は 島 が い く つ あ る か な? . Kaijō Hoanchō (Coast Guard), accessed March 7, 2015 (Japanese).
- ↑ 瀬 戸 内海 . In: 日本 の 地名 が わ か る 事 典 and 日本 大 百科全書 at kotobank.jp. Retrieved March 7, 2015 (Japanese).
- ↑ 島 面積 . (PDF; 136 kB) (No longer available online.) Kokudo Chiriin , October 1, 2015, archived from the original on June 15, 2016 ; Retrieved August 23, 2016 (Japanese). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
Coordinates: 34 ° 13 ' N , 133 ° 21' E



