Daerstorf
|
Daerstorf
Unified municipality Neu Wulmstorf
|
|
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 53 ° 26 ′ 18 ″ N , 9 ° 48 ′ 20 ″ E | |
| Height : | 54-63 m |
| Incorporation : | January 1, 1970 |
| Postal code : | 21629 |
| Area code : | 040 |
|
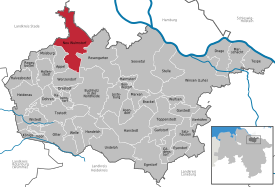
Location of Daerstorf in Neu Wulmstorf
|
|
|
Daerstorf through the town
|
|
(pronunciation: Darstorf,Low German Doasdbod) is part of the unified community ofNeu Wulmstorfinthe Harburg districtin northeastLower Saxonyin theHamburg metropolitan region.
Neighboring communities
In the south Daerstorf borders on Elstorf and Schwiederstorf , in the north on Wulmstorf , in the east on the Tempelberg settlement, the Fischbeker Heide and the southernmost part of Hamburg and in the west on Ketzendorf in the district of Stade. In terms of nature, Daerstorf lies on the northeastern edge of the Apenser Lehmgeest at the transition to the Black Mountains .
history
Burial mounds such as the Daerstorf large stone grave and excavations point to the first settlement by the Neolithic funnel cup culture and in the Bronze Age . Further finds show traces of a settlement around 770.
'Dardestorpe' was mentioned for the first time on June 20, 1295 in a document from the Hildesheim monastery, in which Bishop Konrad zu Hildesheim of the provost St. Andreä zu Hildesheim u. a. leaves the duties of Daerstorf with a farm.
In the Principality of Lüneburg , Daerstorf was part of the Moisburg district with 14 other localities of the Elstorf bailiwick (see list of offices and bailiffs in the Principality of Lüneburg ).
During the French era , Daerstorf had 101 inhabitants and belonged to the Département des Bouches de l'Elbe . Subsequently, it was part of the Landdrostei Lüneburg in the office before it became part of the Tostedt office in 1859 .
From 1835 the settlement of the areas around Daerstorf, Elstorf and Wulmstorf developed. The neighboring town of Neu Wulmstorf was created in 1835 from the settlement of the Daerstorfer farmhand and tenant Peter Lohmann, who had worked in Wulmstorf until then.
Daerstorf were only taken shortly before the end of the war on April 20, 1945 by the "A-Companie" of the infantry unit "1st Rifle Brigade" and the "8th King's Royal Irish Hussars" of the English troops after heavy fighting.

Incorporations
Daerstorf was an independent municipality until January 1, 1970, which also included an exclave in the march between Niederelbebahn and Wulmstorf. Accordingly, the station opened in this exclave in 1905 was called Daerstorf (today's Neu Wulmstorf station).
Population development
| year | 1812 | 1910 | 1925 | 1933 | 1939 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| population | 101 | 132 | 153 | 132 | 144 |
coat of arms
The black fields in the shield foot and shield head symbolize the first five farms, the central plow on a white background refers to agriculture as the main occupation of the locals.
regional customs
Until 1951, de Wood was still made as a sacrifice of thanks to the Germanic god Wodan on the Daerstorfer Wodan oak .
Economy and Transport
Daerstorf is located on the L235 between Wulmstorf and Elstorf and can be reached via the Hamburg-Harburg - Cuxhaven railway, which is operated as the Hamburg S-Bahn . The Neu Wulmstorf station was still called Daerstorf until 1969. The Rade junction of the A 1 and Heimfeld of the A 7 are also nearby . The community will be further developed with the planned A 26 from Stade to Hamburg. Other trunk roads are federal highway 73 and federal highway 3 . Furthermore, the bus companies HVV and KVG connect Wulmstorf to the surrounding communities.
communication
Daerstorf is poorly developed over DSL. Fiber is not available in the entire place. Cable TV is available in the entire village and internet can be used at around 25 Mbit / s. Open WiFi is not available.
See also
- No. 669 in the list of large stone graves in Lower Saxony, Bremen and Hamburg
- Rauchhaus, Daerstorf . Photo archive Photo Marburg. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- Oven in the smoke house, Daerstorf . Photo archive Photo Marburg. Retrieved March 5, 2015.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Reinhard Dzingel: Reasons for the spelling of the Low German place names of the community Neu Wulmstorf, Harburg district , Schwiederstorf, October 31, 2010, p. 2, (PDF; 82 kB)
- ↑ 1200 year old burial ground from the Saxon period discovered near Elstorf . Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ↑ Horse grave - grave goods or animal sacrifice ( memento of the original from August 28, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ New finds from archaeological excavations in Neu Wulmstorf-Elstorf
- ↑ a b From Vosshusen to Neu Wulmstorf . Neu Wulmstorf 2000, p. 41 .
- ↑ Time leaps: Neu Wulmstorf . Sutton, Erfurt 2013, ISBN 978-3-95400-131-6 , p. 96 .
- ^ A b Albrecht Friedrich Ludolph Lasius : The French Kayser State under the government of Kayser Napoleon the Great in 1812. Kißling, Osnabrück 1813, p. 57 f . ( Digitized version ).
- ↑ The story of Neu Wulmstorf. In: neu-wulmstorf.de. Retrieved April 8, 2016 .
- ^ A report compiled from German sources and contemporary witness reports and military records of the English. (No longer available online.) In: nicolai-kirche-elstorf.de. Archived from the original on April 8, 2016 ; Retrieved April 8, 2016 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 1.7 MB)
- ↑ Time leaps: Neu Wulmstorf . Sutton, Erfurt 2013, ISBN 978-3-95400-131-6 , p. 96 .
- ↑ NI GVBl., December 23, 1969, law on the integration of the Daerstorf community into the Neu Wulmstorf community, Harburg district, Niedersächsisches Gesetz- und Verordnungsblatt 1969, (No. 33, pp. 253-254)
- ^ Municipal directory Germany 1900, Kingdom of Prussia, Province of Hanover, District of Lüneburg, District of Harburg
- ^ A b c Michael Rademacher: German administrative history. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on September 24, 2015 ; accessed on March 9, 2015 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Reinhard Dzingel: The Wodan Oak in Daerstorf - A pagan sacrificial custom in the middle of the 20th century , Moisburg 2013 (PDF; 294 kB)