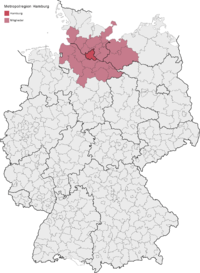
Hamburg metropolitan region
| Hamburg Metropolitan Region since 2017 | |
| Federal states : |
|
| Area : | approx. 28,500 km² |
| Residents : | 5.3 million |
| Population density : | 192 inhabitants / km² |
| North South expansion: | 189 km |
| West-east expansion: | 209 km |
| geographical location : | 52 ° 50 ′ - 54 ° 32 ′ n. Br. 8 ° 30 ′ - 11 ° 37 ′ ö. L. |
| Structure: | 3 independent cities , 17 districts |
| Website: | metropolregion.hamburg.de |
The European metropolitan region of Hamburg is one of eleven metropolitan regions in Germany. It includes the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg as well as parts of the states of Schleswig-Holstein , Lower Saxony and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania . Since March 1, 2017, in addition to the participating states and municipalities, regional chambers and associations have been part of it as supporting organizations.
expansion
In addition to the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, the metropolitan region includes three independent cities and 17 districts:
| city | state | Residents Dec. 31, 2015 |
Area in km² | Inhabitants per km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hamburg | Hamburg | 1,787,408 | 755.22 | 2366.7 |
| Lübeck | Schleswig-Holstein | 216.253 | 214.21 | 1009.5 |
| Neumunster | Schleswig-Holstein | 79.197 | 71.63 | 1105.6 |
| Schwerin | Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | 96,800 | 130.52 | 741.6 |
| Counties | state | Residents Dec. 31, 2015 |
Area in km² | Inhabitants per km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuxhaven | Lower Saxony | 198.103 | 2,057.78 | 96.3 |
| Dithmarschen | Schleswig-Holstein | 132.917 | 1,428.13 | 93.1 |
| Harburg | Lower Saxony | 248.122 | 1,245.03 | 199.3 |
| Heidekreis | Lower Saxony | 140.264 | 1,873.72 | 74.9 |
| Duchy of Lauenburg | Schleswig-Holstein | 192,999 | 1,263.01 | 152.8 |
| Lüchow-Dannenberg | Lower Saxony | 50.128 | 1,220.75 | 41.1 |
| Ludwigslust-Parchim | Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | 214.113 | 4,752.44 | 46.8 |
| Luneburg | Lower Saxony | 180.719 | 1,323.68 | 136.5 |
| Northwest Mecklenburg | Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | 156.270 | 2,118.51 | 73.8 |
| Ostholstein | Schleswig-Holstein | 199,574 | 1,392.55 | 143.3 |
| Pinneberg | Schleswig-Holstein | 307.471 | 664.28 | 462.9 |
| Rotenburg (Wümme) | Lower Saxony | 163.253 | 2,070.45 | 78.8 |
| Segeberg | Schleswig-Holstein | 267.503 | 1,344.39 | 199.0 |
| Stade | Lower Saxony | 200.054 | 1,266.02 | 158.0 |
| Stone castle | Schleswig-Holstein | 131,457 | 1,056.13 | 124.4 |
| Stormarn | Schleswig-Holstein | 239.614 | 766.33 | 312.7 |
| Uelzen | Lower Saxony | 93.131 | 1,454.22 | 64.0 |
organization
As an administrative cooperation, the Hamburg Metropolitan Region is not a corporation and therefore has no legal capacity of its own. The basis of the cooperation is both a state treaty between the participating countries and a cooperation agreement with municipalities and associations. While the state treaty stipulates the funding funds between the participating countries, the cooperation agreement regulates the objectives, the work structure and the financing of the metropolitan region.
Sponsoring organizations
In addition to the states and municipalities mentioned, the following regional business associations have also been the supporting organizations since March 1, 2017:
- Hamburg Chamber of Commerce
- Chambers of Industry and Commerce (IHK) Flensburg, Kiel, Lübeck, Lüneburg-Wolfsburg, Schwerin and Stade
- Chamber of Crafts Hamburg , Lübeck and Schwerin,
- Association of business associations in Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein e. V.,
- German Trade Union Confederation - North District
Decision-making bodies
- Regional council : makes strategic decisions that require top-level political coordination. It was reduced from 51 to 16 members in order to strengthen its ability to act. The principle of consensus is the most important pillar of cooperation in its decisions.
- Local council and company council : advise the regional council and maintain contact with the mayors and entrepreneurs of the region
- Steering Committee : controls the operational work, defines measures and approves grants that are supported by the federal states' development funds as the most important financial instrument. The majority principle has applied to decisions since 2017.
- Specialist working groups develop and support the individual projects
- Office in Hamburg, implements resolutions and serves as a central contact point
history
The states of Hamburg, Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein as well as counties, districts and urban districts have been cooperating since the 1960s. In 1991 the Hamburg Senate and the state governments of Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein decided to intensify their regional political cooperation in the Hamburg region. In view of the high growth pressure at the beginning of the 1990s, a new, long-term basis for cooperation should be created. The first step was the elaboration of a regional development concept across national borders.
At the beginning of 2012, the state treaty on the financing of cooperation in the Hamburg metropolitan region and the continuation of the funding fund was amended to the effect that, since May 1, 2012, the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania districts of Ludwigslust-Parchim (limited to the area of the former district of Ludwigslust ) and northwest Mecklenburg as well as the Schleswig-Holstein district of Ostholstein and the independent cities of Neumünster and Hanseatic City of Lübeck are included. In addition, the new name of the Lower Saxony district of Soltau-Fallingbostel Heidekreis was added. Since March 1, 2017, the Mecklenburg state capital Schwerin has also been a member of the metropolitan region.
Cooperation with neighbors
The basis of the cooperation between the three federal states with the participation of the districts and municipalities was the regional development concept of the Hamburg metropolitan region (1996 / update 2001). In 1997, the two mid-1950s founded Common were country planning Hamburg / Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg / Lower Saxony to the Joint Regional Planning summarized Hamburg metropolitan region. Its bodies are the planning council, the regional conference, the steering committee and the two funding committees Hamburg / Lower Saxony and Hamburg / Schleswig-Holstein (joint funding funds). Sub-organizations are the regional working groups of the districts of Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein ( working group of the Hamburg peripheral districts) and the local recreation association in the surrounding area of Hamburg.
The Hanseatic City of Lübeck and the districts of Ludwigslust and Parchim (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania) have been cooperation partners of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region since 2003.
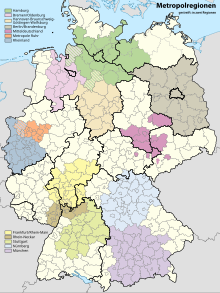
The Hamburg metropolitan region is one of the first seven European metropolitan regions in Germany to be defined at the federal level based on their history. Other metropolitan regions are Berlin / Brandenburg , Munich , Nuremberg , the Rhine-Main area , Rhine-Ruhr , Stuttgart and central Germany . Hamburg's Hanseatic sister city, Bremen, has been the center of the Northwest metropolitan region since 2005 . The metropolitan region of Hanover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg was established south of Hamburg in 2005 .
Via the Vogelfluglinie and Lübeck's ferry ports, such as the Skandinavienkai , there is a close relationship on this transport axis with the neighboring Öresund region , a transnational European metropolitan region consisting of the greater Copenhagen and Malmö areas , which was initiated by the construction of the Öresund Bridge . The construction of the planned fixed Fehmarnbelt link would further improve the future options of the Hamburg metropolitan region.
Delimitation to the metropolitan region northwest
The district of Rotenburg (Wümme) has joined the Hamburg metropolitan region, although it is actually in a middle position between Hamburg and Bremen. A clear assignment of the rural area to one of the two metropolitan areas is not easily possible. The same applies to the old circle Wesermünde the district of Cuxhaven , who is also a member of the Metropolitan Region Northwest is.
Delimitation to the metropolitan region of Hanover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg
The very rural district of Heidekreis in the Lüneburg Heath belongs to both the Hamburg metropolitan region and the Hanover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg metropolitan region . The district was made up of the old district of Soltau, which is oriented towards Hamburg, and the old district of Fallingbostel, which is oriented towards Hanover.
Earlier demarcation to Lübeck and Neumünster
The Schleswig-Holstein state government initially had concerns about the inclusion of the city of Lübeck in the Hamburg metropolitan region. The inclusion, which was finally made in 2012, was taken into account insofar as the southern spatial planning region bordering Hamburg in Schleswig-Holstein was merged into a single planning area with the two spatial planning regions East and Southwest as part of the regional planning in 2014 . A special case is the city of Neumünster , which has been part of the Hamburg metropolitan region since 2012, but is still considered in regional planning together with the Schleswig-Holstein state capital Kiel and the Rendsburg-Eckernförde and Plön districts . In contrast to the former technology association KERN, Neumünster is no longer a member of today's Kiel-Region GmbH business development agency, but has been part of the NORDGATE city network with five other cities in the northern vicinity of Hamburg since 2008.
literature
- Norbert Fischer : From the Hamburg area to the metropolitan region. Stormarn's story since 1980 . Dobu, Hamburg 2008, ISBN 3-934632-31-9
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Official population figures
- ↑ Official population figures
- ↑ Official population figures ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ ndr.de: Metropolitan region is growing ( Memento from April 21, 2012 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on April 20, 2012
- ↑ Announcement on the date of the entry into force of the State Treaty between the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, the State of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, the State of Lower Saxony and the State of Schleswig-Holstein amending the State Treaty between the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, the State of Lower Saxony and the State of Schleswig- Holstein on the financing of the cooperation in the Hamburg metropolitan region and the continuation of the funding fund. In: Nds. GVBl. No. 7/2012, issued. on May 10, 2012
- ↑ a b c d The Hamburg metropolitan region is growing. Retrieved February 28, 2017 .
- ↑ a b c d The numbers in the info boxes of the individual articles have been adopted.
- ^ State treaty between the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, the State of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, the State of Lower Saxony and the State of Schleswig-Holstein on the financing of cooperation in the Hamburg metropolitan region and the continuation of funding. In: Nds. GVBl. No. 4/2012, issued. on March 29, 2012
- ↑ Frank Drieschner: Schwerin is now on the Alster. In: zeit.de. Zeit Online , June 7, 2016, accessed June 7, 2016 .
- ↑ Metropolitan Region Bremen-Oldenburg-Osnabrück 2011
- ↑ Flo: Kiel concerns against the metropolitan region with Lübeck . Die Welt, June 3, 2005