Dehydroepiandrosterone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Prasteron | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3 β -hydroxy-androst-5-en-17-one |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 28 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless needles or leaflets |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 288.43 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
148 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
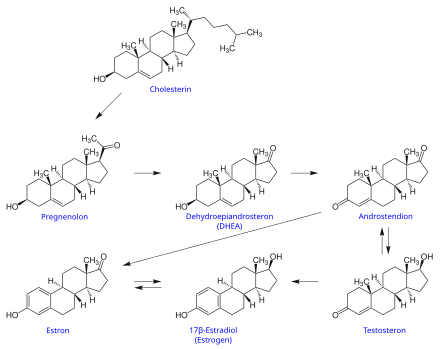
Dehydroepiandrosterone ( DHEA ), prasterone ( INN ), is the most abundant steroid hormone in the human body. Depending on the hormonal level, it can behave like an estrogen or an androgen .
DHEA is the precursor for both male sex hormones ( androgens ) and female sex hormones ( estrogens ).
General
Like androsterone , it is one of the metabolic intermediate stages of testosterone and is therefore also known as a prohormone.
It is forbidden according to the doping regulations of the International Olympic Committee .
DHEA was discovered in urine by Butenandt and Dannenbaum in 1934 . In 1954 it was isolated from blood for the first time. DHEA became known as the so-called anti-aging hormone from around 1980 .
biosynthesis
In men, DHEA is only produced in the inner layer ( zona reticularis ) of the adrenal cortex . In women, only 7/10 of the DHEA is produced there, the other 3/10 are produced in the ovaries .
During DHEA biosynthesis , cholesterol is first converted into pregnenolone . The steroid 17 α -hydroxylase (CYP17A1) first converts pregnenolone into hydroxy-pregnenolone and, in certain cells, also into DHEA.
DHEA is the 3 β -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3bHSD) to 4-androstenedione converted from which, in turn, by the 17 β -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 (HSD17B3, testosterone-17 β -dehydrogenase ) testosterone is produced. In a next step, aromatase (CYP19A1) converts testosterone to 17 β- estradiol . The aromatase can also be prepared from 4-androstenedione estrone form represented by the 17bHSD also to 17 β can be converted to estradiol. The reactions of the CYP enzymes are irreversible, the HSD can, depending on the type, also catalyze the reverse reaction.
| patient | concentration |
|---|---|
| Men 20–50 LJ | 1.5-9 ng / ml |
| Women 20–50 LJ | 1.0-8 ng / ml |
| Children 1-5 LJ | 0.2-0.7 ng / ml |
| Children 10-12 LJ | 0.22-2.54 ng / ml |
| Children 14-16 LJ | 0.42-9.31 ng / ml |
The amount of DHEA produced by the body depends on age and gender, and the DHEA concentration in the blood is subject to a daily rhythm .
The adrenal glands produce only small amounts of DHEA in the first few years of life; larger amounts can be detected for the first time at the age of six to seven years. The production of DHEA peaks around the age of 25 and then continues to decline.
At all ages, men have slightly higher DHEA levels than women.
DHEA is metabolized in the liver to the sulfate DHEA-S (discovered in 1994).
Studies suggest that the concentration of DHEA can be increased by training the heart rate variability , thus producing a pattern of action similar to that of drugs with an anti-depressive effect.
Use and therapeutic effectiveness
In Germany, all prohormones are regarded as medicinal products that require authorization . In evidence-based medicine, it is currently only used as a combination preparation (together with estradiol valerate, for example in Gynodian ® Depot injection ampoules ) for the treatment of characteristic symptoms (hot flashes, sweating, sleep disorders, depression ) in the climacteric of women or after oophorectomy or radiation castration.
Anti aging
In the US, DHEA supplements are classified as over-the-counter dietary supplements . The manufacturers advertise DHEA, among other things, as life-extending. This is justified by the fact that DHEA reduces the energy consumption of the cells, thus increasing their lifespan. These "benefits" of DHEA have not yet been proven. It is not recommended to take DHEA as an antiaging drug.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on Prasteron. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 22, 2014.
- ↑ a b c data sheet trans-Dehydroandrosterone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on dehydroepiandrosterone in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ EE Baulieu et al. : Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate, and aging: contribution of the DHEAge Study to a sociobiomedical issue. In: Proc. Natal. Acad. Sci. USA Vol 97, 2000, pp. 4279-4284. PMID 10760294 .
- ↑ Wiebke Arlt, Bruno Allolio: Therapeutic potential of DHEA . Statement for the hormonal toxicology commission of the German Society for Endocrinology (DGE). In: Communications from the DGE. Issue 1/2003, pp. 4–7.
- ^ OT Wolf: Effects of Dehydroepiandrostone (DHEA) Replacement on Cognitive Performance in Humans: Four Placebo Controlled Double Blind Studies. Verlag Cuvillier, 1998, ISBN 3-89712-062-3 .
- ↑ Recommendation of the Mayo Clinic, accessed October 30, 2017.
literature
- J. Pope, M. Cupp, T. Tracy: Dietary Supplements - Toxicology and Clinical Pharmacology . 2002, ISBN 1-59259-303-8 .
Web links
- Jassal, reactome: Side chain cleavage of 17α-hydroxyprenenolone to yield DHA .
- Jassal, reactome: DHA isomerizes to 4-androstene-3,17-dione .
- ChemSub Online (dehydroepiandrosterone) .