Dithizone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
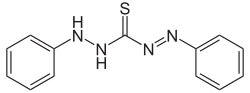
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dithizone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 12 N 4 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
blue-black crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 256.33 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
165–168 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dithizone is a bidentate chelate complexing agent that is used as a sensitive reagent in the (trace) analysis of heavy metals .
Dithizone was synthesized by Emil Fischer in 1878 and introduced by Hellmuth Fischer in 1925 as a heavy metal ion reagent.
presentation
Dithizone is formed by the reaction of phenylhydrazine with carbon disulfide . The diphenylthiocarbazide produced as an intermediate product dehydrates to dithizone when heated in a methanolic potassium hydroxide solution.
properties
Dithizone forms stable complexes with many heavy metal ions which are insoluble in water but dissolve in carbon tetrachloride. The solutions of these dithizonates have a characteristic color:
| Metal ion X | colour | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|
| Fe , Mn , Cu , Co , Ni | violet |

|
| Bi , Sn , Cd , Zn , Pb | red | |
| Ag , ed | yellow |
On the basis of this coloration and the fixed stoichiometry, they can be determined qualitatively and quantitatively by colorimetric or photometric methods .
Based on the different solubilities of metal ions and metal ion complexes, dithizone is used in extractive titration. In this case, the aqueous solution of the analyte is titrated with a standard dithizone solution in chloroform.
Dithizion is temporarily diabetogenic , as this complexes zinc, which is required for the function of insulin .
use
The formation of dithizonate serves as a very sensitive method for the trace analysis of various heavy metal ions. The detection limit for lead is 4 · 10 −8 g at a limit concentration of 1: 1 250,000. The one for zinc, when using extractive enrichment, is at a dilution of 1:50,000,000, ie. H. 1 µg in 50 ml of water. Individual proofs achieve proof of 10 to 100 ppm .
photos
literature
- A. Willmes: Text book chemical substances. 1st edition. Self-published, Thun / Frankfurt am Main 1990, ISBN 3-8171-1214-9 .
- G. Iwantscheff: The dithizone and its application in micro- and trace analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim / Bergstr. 1958, DNB 452279755 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on dithizone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 11, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Entry on 1,5-diphenyl-3-thiocarbazone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on dithizone in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .



