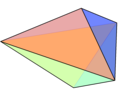
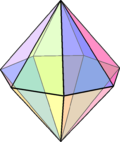
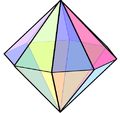
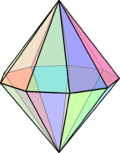
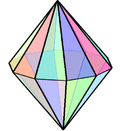
Double pyramid with a hexagon as the base
A -angular double pyramid (also bipyramid or dipyramid , English dipyramid ) is a polyhedron that is created by gluing a -angular pyramid and its mirror image to the base. The corner, which represents the common base of the two pyramids, is not a side surface of the double pyramid, but lies inside the double pyramid, in the plane of symmetry between the two corner pyramids. The double pyramid thus has points, corners and edges and its surface consists of triangles.
n
{\ displaystyle n}
n
{\ displaystyle n}
n
{\ displaystyle n}
n
{\ displaystyle n}
2
{\ displaystyle 2}
2
+
n
{\ displaystyle 2 + n}
3
⋅
n
{\ displaystyle 3 \ cdot n}
2
⋅
n
{\ displaystyle 2 \ cdot n}
Special double pyramids Only three types of double pyramids have the property that all edges can have the same length, so that all side faces are equilateral triangles : the triangular , the square and the pentagonal double pyramid. This special quadrangular double pyramid, the octahedron , is one of the Platonic solids , while the triangular and pentagonal double pyramid belong to the Johnson solids (J12 and J13). These three double pyramids are deltahedra .
Regular double pyramid
One speaks of a regular double pyramid if the generating pyramid is regular, i.e. H. if its base is a regular polygon and the straight line through the double pyramid points intersects the base perpendicularly.
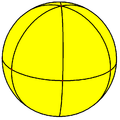
A regular double-pyramid can be applied to the in such a manner sphere one or sphere are projected that their tips on two opposite points (the poles) are mapped onto the sphere, the regular - Eck to the equator about the axis through the two poles and the edges resting on the double pyramid tips in equidistant circles of length through the poles that each perpendicularly intersect the equator. The side surfaces of the double pyramid are mapped onto spherical triangles.
n
{\ displaystyle n}
The symmetry group of a regular double pyramid is the direct product of its rotation group with the two-element group that is created by the reflection on the plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation . The symmetry group of the regular, angular double pyramid is of order except in the case of the octahedron , whose symmetry group is the octahedron group of order 48. The rotation group of a regular double pyramid is the dihedral group of the order except in the case of the octahedron, whose rotation group is an octahedron group of order 24 ( isomorphic to the symmetrical group on the set of space diagonals , i.e. to the group of permutations of the four space diagonals).
n
{\ displaystyle n}
D.
n
H
{\ displaystyle D_ {nh}}
4th
⋅
n
{\ displaystyle 4 \ cdot n}
O
H
{\ displaystyle O_ {h}}
D.
n
{\ displaystyle D_ {n}}
2
⋅
n
{\ displaystyle 2 \ cdot n}
O
{\ displaystyle O}
S.
4th
{\ displaystyle S_ {4}}
4th
!
=
24
{\ displaystyle 4! = 24}
Formulas
Sizes of a regular double pyramid (regular n- corner with side length a as base and height a )
General case
Square double pyramid
Regular triangular double pyramid
volume
V
=
n
⋅
a
2
⋅
H
6th
⋅
cot
(
π
n
)
{\ displaystyle V = {\ frac {n \ cdot a ^ {2} \ cdot h} {6}} \ cdot \ cot \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)}
V
=
2
⋅
a
2
⋅
H
3
{\ displaystyle V = {\ frac {2 \ times a ^ {2} \ times h} {3}}}
V
=
a
2
⋅
H
6th
⋅
3
{\ displaystyle V = {\ frac {a ^ {2} \ cdot h} {6}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {3}}}
Surface area
O
=
n
⋅
a
2
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
⋅
cot
2
(
π
n
)
{\ displaystyle O = {\ frac {n \ cdot a} {2}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2} \ cdot \ cot ^ {2} \ left ({ \ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)}}}
O
=
2
⋅
a
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
{\ displaystyle O = 2 \ cdot a \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2}}}}
O
=
3
⋅
a
2
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
3
{\ displaystyle O = {\ frac {3 \ cdot a} {2}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {3}}}}}
Steep edge length
l
=
(
H
2
+
a
2
4th
⋅
sin
2
(
π
n
)
)
1
2
{\ displaystyle l = \ left (h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {4 \ cdot \ sin ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right )}} \ right) ^ {\ frac {1} {2}}}
l
=
H
2
+
a
2
2
{\ displaystyle l = {\ sqrt {h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {2}}}}}
l
=
H
2
+
a
2
3
{\ displaystyle l = {\ sqrt {h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {3}}}}}
Inc sphere radius
r
i
=
a
⋅
H
4th
⋅
H
2
⋅
tan
2
(
π
n
)
+
a
2
{\ displaystyle r_ {i} = {\ frac {a \ cdot h} {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} \ cdot \ tan ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n} } \ right) + a ^ {2}}}}}
r
i
=
a
⋅
H
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
{\ displaystyle r_ {i} = {\ frac {a \ cdot h} {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2}}}}}
r
i
=
a
⋅
H
12
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
{\ displaystyle r_ {i} = {\ frac {a \ cdot h} {\ sqrt {12 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2}}}}}
Inner angle of the regular base
α
=
n
-
2
n
⋅
180
∘
{\ displaystyle \ alpha = {\ frac {n-2} {n}} \ cdot 180 ^ {\ circ}}
α
=
90
∘
{\ displaystyle \ alpha = 90 ^ {\ circ}}
α
=
60
∘
{\ displaystyle \ alpha = 60 ^ {\ circ}}
Base angle of the isosceles triangles
α
1
=
α
2
=
arctan
(
1
a
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
⋅
cot
2
(
π
n
)
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {1} = \ alpha _ {2} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {a}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ { 2} \ cdot \ cot ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)}} \ right)}
α
1
=
α
2
=
arctan
(
1
a
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {1} = \ alpha _ {2} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {a}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ { 2}}} \ right)}
α
1
=
α
2
=
arctan
(
1
a
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
3
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {1} = \ alpha _ {2} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {a}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {3}}}} \ right)}
Angle at the apex of the isosceles triangles
α
3
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
a
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
⋅
cot
2
(
π
n
)
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {3} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {a} {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2} \ cdot \ cot ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)}}} \ right)}
α
3
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
a
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {3} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {a} {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2}}}} \ right)}
α
3
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
a
4th
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
3
)
{\ displaystyle \ alpha _ {3} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {a} {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} + {\ frac {a ^ {2}} {3} }}}} \ right)}
Angle between base and isosceles triangles
β
1
=
arctan
(
2
⋅
H
⋅
tan
(
π
n
)
a
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {1} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {2 \ cdot h \ cdot \ tan \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)} {a}} \ right)}
β
1
=
arctan
(
2
⋅
H
a
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {1} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {2 \ cdot h} {a}} \ right)}
β
1
=
arctan
(
2
⋅
3
⋅
H
a
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {1} = \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {2 \ cdot {\ sqrt {3}} \ cdot h} {a}} \ right)}
Angle between the isosceles triangles
β
2
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
1
2
⋅
H
⋅
(
4th
⋅
H
2
⋅
sin
2
(
π
n
)
+
a
2
tan
2
(
π
n
)
-
sin
2
(
π
n
)
)
1
2
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {2} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {2 \ cdot h}} \ cdot \ left ({\ frac {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} \ cdot \ sin ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right) + a ^ {2}} {\ tan ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n} } \ right) - \ sin ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right)}} \ right) ^ {\ frac {1} {2}} \ right)}
β
2
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
1
2
⋅
H
⋅
4th
⋅
H
2
+
2
⋅
a
2
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {2} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {2 \ cdot h}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {4 \ cdot h ^ {2} +2 \ cdot a ^ {2}}} \ right)}
β
2
=
2
⋅
arctan
(
1
3
⋅
H
⋅
3
⋅
H
2
+
a
2
)
{\ displaystyle \ beta _ {2} = 2 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ frac {1} {3 \ cdot h}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {3 \ cdot h ^ {2} + a ^ {2 }}} \ right)}
Solid angle at the equator
Ω
1
=
8th
⋅
arctan
(
tan
(
2
⋅
β
1
+
β
2
4th
)
⋅
tan
(
2
⋅
β
1
-
β
2
4th
)
⋅
tan
2
(
β
2
4th
)
)
{\ displaystyle \ Omega _ {1} = 8 \ cdot \ arctan \ left ({\ sqrt {\ tan \ left ({\ frac {2 \ cdot \ beta _ {1} + \ beta _ {2}} {4 }} \ right) \ cdot \ tan \ left ({\ frac {2 \ cdot \ beta _ {1} - \ beta _ {2}} {4}} \ right) \ cdot \ tan ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ beta _ {2}} {4}} \ right)}} \ right)}
Solid angle at the top
Ω
2
=
2
⋅
π
-
2
⋅
n
⋅
arcsin
(
cos
(
π
n
)
⋅
tan
2
(
π
n
)
-
tan
2
(
α
3
2
)
)
{\ displaystyle \ Omega _ {2} = 2 \ cdot \ pi -2 \ cdot n \ cdot \ arcsin \ left (\ cos \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right) \ cdot {\ sqrt {\ tan ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ pi} {n}} \ right) - \ tan ^ {2} \ left ({\ frac {\ alpha _ {3}} {2}} \ right)}} \ right)}
Special cases
For certain values of and , there are relationships with Platonic solids or Johnson solids :
n
{\ displaystyle n}
H
{\ displaystyle h}
For and we get the regular double triangle pyramid with equilateral triangles , the Johnson body J12. It consists of two regular tetrahedra .
n
=
3
{\ displaystyle n = 3}
H
=
a
3
⋅
6th
{\ displaystyle h = {\ frac {a} {3}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {6}}}
For and there is the square double pyramid with equilateral triangles , namely the octahedron .
n
=
4th
{\ displaystyle n = 4}
H
=
a
2
⋅
2
{\ displaystyle h = {\ frac {a} {2}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {2}}}
For and we get the regular pentagonal double pyramid with equilateral triangles , the Johnson body J13. The two halves are regular pyramids that are part of the icosahedron .
n
=
5
{\ displaystyle n = 5}
H
=
a
10
⋅
50
-
10
⋅
5
{\ displaystyle h = {\ frac {a} {10}} \ cdot {\ sqrt {50-10 \ cdot {\ sqrt {5}}}}}
Straight double pyramid If the pyramid that creates a double pyramid is straight, one speaks of a straight double pyramid . The dual body of a straight double pyramid is a straight prism and vice versa.
The cube as a dual of the octahedron
The octahedron as a dual of the cube
General double pyramid volume The volume of a double pyramid is , where the area of the base area of the generating pyramid denotes and the height of a peak above this base area. This formula applies regardless of whether it is a straight double pyramid or not, as long as the height is determined as the orthogonal distance between a tip and the plane in which the base is located.
V
=
2
3
⋅
G
⋅
H
{\ displaystyle V = {\ tfrac {2} {3}} \ cdot G \ cdot h}
G
{\ displaystyle G}
H
{\ displaystyle h}
H
{\ displaystyle h}
Web links
<img src="https://de.wikipedia.org//de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:CentralAutoLogin/start?type=1x1" alt="" title="" width="1" height="1" style="border: none; position: absolute;">