Flag of france
| Flag of france | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vexillological symbol : |
|
| Aspect ratio: | 2: 3 |
| Officially accepted: | First introduced on February 15, 1794, last reintroduced on March 5, 1848 |
The current flag of France ( also known as drapeau tricolore , drapeau bleu-blanc-rouge or drapeau français in French and as les couleurs in the military ) first became the official national flag in 1794 .
description
The national flag is a tricolor of three vertical bars of equal width in blue, white and red (from the mast ) and has an aspect ratio of 2: 3. In the case of the flag at sea (for the French Navy ), the three colors blue, white and red are divided in a ratio of 30:33:37. These so-called "optical proportions" are used so that when flapping in the wind the impression of three equally wide stripes is created and not the ones facing away appear narrower.
The colors were redefined by President Valéry Giscard d'Estaing in the 1980s.
| blue | White | red | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | Blue (0055A4) | White (FFFFFF) | Red (EF4531) |
| CMYK | 100.70.0.5 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.90.86.0 |
history
The flags of the Kingdom of France
Until the French Revolution (from 1789) and during the restoration period (1814–1815, 1815–1830), the pavilion royale , a plain white flag with golden lilies, was the de facto national flag of France. It was also the sea flag and was hoisted in the presence of the king . A plain white flag was used as a naval war flag from the 17th century until 1790. If the king was on board a ship, it sailed under a white flag with golden lilies and a coat of arms in the middle: This consisted, among other things, of the French crown, a blue shield with three golden lilies and two angels as shield bearers.
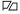 ? The pavilion royal , standard of the royal family of France and de facto national flag of France
? The pavilion royal , standard of the royal family of France and de facto national flag of France
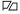 ? The Standard royal , standard of royal France
? The Standard royal , standard of royal France
The tricolor
The tricolor appeared for the first time in 1790 during the revolution and was used as a naval war flag and jack up until 1794 , but with the reverse color arrangement, with red on the mast side.
It represented a combination of the colors of the coat of arms of Paris (red and blue) and the color of the king (white). The arrangement of the colors also dates from this time and symbolizes the limited power of the king (white) by the people (the Colors of Paris). Other historians believe that the red stands for the oriflamme , the banner of Saint Denis de Paris , the patron saint of the French Empire, and that blue is the color of the coat of the French king. With the abolition of the monarchy on September 21, 1792, this symbolism became obsolete, but the tricolor remained a symbol of the revolution.
On February 15, 1794, the National Convention declared the flag with the current color sequence to be the official national flag of the First Republic . A secondary but early reinterpretation is the reference to the motto of freedom, equality, fraternity ( liberté, égalité, fraternité ) , with blue for freedom, white (heraldic: silver) for equality and red for brotherly love.
The tricolor as a symbol of the revolution ( Eugène Delacroix , Freedom leads the people , 1830)
Overseas territories
The flag of France is also the national flag of the overseas territories or overseas departments that are dependent on France . The French overseas regions also carry regional flags. Some territories with a special status, French Polynesia as well as Wallis and Futuna , also have their own flags that can be hoisted next to the tricolor. In New Caledonia , the use of local flags together with the French flag is also permitted.
Main Products:
- French Guiana flag
- French Polynesia flag
- Flag of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- Flag of Guadeloupe
- Martinique flag
- Mayotte flag
- Flag of New Caledonia
- Reunion flag
- Flag of Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martins flag
- Flag of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Flag of Wallis and Futuna
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Archived copy ( memento of the original from August 20, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ; Archive link ( Memento of the original from August 20, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ; http://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/fr/article-imprim.php3?id_article=5157 ; http://www.assemblee-nationale.fr/histoire/SYMBOLES/sommaire.asp
- ↑ See image on http://digitalgallery.nypl.org / ( Memento of the original from April 6, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b The symbol: The French flag. (No longer available online.) In: Karambolage . ARTE , February 26, 2006, archived from the original on April 14, 2009 ; Retrieved October 22, 2008 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.





