Union Jack
| Union Jack | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vexillological symbol : |
|
| Aspect ratio: | 1: 2 |
| Officially accepted: | January 1, 1801 |
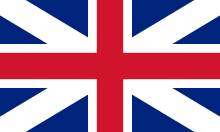
Union Jack is the popular name for the national flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland , officially called the Union Flag . The flag has been used in its current form since 1801.
layout
The Union Jack is an overlay of the English flag (red cross on a white background, the so-called St. George's Cross ), the Scottish flag (white St. Andrew's cross on a blue background) and the Northern Irish flag (red St. Andrew's cross on a white background, the so-called Patrick's cross ).
Colours
The colors of the Union Flag correspond to the values in the following table.
| blue | White | red | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB decimal a | 0, 36, 125 | 255-255-255 | 207, 20, 43 |
| RGB hexadecimal a | # 00247D | #FFFFFF | # CF142B |
| CMYK | 100/72/0 / 18.5 | 0/0/0/0 | 0/91/76/6 |
| Pantone | 280 C | "safe" | 185 C |
The blue of the Union Flag was lighter between 1600 and 1700 and darker around 1800 than it is today.
history
Emergence
The Union Jack was first introduced under King James I in 1606 as a result of the personal union between Scotland , Ireland and England and was used until 1649. After the unification of Scotland and England, both flags were initially carried on ships at sea. This meant that two flags had to be hoisted in one place, one above the other. Since hoisting one national flag over the other means that the lower nation was defeated by the one above, Scottish ships carried the St. Andrew's cross over the St. George's cross and the English did it the other way around.
Thereupon James I commissioned his heralds to unite both flags equally.
Originally the Union Jack was just an overlay of the flags of England and Scotland. The first Union flag emerged from the English red George Cross and the Scottish St. Andrew's Cross. Many Scots were dissatisfied with the dominance of the English cross and for a time hoisted a different version of this flag, in which the St. Andrew's cross was in the foreground.
After the English Civil War , the flag of England was supplemented by the Irish harp by Cromwell until 1654 due to the protectorate, which was in the center of the flag until 1660. Between 1660 and 1801 the original Union Jack was used again.
In 1801, with the political integration of the neighboring island of Ireland , the red St. Andrew's cross was added to the Union Jack , the then Irish flag ( St. Patrick's Cross ) and replaced the Irish coat of arms. The asymmetry of the Union Jack stems from the fact that the Scottish St. Andrew's Cross and the Irish St. Patrick's Cross should stand “next to each other” on an equal footing. Heraldically, this is achieved by not placing the relevant symbols in the middle, but rather “shifting” them against each other. The English St. George's Cross, on the other hand, is centrally located on all other crosses, which symbolizes the dominance of England over the countries of Scotland and Ireland.
1809 was Union Jack by the Parliament declared a British national flag.
The flag of Wales , on the other hand, was never included in the Union Jack , since Wales was annexed to England by the Act of Union 1536 , long before the founding of the United Kingdom, and was considered to be adequately represented by the English Cross of St. George; there are, however, designs for a Union Jack with the Welsh Cross of David (yellow cross on black background). The British Minister of Culture Margaret Hodge did not rule out a redesign in 2007.
Designation Union Jack

The designation "Jack" refers to the original use as a bow flag in (war) ships under Charles II (in German : " Gösch "). Other explanations of the name are that "Jack" is derived from the soldier's clothing or the name Jacob I , who introduced this flag in its original form.
Union Jack and Multicultural United Kingdom
Since the 1990s it has been discussed at times to change the flag against the background of the multicultural composition of the population of the United Kingdom, for example by adding a black Andrew's cross. The background to this debate is u. a. the slogan "There ain't no black in the union jack" , which was originally used by racist movements in the 1960s to express that there was no place in the country for non-European immigrants. He was later picked up by anti-racist groups from the 1980s to express the exclusion and alienation of immigrants from the white majority society.
Service flags
3: 5 ? Union Jack in the army

The British Army uses a Union Jack with an aspect ratio of 3: 5.
Since only the service flags at sea differ from the national flag, they are also known as Ensign , the term for the stern flag of a ship. The Royal Navy used three variations of the Union Jack until the naval reform of 1864 . Since the naval reform of 1652, the Royal Navy had three main fleets, each sailing under its ensign and responsible for different regions:
- White Ensign in the broadest sense of Europe
- Red Ensign in the broadest sense of the West Indies (Caribbean, North Atlantic)
- Blue Ensign in the broadest sense of the East Indies (South Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Ocean)
Since 1865:
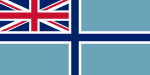
- The White Ensign has been the Royal Navy's only flag since 1864 . It is the naval war flag .
- The Red Ensign (also civil ensign ; English : Bürgerflagge) became the trade flag. Great Britain, dependent areas and also former colonies use the Red Ensign as the flag of their merchant ships to this day . It is the basis of the flags of Bermuda and some Canadian provinces .
- The Blue Ensign serves as the service flag at sea. Their use is reserved for state authorities. Since 1865 the dependent areas have been allowed to add a coat of arms (badge) to them and to create their own flags, from which various colonial flags emerged, some of which have survived to this day and which have become the basis of some of today's national flags. (see flag of Australia , flag of New Zealand , flag of Fiji )
More ensigns
Pilots flag
Flag of the queen
Since the monarch of Great Britain is not only head of state of Great Britain, but also formally some other countries in the Commonwealth , the Queen uses their own flags in these countries, which are called Royal Standard and differ from the Union Jack . The coat of arms of the respective country is usually used.
Royal Standard of Great Britain used in Scotland
Dependent areas
In order to be able to use the same aspect ratio as in the Union flag of South Africa , a Union Jack version with an aspect ratio of 2: 3 was allowed there between 1929 and 1957 .
Since 1865, English colonies and dependent territories were allowed to add their own coat of arms to the Blue Ensign . Private individuals were also allowed to run a corresponding Red Ensign . In some cases, such as B. in South Africa or Canada , the Red Ensign became the national flag with independence. The only exception is the flag of the British Antarctic Territory , which is a version of the White Ensign .
Dependent territories with Union Jack flags
- Flag of Anguilla
- Flag of the British Antarctic Territory
- Bermuda flag
- British Virgin Islands flag
- Cayman Islands flag
- Falkland Islands flag
- Montserrat flag
- Flag of the Pitcairn Islands
- Flag of St. Helenas / Flag of Ascensions / Flag of Tristan da Cunhas
- Flag of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Flag of the British Indian Ocean Territory
- Flag of the Turks and Caicos Islands
Dependent territories with flags without Union Jack
Other states with the Union Jack
Numerous former colonies kept the Union Jack in their national flags in the front Obereck (on the left as viewed from the viewer, on the side facing the mast) . In some of these countries, corresponding Red Ensigns are used as trade flags and White Ensigns as naval flags. Various provincial flags also use the Union Jack in the canton.
Current national and provincial flags with the Union Jack
- Flag of Australia
- Flag of Fiji
- Canada has been using the maple leaf flag instead of the Red Ensign since 1965 . However, the Union Jack is still the official Canadian symbol of membership of the Commonwealth and the monarchy.
(See also: Canadian Red Ensign )
- British Columbia flag
- Manitoba flag
- Standard of the Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia
- Flag of Ontario
- New Zealand flag
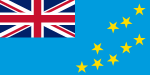
- Flag of Tuvalus
- The US has not used a Union Jack since 1776
Also leads Baton Rouge (US state of Louisiana ) a Union Jack flag in the city.
Historic Union Jacks
Since colonies and dependent areas had been allowed to use their own flags since 1865, most of which were based on the Blue Ensign , various colonial flags were created, some of which survived independence.
A special feature is the flag of South Africa , which was used until 1994 . Together with the flags of the Boer Republics Orange Free State (vertical) and Transvaal , the Union Jack formed the coat of arms on a modified Dutch flag .
 United States of America , 1776
United States of America , 1776
 British East India Company , 1801 to 1858
British East India Company , 1801 to 1858
 Canada , 1921 to 1957
Canada , 1921 to 1957
 South Africa until 1994
South Africa until 1994
Historical flags
- Historic flag of the Commonwealth of England from 1653 to 1659
- Historic flag of the British East India Company until 1858
- Historic flag of the Ellice Islands until 1978
- Historical flag of Fiji until 1970
- Historical flag of the Gambia until 1965
- Historical flag of Ghana until 1957
- Historical flag of the Gilbert Islands until 1979
- Historic flag of Grenada until 1967
- Historical flag of Guyana until 1966
- Historical flag of the Kingdom of Hanover until 1867
- Historical flag of Heligoland from 1807 to 1890
- Historical flag of Hong Kong until 1997
- Historical flag of British India until 1947
- Historic flag of Jamaica until 1962
- Historic flag of Canada until 1965
- Historical flag of Kenya until 1963
- Historical flag of Malawi until 1963
- Historic flag of Malta until 1947
- Historic flag of Mauritius until 1968
- Historic flag of Nigeria until 1960
- Historic flag of Northern Rhodesia until 1963
- Historical flag of Sarawak until 1963
- Historic flag of South Africa until 1928
- with Union Jack as part of the coat of arms until 1994
- Historical flag of South Yemen until 1963
- Historical flag of Southern Rhodesia until 1964 (light blue until 1968)
- Historical flag of Uganda until 1962
- Historical flag of the USA (only partially and briefly 1776)
- Historic flag of the Central African Federation until 1963
- Historical flag of Cyprus until 1960
See also
- List of British flags
- Flag of england
- Flag of Scotland
- Shetland Islands flag
- Flag of wales
- Northern Ireland flag
- Royal Standard
Web links
- Rebranding puts black marks against UK flag (article on the discussion about the Union Jack today and the inclusion of the color black, English)
- Royal Navy national and command flags in the 17th and 18th centuries
- Flags of the World - United Kingdom (English)
- Martin Herzog: April 12th, 1606 - Flag for England and Scotland WDR ZeitZeichen from April 12th, 2016. (Podcast)
Individual evidence
- ↑ United Kingdom. Name of the flag. In: Flags Of The World website. Retrieved August 19, 2011 .
- ↑ a b c Union Jack. In: The official website of The British Monarchy. The Royal Household, accessed on August 19, 2011 (English): “The cross of St George, patron saint of England since the 1270's, is a red cross on a white ground. After James I succeeded to the throne, it was combined with the cross of St. Andrew in 1606. […] This was combined with the previous Union Flag of St George and St Andrew, after the Act of Union of Ireland with England (and Wales) and Scotland on 1 January 1801, to create the Union Flag that has been flown ever since. "
- ↑ a b United Kingdom: color of the flag. Color of the flag. In: Flags Of The World website. Retrieved February 6, 2012 .
- ^ Patrick Wintour: Minister proposes a redesign for the union flag. In: The Guardian . November 28, 2007, accessed August 19, 2011 .
- ^ Royal Union Flag. In: Canadian Heritage / Patrimoine canadien. Archived from the original on April 13, 2008 ; accessed on August 19, 2011 .