Flag of Australia
| Flag of Australia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vexillological symbol : |
|
| Aspect ratio: | 1: 2 |
| Officially accepted: | May 22, 1909 |
A variant based on the British Blue Ensign was declared the official flag of Australia ( national flag ) on May 22, 1909 .
description
The Australian flag is based on the Blue Ensign and can be divided into three elements:
- The Australian flag is nicknamed the Southern Cross, the upper left corner bears the Union Jack , the flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland , whose colony Australia was until 1901 and to which it is still loosely bound by its membership in the Commonwealth .
- To the left, under the Union Jack, is a large white seven- pointed star called the Commonwealth Star . Six rays stand for the six states of Australia , the seventh for the so-called territories.
- The right half of the flag shows an arrangement of five stars another white, different sizes, which the constellation Southern Cross represent. One of them has five rays, the other four seven rays.
Colours
| blue | White | red | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | 0-0-139 | 255-255-255 | 255-0-0 |
| hex | # 00008B | #FFFFFF | # FF0000 |
| CMYK | 100.80.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.100.100.0 |
| Pantone | 280 C | "safe" | 185 C |
history
The first recorded attempt to introduce a "national" flag for Australia dates back to 1822 and 1823 and goes back to the two captains John Nicholson and John Bingle. The flag, known as the National Colonial Flag , consisted of a white cloth with a red Georgian cross , which had a white star on each end, which should stand for the Southern Cross . Some time later a fifth star was added to represent the colonies of Australia. Bingle was beside himself and wrote in his 1881 memoir:
"Anyone adding another star to symbolize another colony was moved by 'American Notions' and had not comprehended the original intention, which was simply to represent 'the emblem of our Hemisphere the great Southern Cross'."
"The person who added another star for another colony was moved by the 'American idea' and did not understand the original intention, which simply showed the emblem of our hemisphere, the Southern Cross."

The correct appearance of the National Colonial Flag is controversial. Versions based on the White Ensign (Georgskreuz with the Union Jack in the Obereck) and featuring stars with five or eight points are discussed. It is undisputed that from this point onwards the stars, symbols of the Southern Cross, dominated the rest of the Australian flag symbolism.
In 1831, Captain John Nicholson proposed a flag at sea for New South Wales , the New South Wales Ensign . This flag became increasingly popular and gained importance as a federal symbol in Australia . The Federation movement, with groups such as the Australian Natives Association and the Australian Federation League , flourished in the 1880s and 1890s, and used this flag. The motto of the said league was:
- one people, one destiny, one flag ( One people, one destiny, a flag )
The New South Wales Ensign is therefore also known as the Australian Federation Flag or Australian Ensign and for many represents the first real Australian flag. This was also available in numerous similar versions with four, five or six stars, which in turn consisted of five to eight points passed.
Meanwhile, the star symbolism was featured in many other flags in Australian history. In 1851 the Anti Transportation League was formed , which resisted the further transport of convicts to Australia and New Zealand. The five gold-colored stars of the Southern Cross also stood for the colonial settlements in Tasmania , Victoria , New South Wales, South Australia and New Zealand . The name and year of foundation of the league and the name of the colony were written on the white border. The flag of the Anti Transportation League was very similar to today's national flag and its influence can be seen on the current flag of Victoria.
Another important flag in the flag history of Australia was the so-called Eureka Stockade flag . In 1854 it blew over the Eureka Stockade , the camp of some gold miners in Ballarat , Victoria. These miners, united under the leadership of Peter Lalor , campaigned for the release of captive compatriots, general elections, secret ballots and many other reforms. Their flag only flied from November 29th to December 3rd, before the police forcibly dismantled the camp. This blue and white flag with stars is now in the Eureka Stockade Center museum in Ballarat.

On January 1, 1901, the day the Commonwealth of Australia was founded , the country still had no official flag. The Australians therefore sought their own identity by creating a new flag without denying their loyalty to the British crown. As early as 1900 the Evening Herald and later in October the Review of Reviews Australasia , both magazines from Melbourne , called for an award-winning flag competition. Finally, on April 29, 1901, a competition called by the government followed, in the evaluation of which the submissions to the Review of Reviews Australasia were taken into account. The prize money rose from £ 50 to £ 200 through government and the Havelock Tobacco Company's commitment , which was a substantial amount for the time. The competition did not fail to have an impact and 32,823 designs were submitted. It was clear from the start that it would boil down to a flag containing the Union Jack and the Southern Cross. Other flags were given little chance of victory. In addition to this symbolism, many designs contained motifs from the local animal world. Some of the most unusual designs included a kangaroo jumping through the Southern Cross, cricket-playing Australian animals, a six-tailed kangaroo for the six Australian states, and a fat kangaroo aiming a pistol at the Southern Cross.
The prize money was ultimately shared by five participants whose suggestions were very similar and only differed in details. A dark blue flag with a Union Jack ( Blue Ensign ) with a large Commonwealth star and five smaller stars arranged as the constellation of the Southern Cross was selected . This winner's flag was thus almost the same as today's flag and differs from it only in two points: The large main star ( Commonwealth Star ) still consisted of 6 points and the stars of the Southern Cross originally had increasingly five to nine points to keep the apparent brightness within of the constellation. This flag was first hoisted on September 3, 1901 at the Royal Exhibition Building in Melbourne.

The flag proposal was never discussed in the Australian Parliament. Edmund Barton , the first Prime Minister of Australia favored the "Australian Ensign" and sent it to King Edward VII for selection together with a simplified version of the flag of the competition . Only on January 20, 1903, the government could announce that Edward VII. approved the contest proposal as the official flag. On June 2, 1904, the Australian Parliament passed a resolution to pass the flag, giving it the same status as the Union flag in Great Britain.
There were two versions of the flag: red for merchant ships ( Commonwealth red ensign ) and blue for other uses ( Commonwealth blue ensign ), which led to some confusion in the flag management. On February 14, 1954, Elizabeth II approved the Flags Act (Cwth, 1953). In Section 3, the Commonwealth Blue Ensign is confirmed as the national flag.
The Commonwealth Star was supplemented by a point on May 22, 1909, which stands for the two territories. The flag of Australia, along with the flag of Jordan, is one of the only two flags to have a seven-pointed star.
Flags at sea
Main article: Australian White Ensign
Australia uses the British flag system with the various ensigns ( White Ensign , Red Ensign and Blue Ensign ). The Australian White Ensign has been used by the Royal Australian Navy since 1967 . Before that, Australian warships used the British White Ensign. The Australian Red Ensign is intended for civilian guidance at sea. It is mandatory for registered vessels over 24 meters. Smaller ships and unregistered ships that have a corresponding certificate can choose between the Blue and Red Ensign. The Australian Red Ensign has been in use since 1904. Until 1953, the red Ensign was the only flag that private individuals were allowed to use on land. It was not until the 1953 Flags Act that non-state persons were allowed to use the blue Ensign and the use of the red Ensign was restricted to the sea.
 ? Trade Flag
? Trade Flag
(Australian Red Ensign)
Australia's flag issue
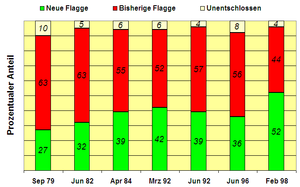
The relationship between the Australian population and its flag is twofold. While one side is determined to stick to the current flag, the other side is pleading for a new flag without the Union Jack.
Arguments for keeping
Due to the growing public interest in new flag designs, the supporters of the previous flag founded the Australian National Flag Association to prevent all attempts to change flags. Proponents of the previous flag argue:
- The flag uniquely and explicitly represents Australia and its status as an independent Commonwealth Realm . The Union flag stands for Australia's historical roots, its membership in the Commonwealth of Nations , as well as parliamentary democracy modeled on Westminster and the Common Law practiced in Australia. The Commonwealth Star symbolizes the six states and Australian territories. The Southern Cross stands for Australia's location in the southern hemisphere and has been known to the Aborigines of the country since ancient times and plays a role in their numerous traditional legends.
- The flag does not represent subordination of the country to Great Britain: The Fiji Islands are a republic and have since held on to the Union Jack in the Obereck; just to the United States belonging Hawaii Islands, although they were never a colony of Great Britain.
- The flag is a very common and popular symbol and is displayed by the Australian people regardless of their ethnicity or origin. No alternative flag, such as the Boxing Kangaroo , could achieve this status.
- The flag is strongly linked to the history of Australia and therefore has historical significance. It contains elements from previous flags, such as those of the Anti-Transportation League .
- The flag was used by the armed forces. Ignoring this would mean insulting the 102,000 dead who fell under this flag in the war.
- The flag was created by the people of Australia and selected through a public competition.
Arguments for a change
The other side is managed by an organization called the flagging out . The organization does not favor a specific flag design, but supports several flag competitions that should lead to an alternative flag.
The opponents of the previous flag argue:
- The flag is not distinctive, as is the case with national flags of other countries. In particular, it is difficult to distinguish from some other flags based on a Blue Ensign , most notably the flags of New Zealand and the flags of Victoria .
- The flag does not emphasize Australia's status as an independent nation. The Union flag in the Obereck suggests that Australia is a British colony or a dependent territory. New Zealand, the Fiji Islands and Tuvalu are the only other independent states in the world that display the Union flag in their flags. Other Commonwealth nations whose flags once carried the Union Jack , like Canada , have since changed them without becoming republic. The colors red, white and blue are not Australia's official colors ( green and gold) nor are their heraldic colors (blue and gold).
- Representing only British heritage, the flag is anachronistic and does not reflect the shift towards a multicultural and pluralistic society. In particular, she does not go into the natives of Australia; many of them view the Union flag as a reminder of colonial oppression and dispossession.
- Historically, the flag has not been the primary national symbol. For most of the time since the Confederation was founded, the flag has flown next to the Union flag. The number of pips has changed since 1901, and the current blue version was not officially adopted as the national flag until 1954 . Previously, there was confusion as to whether the red or blue version should be preferred, with the red often emerging as the winner.
- Claims that Australians "fought and died under this flag" are false, since most of the wars in which Australia was involved were fought under the Red Ensign and the Union's flag.
Subnational flags
Flags of the Australian states and territories
See also: flags and coats of arms of the Australian states
The flags of the Australian states are always set up in the same way: An emblem is shown on a Blue Ensign , which is usually derived from the Colony Badge , the identification symbol of the colony. In contrast, there are the flags of the two Australian territories, which are similar in structure and are more recent.
| flag | location | description |
|---|---|---|
 |
The flag of the Australian Capital Territory was inspired by that of the Northern Territory. The slightly modified city coat of arms of Canberra is depicted in gold and the constellation Southern Cross in blue. | |
 |
The emblem of the flag of New South Wales shows the George Cross with the Aquitaine lion surrounded by four eight-pointed stars. A further meaning is not known. | |
 |
The Northern Territory flag is different from the usual Blue Ensign motifs. The local plant Sturt's Desert Rose is depicted in the ocher-colored field, and the Southern Cross in the black field. | |
 |
The emblem of the flag of Queensland features a blue Maltese cross and a crown, which indicates the governor's status as representative of the British monarch. | |
 |
The flag of South Australia features a yellow emblem with a native bird, the flute bird . | |
 |
The flag of Tasmania bears an emblem of a red heraldic lion that may have a reference to England . | |
 |
The crown over the Southern Cross on the flag of Victoria indicates the governor's status as a representative of the British monarch. The flag is considered to be trend-setting in the flag history of Australia. | |
 |
The Black Swan depicted on the flag of Western Australia was the symbol of the Swan River Settlement Colony on the Swan River as early as the 1830s . |
Outskirts of Australia
The Norfolk Island flag has been the island's official symbol since January 17, 1980. The Cocos Islands officially adopted their flag on April 6, 2004. The Christmas Island flag has had official status since 2002 . The flag of Lord Howe Island designed in November 1998 has no official status . The other overseas territories also do not have their own official flag, but only use the national flag of Australia.
Unofficial flag of Lord Howe Island
Municipal flags
The lower administrative levels in Australia also have their own flags. Here are a few examples.
Flags of the indigenous people
1995 were officially flag of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Flag as "Flags of Australia" was introduced. They received official recognition in extensions to the Australian Flag Act 1953 .
More flags of Australia
As the head of state of Australia, Queen Elizabeth II has her own flag when she is in Australia. Your representative, the Governor General, wears a flag that corresponds to the usual design for British governor flags. Royal Australian Air Force and Customs conduct their own Ensign with the Union Jack in the Gösch .
Flag of Queen Elizabeth II in Australia
Flag of the Royal Australian Air Force
Sport flag boxing kangaroo
See also
literature
- Whitney Smith, Ottfried Neubecker: coats of arms and flags of all nations. Battenberg, Munich 1980, ISBN 3-87045-183-1 .
Web links
Official pages
Other sides
- Australian Red Ensign (Shipping) Regulation
- Australia . Flags of the world - Australian flags and their history
- Flag. Charles Sturt University
- Australian National Flag Association - Organization of Current Flag Proponents
- Flag out - Organization of the advocates of a new flag
Individual evidence
- ^ Cocos (Keeling) Islands . Flags of the World
- ^ State flags . Flag Society of Australia Inc.