Graham Bell Island
| Graham Bell Island | ||
|---|---|---|
| The east of Franz Josef Land with Graham Bell Island | ||
| Waters | Arctic Ocean | |
| Archipelago | Franz Josef Land | |
| Geographical location | 80 ° 52 ′ N , 64 ° 17 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 69 km | |
| width | 36 km | |
| surface | 1 560 km² | |
| Highest elevation | Windy ice cap (Kupol Wetreny) 509 m |
|
| Residents | uninhabited | |
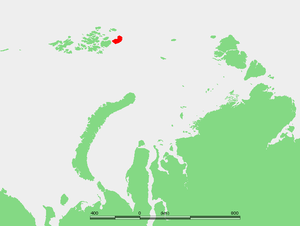
| Location of Graham Bell Island | ||
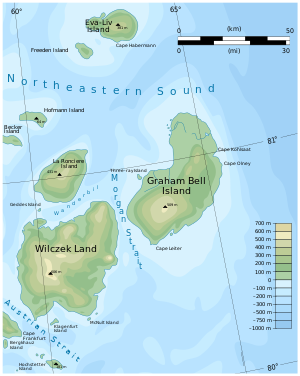
The Graham Bell Island (Russian Остров Греэм-Белл - Ostrow Greem Bell ) is the easternmost island of the Franz Josef Land archipelago belonging to Russia in the Arctic Ocean .
geography
With around 1560 km², Graham Bell Island is the third largest in the archipelago. Parts of the island are covered by ice all year round. Its highest point, the Windy ice cap (Kupol Wetreny) is given at 509 meters, according to other information 580 meters. The ice cap is the largest in the entire archipelago. Their thickness reaches almost 500 meters.
The easternmost point of the island is Cape Kohlsaat (Russian Мыс Кохлсаат - Mys Kohlsaat ). Since the area is close to the pack ice border, the sea around the cape is full of drift ice year round . At the same time, Cape Kohlsaat marks the northwesternmost point of the Kara Sea .
Graham Bell Island is separated from its western neighbor island Wilczek Land (not to be confused with Wilczek Island ) by only a 6 km wide waterway, known as Morgan Sound (Russian Пролив Моргана - Proliw Morgana ). The 1.5 km², offshore mother-of-pearl island to the south disappeared after its ice cap melted at the end of the 20th century.
history
The official discovery of Graham Bell Island is attributed to Evelyn Baldwin , who crossed the island four times in a dog sled during the Walter Wellman Expedition (1898–1899) and roughly mapped it. However, it can be assumed that the island and the entire archipelago were sighted by seafarers much earlier. Wellman named the island after the then President of the National Geographic Society , the inventor Alexander Graham Bell .
In 1926, the entire Franz Josef Land archipelago was taken over by the Soviet Union . Later, during the Cold War , the Soviet Union established the secret Greem Bell military airfield and radar station on the largely ice-free Cholmisty Peninsula (Полуостров Холмистыӣ). It was the northernmost base in the country. It had a 2.1 km long runway, which has been regularly approached by large transport aircraft and long-range bombers since the late 1950s . The military base has been abandoned since the late 1990s. Efforts have been made in recent years to clean up the polluting legacy left by the military on the islands.
Web links
- UNEP Islands (English)
- Polar Foundation, 2006 (English; PDF file; 2.65 MB)
Individual evidence
- ^ Andreas Umbreit: Graham-Bell-Insel on the Franz-Joseph-Land Info page , accessed on June 4, 2011
- ↑ Oceandots: Franz Josef Land ( Memento of 22 July 2012 at the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Aleksey I. Sharov: Studying changes of ice coasts in the European Arctic (PDF; 854 kB). In: Geo-Marine Letters 25, 2005, pp. 153-166. doi : 10.1007 / s00367-004-0197-7
- ^ William James Mills: Exploring Polar Frontiers - A Historical Encyclopedia , ABC-CLIO, 2003, ISBN 1-57607-422-6 , p. 268
- ^ PJ Capelotti: EB Baldwin and the American-Norwegian discovery and exploration of Graham Bell Island, 1899 . In: Polar Research 25, No. 2, 2006, pp. 155-171. doi : 10.3402 / polar.v25i2.6245
- ↑ Polar Foundation, 2006 (PDF; 2.8 MB), cf. P. 10ff. (English)