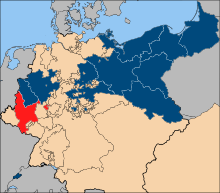
Province of the Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine
The Grand Duchy of the Lower Rhine was until 1822 one of first ten provinces ( 1822 : 9, 1824 : 8, 1850 : 9, 1866/8 : 12, 1878 : 13), in which the state of Prussia after the Congress of Vienna in 1815 by the due Regulation improved institution of the provincial authorities of April 30, 1815 was assigned. It hardly overlapped with the now known Lower Rhine region .
The province essentially comprised certain areas south and west of Cologne, the Electorate of Trier , parts of Luxembourg and Limburg , Manderscheid , Malmedy , goods of the Palatinate , the Rhine Counts , the Duchy of Jülich , the city of Aachen and other smaller domains. After the end of the Napoleonic Wars , the Generalgouvernements Mittelrhein and Niederrhein were initially provisionally formed, from which the Province of Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine emerged.
The seat of the high presidium (provincial government) of the province of Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine was in Koblenz . The upper presidents were Johann August Sack from 1815 to March 28, 1816 and Karl Freiherr von Ingersleben from 1816 to June 27, 1822 .
Downfall of the name
When the Prussian state territory was divided into electoral districts for the Prussian manor house , which was valid from 1854 to 1918, the three administrative districts of the former province of the Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine were given the names Moselland (administrative district Trier), West-Jülich (administrative district Aachen) and Upper Rhine ( Koblenz administrative district).
development
From April 30, 1815, the province of the Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine comprised two districts:
The Second Peace of Paris, concluded on November 20, 1815, resulted in the third
added. The respective administrations began their work on April 22, 1816.
After the administrative district of Kleve was incorporated into the administrative district of Düsseldorf on January 1, 1822 , the provinces of the Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine and Jülich-Kleve-Berg were also united by royal cabinet order on June 22, 1822 . Until 1830 people spoke of the Rhine provinces , after that only the Rhine province . The administrative seat of the Rhenish High Presidium became Koblenz. The Prussian Rhine province (s) consisted of five administrative districts since June 27, 1822:
- Administrative district of Aachen
- District of Düsseldorf
- Cologne district
- Koblenz administrative district
- Trier district
Provincial coat of arms
In 1817 the Grand Duchy of Lower Rhine was given a coat of arms showing the Prussian eagle with a heart shield . The heart shield bears a white (silver) wavy bar running from bottom right to top left, which symbolizes the Rhine and the Rhineland . The coat of arms was transferred to the Rhine Province in 1822 . The colors and symbols of the heart shield were not only used by the province of North Rhine-Westphalia , but also by the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in its state coat of arms designed in 1947 .
literature
- Georg Mölich, Veit Veltzke, Bernd Walter : Rhineland, Westphalia and Prussia - a relationship story . Aschendorff-Verlag, Münster 2011, ISBN 978-3-402-12793-3 .
- Horst Romeyk : The leading state and municipal administrative officials of the Rhine Province 1816–1945 (= publications of the Society for Rhenish History . Volume 69 ). Droste, Düsseldorf 1994, ISBN 3-7700-7585-4 , p. 279 .
Individual evidence
- ^ The coat of arms of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia . In: North Rhine-Westphalia yearbook . 11th year (2010), Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-598-23960-1 ( Google Books )