Hessen-Nassau
| flag | coat of arms |
|---|---|

|

|
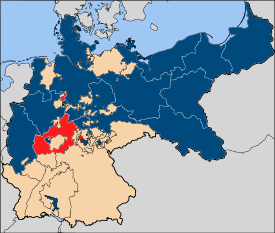
| Situation in Prussia | |
|
|
| Consist | 1868-1944 |
| Provincial capital | kassel |
| surface | 15,703 km² (1925) 16,847 km² (1939) |
| Residents | 2,675,111 (1939) |
| Population density | 159 inhabitants / km² (1939) |
| Religions | 988 041 Ev. 371 736 Roman Catholic 36 390 Jews 4 201 others (1871) |
| administration | 2 administrative districts |
| License Plate | IT |
| Arose from |
Electorate of Hesse, Duchy of Nassau, Free City of Frankfurt , Grand Duchy of Hesse (Homburg, Biedenkopf, Vöhl), Bavaria (Gersfeld, Orb), from 1929 Waldeck |
| Incorporated into | Province of Kurhessen , Province of Nassau |
| Today part of | predominantly Hesse , also Rhineland-Palatinate (Montabaur), Thuringia (Schmalkalden) and Lower Saxony (Rinteln) |
| map | |

|
|
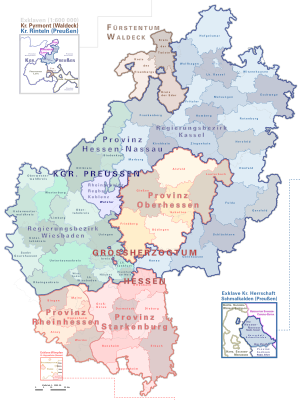
The Prussian province of Hessen-Nassau emerged in 1868 from the states of Kurhessen and Nassau annexed by Prussia in 1866 , the former Hessen-Homburg and the Biedenkopf ( Hessian hinterland ) and Vöhl districts of the Grand Duchy of Hesse, the Free City of Frankfurt and the Bavarian districts of Gersfeld and Orb . It comprised the northern and central part of today's State of Hesse , in which Upper Hesse, a province of the Grand Duchy of Hesse (Hesse-Darmstadt), was embedded as an enclave . Furthermore, parts of what is now Rhineland-Palatinate , Lower Saxony and Thuringia belonged to Hessen-Nassau . The province existed until 1944. The largest cities were Frankfurt am Main , the provincial capital Kassel and Wiesbaden .
Establishment of the Province
After the German War in 1866, the Electorate of Hesse (residential city of Cassel), the Duchy of Nassau (residential city of Wiesbaden), the Free City of Frankfurt and the Bavarian offices of Gersfeld and Orb came under Prussian rule. Furthermore, the Grand Duchy of Hesse had to cede the Biedenkopf district , the so-called Hessian hinterland , the Vöhl district and the recently acquired Landgraviate Hessen-Homburg to Prussia through the peace treaty of September 3, 1866 with Prussia ; However, it received the previously Kurhessische Bad Nauheim .
Since the former Free Imperial City of Wetzlar, located in the middle of Hesse, had already become Prussian in 1815 and the district seat of the newly created Prussian district of Wetzlar in 1822 , it remained in the administrative district of Koblenz of the Rhine province . It was not until October 1, 1932, that the city and district of Wetzlar were incorporated into the Wiesbaden administrative district of the Hesse-Nassau province.
The new Prussian areas were initially united in the administrative districts of Kassel and Wiesbaden under a provisional Prussian high presidium in Kassel. On December 7, 1868, the new Prussian province of Hessen-Nassau emerged from this . As usual in Prussia, it was divided into circles; only where a city was excluded from the district because of its size (at least 25,000 souls / inhabitant), there was an urban district and a rural district .
insignia
The colors of the flag of the province were, from top to bottom, red-white-blue, identical to the flag of the Netherlands . The Duchy of Nassau is the home of the royal family of the Netherlands .
The coat of arms is divided into three parts and shows the coats of arms of the three annexed states: on the right (seen from the bearer) the crowned, silver-red cross-striped lion of the Electorate of Hesse, on the left a crowned golden lion, like the first in the blue field, for Nassau, in the red tip of the gold-armored silver eagle of the Free City of Frankfurt.
Population development
| year | Residents |
|---|---|
| 1871 | 1,400,370 |
| 1880 | 1,554,376 |
| 1890 | 1,664,426 |
| 1900 | 1,897,981 |
| 1910 | 2,221,021 |
| 1925 | 2,396,871 |
| 1933 | 2,584,828 |
| 1939 | 2,675,111 |
politics
Chief President
The Oberpräsident was the head of administration in a Prussian province. Like the top officials of the administrative districts, the regional presidents , they were appointed by the Prussian state government or by the king. The population of the province had no influence on the election of the senior president.
- 1867–1871: Eduard von Moeller
- 1872–1875: Ludwig von Bodelschwingh
- 1876–1881: August from the end
- 1881–1892: Botho zu Eulenburg , 1892–1894 Prime Minister of Prussia
- 1892–1898: Eduard von Magdeburg
- 1898–1903: Robert von Zedlitz-Trützschler
- 1903–1907: Ludwig von Windheim
- 1907–1917: Wilhelm Hengstenberg
- 1917–1919: August von Trott zu Solz
- 1919–1930: Rudolf Schwander
- 1930–1932: August Haas
- 1932–1933: Ernst von Hülsen
- 1933–1943: Philipp von Hessen
- 1943–1944: Ernst Beckmann
Representatives of the people
The parliament of the province was the provincial parliament of the province Hessen-Nassau from 1886 to 1933 . In addition, at the level of the two administrative districts, there was the Nassau Municipal Parliament (Wiesbaden Municipal Parliament) from 1866 to 1933 and the Hessian Municipal Parliament ( Kassel Municipal Parliament) from 1868 to 1933 .
Cities
By far the largest city in the province was the former federal city of Frankfurt am Main. Although most of the other larger cities were also located in the densely populated, trade and industrial Rhine-Main area in the south of the province, Hessen-Nassau was governed from Kassel in the north of the province. The following table contains all cities in the province that had more than 10,000 inhabitants, with their population figures from 1871, 1910 and 1939:
| city | 1871 | 1910 | 1939 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frankfurt | 91.040 | 414,576 | 548.220 |
| kassel | 46,378 | 153.196 | 211,624 |
| Wiesbaden | 35,450 | 109.002 | 165,646 |
| Hanau | 20,294 | 37,472 | 40,260 |
| Fulda | 9,470 | 22,487 | 31,645 |
| Marburg | 8,950 | 21,860 | 28,439 |
| Wetzlar | - | - | 19,327 |
| Bad Homburg vor der Höhe | 8,626 | 14,334 | 18,541 |
| Eschwege | 7,371 | 12,542 | 15,462 |
| Hersfeld | 6,438 | 9,612 | 14,095 |
| Limburg on the Lahn | 4,794 | 10,965 | 11,772 |
| Oberursel | 3,484 | 7,083 | 11,481 |
| Schmalkalden | 5,790 | 10,018 | 10,661 |
| Biebrich | 6,644 | 21.199 | - |
| High on the Main | 3.133 | 17,240 | - |
| Griesheim am Main 1 | 1,605 | 11,514 | - |
Administrative division of the province of Hessen-Nassau
The province was divided into two administrative districts based on the borders of the states occupied in 1866 . The administrative district of Wiesbaden comprised the previous area of Nassau, Frankfurt and the Hessian hinterland ( Biedenkopf district ) belonging to the Grand Duchy of Hesse . The administrative district of Kassel continued the territory of the Electorate of Hesse and the districts of Gersfeld and Vöhl; In 1929 the Free State of Waldeck was added.
Kassel administrative district
| District of Kassel | |
|---|---|
|
City districts 1867–1927 |
City districts 1927–1944 |
|
Circles 1867-1932 |
Counties / districts 1932 / 1939–1944
|
Wiesbaden administrative district
Administrative reforms
On March 31, 1886, the districts in the Wiesbaden administrative district were fundamentally reorganized. The Mainkreis was divided into the new districts of Wiesbaden and Höchst . In addition, the new districts of Limburg , Sankt Goarshausen , Usingen and Westerburg and a new district of Frankfurt were formed. On the same day, the city of Hanau became a district in the Cassel administrative district.
The district of Frankfurt was dissolved on April 1, 1910, when all the communities in the district were incorporated into Frankfurt am Main. The city, district and administrative district of Cassel have had their names with "K" at the beginning since December 4, 1926.
On April 1, 1927, the city of Fulda became a district. On April 1, 1928, the urban districts of Wiesbaden and Frankfurt am Main expanded through incorporations, including the large cities of Höchst am Main and Biebrich . The new Main-Taunus-Kreis emerged from the remnants of the districts of Höchst am Main and Wiesbaden . Höchst, now a district of Frankfurt, remained the administrative seat of the new district until 1987. Following a referendum on April 1, 1929, the Free State of Waldeck was incorporated into the Free State of Prussia and assigned to the Kassel administrative district. At the same time the city of Marburg became a district.
On October 1, 1932, the Wetzlar district moved from the Rhine province , Koblenz district , to the Hesse-Nassau province and Wiesbaden district , while the Schaumburg district , the former Rinteln district , from the Hesse-Nassau province, Kassel district , to the province Hanover and the administrative district of Hanover was incorporated. Thus two isolated districts ( exclaves ) were incorporated into the surrounding provinces. Due to the requirements in the savings regulations of the Reich President , the districts of Biedenkopf , Gersfeld , Homberg , Kirchhain , Westerburg and Usingen were dissolved and merged with neighboring districts. The districts of Biedenkopf and Usingen were restored to a smaller extent in 1933.
On February 1, 1942, the former Waldeck districts of Eder , Eisenberg and Twiste formed the new Waldeck district with its headquarters in Korbach .
On July 1, 1944, the province of Hessen- Nassau was divided into the new provinces of Kurhessen and Nassau on the basis of the Reich defense districts and the Gaue of the NSDAP . The district of Herrschaft Schmalkalden changed from the province of Kurhessen to the administrative district of Erfurt in the province of Saxony and the urban district of Hanau and the districts of Hanau , Gelnhausen and Schlüchtern to the new province of Nassau.
The Reichsstatthalter and Gauleiter of the NSDAP, Jakob Sprenger in Darmstadt, was appointed as the Oberpräsident in Wiesbaden for the province of Nassau . The Gau Hessen-Nassau , however, still included Frankfurt, Nassau and Hessen-Darmstadt. The district of Kassel formed the Gau Kurhessen .
Gauleiter Karl Gerland in Kassel was entrusted with the deputizing for the Oberpräsident in Kassel for the province of Kurhessen .
Most of the province of Hessen-Nassau became part of the American occupation zone in 1945 . However, the western part of the administrative district of Wiesbaden fell under the French occupation zone , namely the Oberwesterwaldkreis , the Unterwesterwaldkreis , the Unterlahnkreis and the Sankt Goarshausen district .
The American-occupied parts of the country were united on September 19, 1945 with the main part of the People's State of Hesse on the right bank of the Rhine to form " Greater Hesse ", which was renamed Hesse on December 1, 1946 after the new constitution was adopted. Within the new state of Hesse, the two administrative districts of Kassel and Wiesbaden initially continued to exist , as well as the administrative district of Darmstadt , which included the part of the "People's State of Hesse" on the right bank of the Rhine.
The French occupying power united the northern part of their territory, including the aforementioned Nassau districts, to form the state of Rhineland-Palatinate . There, this area formed the administrative district of Montabaur , which became part of the administrative district of Koblenz in 1968 .
The exclave Schmalkalden was already since 1944 by the annexation to the administrative district of Erfurt in Thuringia Reichsstatthalter Fritz Sauckel assumed and in 1945 finally part of the country Thuringia .
Others
The Catholic student union K. D. St. V. Hasso-Nassovia Frankfurt am Main and the Corps Hasso-Nassovia are named after the province . Their student coats of arms contain the lions of Hessen-Nassaus and Kurhessen . In 1913 the aforementioned connection borrowed its color from the Kurhessian colors.
The fire brigades in the Nassau area joined forces on July 27, 1872 in Wiesbaden to form the fire brigade association for the Wiesbaden administrative region, which continues to operate as the Hessian district fire brigade association under the name Nassau Fire Brigade Association.
The town of Hessisch Oldendorf is located in the Hameln-Pyrmont district in Lower Saxony . The name addition, which appears anachronistic today, is explained by the fact that it belongs to the former Grafschaft Schaumburg district , which was once an exclave of the Electorate of Hesse and then, until 1932, of the Province of Hesse-Nassau.
See also
With the name of this church, however, it should be noted that it does not cover the area of the former province of Hesse-Nassau, as the term Hesse in the name of the church does not stand for the former Electorate of Hesse , but for the former Grand Duchy of Hesse .
Further articles
- Predecessor states: Electorate of Hesse , Duchy of Nassau , Free City of Frankfurt , Waldeck
- Successor lands: Greater Hessen , Hessen , Rhineland-Palatinate
- The non-Prussian part of Hesse: Grand Duchy of Hesse , People's State of Hesse
- History of Hesse
literature
- Karl Müller: Prussian Eagle and Hessian Lion - One Hundred Years of Wiesbaden Government 1866–1966 . Wiesbaden 1966.
- O. Witte: 80 years of the municipal association of the Wiesbaden administrative district . Ed .: O. Witte [governor]. Wiesbaden 1948.
Web links
- Province of Hessen-Nassau on deutsche-schutzgebiete.de
- Province of Hesse-Nassau (counties and municipalities) 1910
- Holdings in the Hessian Main State Archive
Individual evidence
- ↑ Section 4 (1) of the district regulations for the province of Hessen-Nassau from June 7, 1885
- ^ A b Michael Rademacher: German administrative history from the unification of the empire in 1871 to the reunification in 1990. p_hessen.html. (Online material for the dissertation, Osnabrück 2006).
- ^ The municipalities and manor districts of the Hesse-Nassau province and their population in 1871
- ^ Municipal directory Germany 1900 - Kingdom of Prussia - Province of Hessen-Nassau
- ^ District regulation for the province of Hesse-Nassau from June 7, 1885 (digitized version)
- ↑ "Leader's Decree on the Formation of the Provinces of Kurhessen and Nassau" of April 1, 1944, RGBl. I 1944, pp. 109–111 , with effect from July 1, 1944.
- ^ Franz-Josef Sehr : The foundation of the Nassau fire brigade association . In: Yearbook for the Limburg-Weilburg district 2012 . The district committee of the district of Limburg-Weilburg, Limburg / Weilburg 2011, ISBN 3-927006-48-3 , p. 65-67 .