kassel
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 19 ′ N , 9 ° 30 ′ E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Hesse | |
| Administrative region : | kassel | |
| Height : | 167 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 106.78 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 202,137 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 1893 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postcodes : | 34117-34134, 34355 | |
| Primaries : | 0561, 05543 | |
| License plate : | KS | |
| Community key : | 06 6 11 000 | |
| LOCODE : | DE KAS | |
| NUTS : | DE731 | |
| City structure: | 23 districts | |
City administration address : |
Obere Königsstrasse 8 34117 Kassel |
|
| Website : | ||
| Lord Mayor : | Christian Geselle ( SPD ) | |
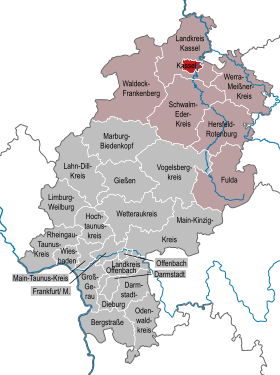
| Location of the city of Kassel in Hesse | ||
Kassel (until 1926 officially Cassel ) is an independent city , the administrative seat of the administrative district of the same name and the district of Kassel . The only major city in North Hesse is the third largest city after Frankfurt am Main and Wiesbaden and one of ten regional centers in the State of Hesse . According to the Hessian State Statistical Office, Kassel had 202,137 inhabitants on December 31, 2019. The city states 205,076 inhabitants for December 2018.
From 1277 Kassel was the capital of the Landgraviate of Hesse , the Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (from 1567 to 1803) and the Electorate of Hesse (until 1866). To date, evidence residences and palaces of them, particularly the Orangerie in the Karlsaue and the Wilhelmshöhe Castle in 2013 and the World Heritage Site of UNESCO counting Mountain Park . With the documenta , the city also hosts a globally important exhibition of contemporary art every five years ; therefore, since March 1999, Kassel has had the additional official title of documenta city . With the establishment of the first comprehensive university in Germany (today's University of Kassel ), Kassel became a university town in 1971.
geography
location
Kassel is located about 70 kilometers northwest of the geographic center of Germany . After Erfurt and Göttingen (each around 50 kilometers from the center) Kassel is the third closest major city to the geographical center of Germany.
The city is located in northern Hesse near the borders with Lower Saxony and Thuringia in the Kassel Basin , which is not a basin in the geomorphological sense , but a vast basin in which there is an extensive valley of the Fulda , especially in the area of the Karls- and Fuldaaue . The Kassel Basin is part of the West Hessian Depression , which in turn is part of the Mediterranean-Mjosen Zone .
In this basin, the city is surrounded by the somewhat distant Langenberge in the southwest and the Hohen Habichtswald in the west (each part of the Habichtswälder Bergland ) as well as the southern foothills of the Reinhardswald (part of the Weserbergland ) in the northeast, the Kaufunger Wald in the east and the Söhre framed in the southeast and south (both parts of the Fulda-Werra-Bergland ). These five low mountain ranges are connected by two ridges north and south of the city and running in a west-east direction, so that the Kassel basin - apart from the Fulda river valley, which cuts through it from south to north - is surrounded by mountain ranges.
In the city of Kassel trench with rocks of the forming shell limestone by inverted relief a striking ridge ( Weinberg ).
Since the Habichtswälder Bergland and the West Hessian Depression belong to the West Hessian Uplands , the Weser Uplands to the Lower Saxon Uplands and the Fulda-Werra Uplands to the East Hessian Uplands , the city is located at the immediate interface of three main groups of natural areas.
The nearest large cities are - measured as the crow flies / road - Hanover (approx. 120/164 km north) and Göttingen (approx. 40/55 km northeast) in Lower Saxony , Erfurt (approx. 115/185 km east) in Thuringia , Frankfurt am Main (approx. 150/193 km south) in Hesse and Siegen (approx. 115/165 km southwest), Hamm (approx. 122/153 km west), Dortmund (approx. 145/165 km west) and Paderborn (approx. 70/84 km northwest of Kassel) in North Rhine-Westphalia .
Kassel is traversed by the Fulda and the tributaries and brooks that flow into this river partly within the urban area , including Ahne , Drusel (called "Kleine Fulda" in the lower reaches ), Geile (called Döll in the lower reaches), Grunnelbach , Haargraben , Jungfernbach , Losse , Nieste and Wahle .
Kassel's deepest point is in the northeastern Fulda valley at 132.9 m above sea level. NHN (river level slightly north of the Graue Katzen restaurant ); If you also consider the exclave Kragenhof in this valley, the deepest point of the city is a few meters below the barrage on the city limits of Fuldatal - Wahnhausen at a height of only 131.4 m . The city is located on King Square 163 m and the town hall 169 m high. The Wilhelmshöhe Castle stands at about 282 m height, the Hercules to around 515 m and the highest point of the urban area is located on the border with the municipality Schauenburg with 614.8 m on the top of the High Habichtswald belonging Tall Grass , the highest mountain of the Hawk forests of mountainous regions . The inner city area has a distinctive hillside location and extends from approx. 140 m (Karlsaue) over the Wilhelmshöhe train station (approx. 195 m ) to approx. 300 m at the upper edge of Bad Wilhelmshöhe.
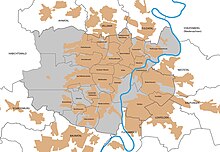
City structure
The urban area of Kassel is divided into 23 local districts, each of which has a local council with a local mayor as chairman. The local councils are elected every five years by the population of the local districts. The local advisory board can be heard on all important issues affecting the local district. However, the final decision on a measure rests with the Kassel city council.
In addition to the historically grown districts, some formerly independent communities and districts have been incorporated into Kassel. The boundaries of these districts partly do not coincide with the boundaries of the 23 local districts. The year of incorporation can be found in brackets.
Overview of the 23 districts (districts) of Kassel:
| Local office / district |
Residents (main residence) (31 Dec 2011) |
Area in km² |
Density in population / km² |
Districts / districts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| center | 7,835 | 1.94 | 4.018 | Terrace (vineyard), Oberneustadt , Schöne Aussicht, Entenanger, Bahnhofsviertel (Lutherplatz) |
| Südstadt | 7.123 | 3.61 | 1,990 | Auefeld, Karlsaue |
| Front west | 15,546 | 1.94 | 8.097 | Fir groves, Samuel Beckett enclosure, Goethe enclosure |
| Wehlheiden (1899) | 13,621 | 2.88 | 4,665 | Park Schönfeld |
| Bad Wilhelmshöhe | 11,964 | 15.22 | 783 | Wilhelmshöhe (1906), Mulang , Wahlershausen (1906), Marbachshöhe, Neuholland |
| Brasselsberg | 4,005 | 7.89 | 508 | - |
| Süsterfeld-Helleböhn | 5,773 | 2.18 | 2,566 | documenta urbana , Süsterfeld, Holzgarten |
| Harleshausen (1936) | 12,744 | 14.19 | 899 | Garden City Harleshausen, To the field camp, In the floodplain |
| Kirchditmold (1906) | 10,507 | 3.60 | 2,919 | Hessenschanze |
| Rothenditmold (1906) | 6,578 | 2.77 | 2,383 | Rothenberg, midfield |
| North Holland | 14,461 | 3.52 | 4,108 | Schillerviertel , Friedrich-Wöhler-Siedlung, Hegelsberg, Campus HoPla |
| Philippinenhof-Warteberg | 4,070 | 1.19 | 3,392 | Am Sandkopf, Von-Trott-zu-Solz-Siedlung |
| Fasanenhof (1926) | 8,536 | 2.17 | 3,952 | Iron forge, Bossental |
| Wesertor | 9,202 | 1.56 | 5,937 | Horse market, Finkenherd |
| Wolfsanger hare hedge | 6,806 | 7.38 | 923 | Wolfsanger (1936), Kragenhof |
| Bettenhausen (1906) | 8,277 | 6.21 | 1,457 | Eichwald, Salzmannshausen, AEG-Wohnstrasse |
| Forest field | 6,767 | 1.66 | 3,580 | Am Lindenberg, Heinrich-Steul-Strasse |
| Waldau (1936) | 6,477 | 6.48 | 998 | Industrial park, Fuldaaue , Alt-Waldau |
| Niederzwehren (1936) | 11,255 | 8.26 | 1,373 | Märchenviertel, Graf-Haeseler-Kaserne, Neue Mühle |
| Oberzwehren (1936) | 12,752 | 3.39 | 3,718 | Brückenhof, Keilsbergsiedlung, Mattenbergsiedlung |
| Nordshausen (1936) | 2,040 | 2.44 | 836 | - |
| Maiden head | 3,802 | 1.8 | 2.112 | Osterberg |
| Untereustadt | 3,968 | 2.51 | 1,402 | Blücherviertel, Hafenstrasse |
| Kebabs | 0 | 1.73 | 0 | - |
| (Matching / not assignable) | - | 1.93 | - | - |
| total | 194.109 | 106.798 | 1,818 | - |
Within the Kassel districts there are still settlements with their own names, such as Mulang, Marbachshöhe and Wahlershausen , which belong to the Bad Wilhelmshöhe district , the exclave Kragenhof , which belongs to the Wolfsanger- Hasenhecke district, Osterberg, which belongs to the Jungfernkopf district, or that that Blucher district local district Unterneustadt belongs. The Dönche , which is located as an undeveloped nature reserve in the southwest of Kassel , does not count as a district, but as a district-free area .
Land use
The area of the city of Kassel is 106.798 km². The space usage in percent (%) is distributed as follows:
| Land use in% | 1999 | 2003 | 2009 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings and open spaces | 34.4 | 34.5 | 34.95 | 34.96 |
| Forest areas | 21.6 | 21.6 | 21.6 | 21.6 |
| Agriculture | 17.3 | 17.0 | 15.96 | 15.89 |
| traffic | 12.8 | 13.0 | 12.92 | 12.92 |
| recreation | 9.6 | 10.0 | 10.56 | 10.6 |
| water | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.10 | 2.11 |
| other use | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| Operating area | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.44 | 0.44 |
Neighboring communities
The following cities and municipalities border the city of Kassel ( starting clockwise in the north): Ahnatal , Vellmar , Fuldatal , Staufenberg , Niestetal , Kaufungen , Lohfelden , Fuldabrück , Baunatal , Schauenburg , Habichtswald . Of these, Vellmar and Fuldatal in the north, Kaufungen in the east, Lohfelden in the southeast and Baunatal in the south are growing ever closer to the urban area. With the exception of Staufenberg, which is part of the Göttingen district in Lower Saxony, all communities belong to the Kassel district . The communities cooperate in the Kassel area association .
climate
The climate in Kassel is much milder and warmer than in the surrounding low mountain range. Because of the valley basin and the higher forest areas, the city is well protected from storms. Due to the accumulating air masses, it is sometimes 3 to 5 degrees Celsius warmer in the lower urban areas than in the surrounding areas, especially in summer. The annual mean temperature is approx. 9.1 ° C.
In the outskirts of the west of Kassel, natural aisles have been built in recent years , which serve the microclimatic circulation and natural ventilation of the city. New commercial buildings in neighboring communities, such as on the Rüsterberg in Niestetal (Gut Ellenbach), also favor heating. Similar dangers emanate from a possible development on the Long Field in Niederzwehren . The Fulda as a water area with floodplains and floodplains as well as tributaries within the urban catchment area also forms a sensitive starting point for dealing with sustainable nature conservation and sustainable development. Renaturation approaches , such as the Loss delta , which is used to protect birds and the artificial river delta of the Losse , are projects of transitory development within the framework of the implementation of EU guidelines. At the University of Kassel , extensive studies are being carried out and evaluated as part of the KLIMES research project.
| kassel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Kassel
Source: DWD, data: 1971–2000;
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
history
name of the city
The first mention of the royal court Chass a lla (or Chass e lla ; it later became Cassel and since 1927 Kassel) can be found on two documents from February 18, 913 that have survived to this day. At that time, King Konrad I stayed in the fortified area the Fulda royal court. But neither the content of the documents nor the persons named in them are related to today's city.
There have been different explanations for the name Kassel for around 400 years; The derivation from the Latin word castellum / castella is particularly popular. According to the most recent name research , the name can also be understood as a compound of Germanic-German origin, consisting of kas- "Mulde, recess" and -sella, a derivation from sali / seli, "building". The original meaning of the name Kassel would then have to be translated as "building in or on a hollow in the terrain". The name could therefore go back a long way in the prehistory of the city.
First traces of settlement and founding of the city
Kassel was first mentioned in writing in 913. During excavations in the area of the Altmarkt, however, older finds were found that were archaeologically secured during the preparatory work for the financial center (FIZ), which was completed at the end of 2008. These made it clear that there must have been pre-Christian settlements in the area of the lowlands on today's Schlagd.
The documentary mention, however, is the first written evidence for the existence of Kassel and thus the proof that the city can look back on a development of more than a thousand years. At first, however, one could not speak of a city. Rather, there was a fortification in the place of today's regional council, under whose protection a settlement developed over the next centuries, the small size of which can still be seen today on the street “Graben”. The former Franconian royal court was built around 1150 as the residence of the Counts of the Franconian Hessengau , d. H. the county of Maden or Gudensberg , expanded.
Between 1140 and 1148 Heinrich Raspe and his mother Hedwig von Gudensberg founded the Premonstratensian monastery on the Ahnaberg on the northern edge of the former settlement, the Ahnaberg Monastery . The courtyard, monastery and settlement were soon walled, and Kassel was granted city rights before 1189 . Although the associated hand-held festival was lost, the rights of council officials and citizens of Kassel documented in it were confirmed in 1239 by Landgrave Hermann the Younger of Thuringia .
middle Ages
In 1189 Kassel was first attested as a city in today's sense. After the end of the Ludowingian era, the Brabant line of Duchess Sophie initially gained independence from the Wettins in Saxony and thus strengthened the close ties between the Landgrave of Hesse and Holland.
In 1239, Landgrave Hermann II the Younger of Thuringia renewed some city rights, and in 1277 Cassel became the main residence of the first Hessian Landgrave Heinrich I of the newly created Landgraviate of Hesse .
16th to 18th century
At the beginning of the 16th century, Landgrave Philipp developed into an important protagonist of the Reformation . Landgrave Karl had a decisive influence on the cityscape from 1700 on with his ambitious baroque building projects such as the Karlsaue or the Hercules . During the Seven Years' War the Prussian-British allies , which also included Hessen-Kassel, and the French fought for the city on the side of the Habsburg Maria Theresa . The exhibition Kassel was founded 1763rd
The Oberneustadt is based on plans by the court architect Simon Louis du Ry , who redesigned Kassel into a residential city and laid out Friedrichsplatz and Königsplatz , administrative and cultural buildings as well as classicist commercial buildings were also built.
Shortly after the Landgrave of Hessen-Kassel became elector in 1803, Napoleonic troops occupied the city in 1806 and made Kassel the capital of the newly founded Kingdom of Westphalia and residence of Napoleon's brother Jérôme until 1813 .
City map of Kassel by Matthäus Merian , 1648
Cassel, city view from the Topographia Hassiae by Merian , 1655
Unveiling of the monument to Landgrave Friedrich II, painting by JH Tischbein the Elder , 1783
19th century to World War II
In the early 19th century, a circle of romantics formed in Kassel with people like Achim von Arnim , Clemens Brentano and the Brothers Grimm . Chemists such as Friedrich Wöhler and Robert Bunsen and the physicist Rudolf Kohlrausch worked at the Kassel Polytechnic , and industrialization turned Kassel from a royal seat into an important industrial location. After the German War of 1866, Kurhessen lost its independence and was annexed by Prussia together with the Kingdom of Hanover . From then on, the emperor's family spent the summer months in Kassel. By the turn of the century, spacious residential areas were built, and the 100,000 population mark in the city center was soon exceeded, and incorporations followed. Between 1920 and 1925, Philipp Scheidemann was Lord Mayor of Kassel.
The 9th German Fire Brigade Day took place in Kassel from July 11-14, 1874 .
General staff plan for the region around Cassel before the start of industrialization , 1835
Fulda Bridge in the center of Kassel, photochromic print around 1900
Untereustadt 1895
View from the beautiful view of the Kaufunger Wald (Bellevue), Louis Kolitz around 1900
In addition to the “Reich Warrior Day”, which was held in Kassel in 1933, the city played the role of a “Nazi armory” under the rule of the NSDAP . There are many traces of this in the past and present of the city, such as B. the former production sites for tanks (today Rheinmetall Landsysteme GmbH ), Wehrmacht trucks (today Mercedes-Benz factory in Kassel ) and aircraft engines (today Volkswagen factory in Kassel ).
Members of the SA and SS began to devastate the Kassel synagogue and other Jewish facilities in Kassel on the evening of November 7, 1938 . They appeared in civilian clothes to mime “popular anger” two days before November 9, the pogroms of which were to go down in German history as the November pogroms . Since the early 1930s, the city could largely be considered " synchronized ". The resistance was limited to a few anti-fascist groups. After the pogroms of the Reichskristallnacht, Jews from Kassel were deported from the main train station .
In the course of the Second World War , several air raids on Kassel destroyed large parts of the previously very important old town and the other urban developments, and claimed many lives. The city experienced the worst attack on October 22nd, 1943. That night over 10,000 people died and 80% of the houses were destroyed. Because Kassel was a city with many half-timbered houses, especially in the old town, it became the perfect target for fire bombing attacks according to the " Area Bombing Directive ". The targeted mass drop of phosphorus and stick incendiary bombs caused a firestorm, for example in Dresden , Hamburg , Pforzheim , Würzburg or Darmstadt , as a result of the wood set on fire .
At the beginning of April 1945, Kassel was occupied by US troops. Elsewhere in Germany, the war continued until the beginning of May. It finally ended on May 8th with the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht .
Post-war period until German unification
Kassel was in the American zone of occupation . Alongside Bonn , Frankfurt am Main and Stuttgart, it applied to be the new capital of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949 . One of the main reasons against the city as the seat of government , which the commission formed specifically to examine the four applicants cited in its final report for the Parliamentary Council , was its exposed location near the then inner-German border . Kassel became the seat of the Federal Labor Court as well as the Federal Social Court in 1953 . The city had to cede the former to Erfurt in 1999.
The Schlagd in Kassel. Reconstruction ensemble by Paul Bode , 1953
The reconstruction of the city was carried out according to plans from the Nazi era and according to the concept of the " car-friendly city ". Among other things, a road ring was created around the city center with the inner city ring. Horse market and Entenanger were rebuilt. With the staircase street, which opened on November 9, 1953 , the first pedestrian zone in the Federal Republic of Germany was created. There were also numerous underpasses, including one from stairs street to the main train station, in which the subway station Hauptbahnhof of the Kassel tram was. In 1961 Kassel was the first city in Germany to introduce the parking disc .
When accompanying the Federal Garden Show in 1955 was of Arnold Bode , the documenta 1 initiated which has become the world's most important contemporary art ever since. Between 1980 and 1982, under the name documenta urbana , a settlement was built in the southwest of Kassel for demonstration and exhibition purposes. The so-called Kassel School set new impulses in the graphic design of the young Federal Republic and stood in the tradition of the New Frankfurt .
Since 1990
Between May 29 and June 1, 1991, the new Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe train station was inaugurated. It was the first train station in Germany in decades whose design had been selected from an architectural competition, and the first to be planned as an ICE train station. The documenta hall was inaugurated in 1992 . The RegioTram Kassel light rail concept was implemented in 1995 .
From the 1990s, the Untereustadt , which had not been rebuilt after its destruction in the Second World War, was rebuilt.
Since 2013, the Mountain Park World Heritage Site is one of UNESCO .
Incorporations

Formerly independent communities and districts that were incorporated into Kassel:
| year | places | Increase in ha |
|---|---|---|
| April 1, 1899 | Wehlheiden | 372 |
| April 1, 1906 | Wahlershausen , Kirchditmold , Rothenditmold , Bettenhausen | 1770 |
| January 4, 1926 | Fasanenhof Manor District ( Fasanenhof) | 142 |
| November 15, 1928 |
Gutsgebiet Oberförsterei Kirchditmold , Wilhelmshöhe , Kragenhof , Oberförsterei Ehlen |
2968 |
| 1936 |
Waldau , Niederzwehren , Oberzwehren , Nordshausen , Harleshausen , Wolfsanger |
2483 |
While many other large German cities were able to increase their population through the redefinition of the communal borders, there were no incorporations into the city of Kassel as part of the regional reform in Hesse in the 1970s, so an incorporation of Lohfelden failed due to the resistance of the local community. The Kassel city area has the borders of 1936 to this day, so that the course of the population is based on the same area.
The independent neighboring communities benefited from the location, not least because its settlement and commercial areas are seamlessly transferred to Kassel. As compensation, Lohfelden had to cede municipalities in the industrial area in 1975, and the city of Kassel in turn enabled the community to jointly develop the border area.
Population development
At the beginning of the 19th century, Kassel had around 20,000 inhabitants. This number had quadrupled through industrialization by 1895. In 1899 the population of the city exceeded the limit of 100,000 inhabitants, making what was then Cassel a big city . By 1943 it had risen to 225,694, which is the historic high in Kassel. After a war-related decline and an increase in the number of inhabitants in the outer districts of the city, the number of main residents exceeded the 200,000 mark several times from 1961. This mark was reached again in December 2015, with a population increase of almost 6,000 compared to December 2014.
Foreigners
Approx. 31,811 foreigners live in Kassel (automated register of the city of Kassel, as of December 31, 2015). The proportion of all foreigners in the total population is 12.5% and is thus above the average in Germany of around eight percent. However, since foreign citizens generally live much more frequently in large cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants than German citizens (47% to 29% of the respective population group), the proportion of foreigners in cities of this size (around 15% in western Germany) is below average.
The distribution across the city is very different. The proportion of foreigners in Jungfernkopf is 5.4% and in Nordstadt 39.1%.
life quality
In a ranking commissioned by Wirtschaftswoche and the New Social Market Economy initiative , Kassel came first in a so-called “dynamic ranking ” of the 50 largest German cities in 2011. The decisive factors were the increase in the number of employees subject to social security contributions, the decrease in the unemployment rate and the increase in the average disposable income in Kassel. The study was based on 91 indicators, including those from the national accounts, data from the Federal Statistical Office and the Federal Employment Agency. Kassel took third place in the quality of life category. Decisive were indicators such as the accessibility of motorways, the density of doctors, the childcare rate and the number of recreational areas.
Religion and churches
Denomination statistics
According to the 2011 census, members of religious communities outside the major Christian churches predominate in the Rhine-Main conurbation and Kassel. According to the results of the census on May 9, 2011 , 15.0% of the residents were Catholic, 42.1% Protestant and 42.9% were assigned to the categories "Other" or "Not belonging to any Austrian religious community". According to a calculation from the census figures for people with a migration background, the proportion of Muslims in Kassel in 2011 was 9.4% (around 17,900 people). In mid-2019, the number of Protestant church members was around 70,000, which corresponds to around 35% of the population. At the end of July 2014, the number of Protestant church members in Kassel was around 79,000 (around 40%); at the same time there were 32,000 (around 16%) Catholics. According to church statistics (as of 2020) not even half of the population belong to a church.
history

Before the Reformation, Kassel belonged to the Archdiocese of Mainz . In 1526, Landgrave Philipp initiated the Reformation in Hesse. At the beginning of the 17th century, the Landgrave of Hessen-Kassel, Moritz the Scholar, enacted the Reformed Confession. In 1907, following sermons by the evangelist Heinrich Dallmeyer, there was a revival movement (see the Berlin Declaration and the Kassel Declaration ). The church, later named "Evangelical Church in Hessen-Kassel", merged with the Evangelical Church in Waldeck to form the Evangelical Church of Kurhessen-Waldeck . Within this regional church, the parishes of Kassel - if they do not belong to a free church - belong to the parishes of Kassel-Mitte, Kassel-East and Kassel-West (from January 1, 2005: Stadtkirchenkreis Kassel) of the Kassel district. The new apostolic congregation Cassel was founded on February 1, 1900. The New Apostolic Church in the church district of Kassel currently comprises five urban parishes and ten parishes in the region with a total of over 2,000 members. An evangelical free church congregation ( Baptists ) has existed in Kassel since 1847. Today, three Baptist congregations with a total of 550 baptized members are active in the Kassel city area. They belong to the Evangelical Free Church Association Hesse-Siegerland. The Free Evangelical Congregation has existed in Kassel since 1910. The original community is based in Wilhelmshöhe on Kurhausstrasse. In 2000 a second was added in Sandershäuser Strasse in Bettenhausen. Both belong to the Federation of Free Protestant Congregations in Germany . In 1873 the Evangelical Lutheran St. Michaelis Congregation was founded.
After all the Catholic parishes in Kassel dissolved due to the Reformation , there have been Roman Catholic parishioners again in Kassel since 1731. From 1776, church services were allowed again, especially since the then Landgrave Friedrich II himself had become a Roman Catholic. The proportion of Roman Catholics increased thereafter, so that independent parishes soon formed again. These belong to the diocese of Fulda since 1821 . The old Catholic community, which was founded after the Second World War especially for the displaced old Catholics from the Sudetenland (Warnsdorf diocese), has its community center in the front west. There are also some Orthodox parishes in Kassel . Including an Antiochene Orthodox , a Russian Orthodox (congregation in honor of the Holy New Martyrs of Russia) and a Serbian Orthodox congregation.
A large number of small houses of prayer for the Islamic population and the multitude of individual currents have existed since the 1960s. One of the oldest communities is that of the DİTİB City Mosque (Merkez Camii) in the north of the city . It houses a prayer room, a tea room and a garden. A larger new building has been located on the grounds of the Graf-Haeseler barracks in Niederzwehren since 2008 , and in the same year the foundation stone for the Mevlana Mosque Kassel-Mattenberg for around 300 believers in the Mattenberg settlement was laid. With the Mahmud Mosque of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jamaat with minaret and dome, there is another mosque in Kassel.
There is evidence of a Jewish community in Kassel since the Middle Ages . It was an integral part of society for centuries and lasted uninterrupted until the 1930s, when the barbarism of the National Socialists almost ended Jewish life in Kassel as well. The destruction of Jewish religious institutions in the city began on November 7, 1938 by members of the SA and SS in civilian clothes, two days before the pogroms of the Reichskristallnacht . Of 2301 people of the Jewish faith (1933), around 300 people founded the community again after the end of the Nazi dictatorship. Due to strong immigration in the 1990s, the community has grown again to around 1300 community members (as of 2006). Since the year 2000 the new building of the synagogue was completed not far from the location of the old synagogue and inaugurated on May 28, 2000.
In Kassel there is a small community of Tibetan Buddhists as well as Afghan Hindus and Sikhs . There is also a community of Alevis who do not see themselves as an Islamic community. They maintain a house of prayer on the star .
politics


The independent city of Kassel was ruled from 2006 to 2016 by a coalition of the SPD and the Greens . After the local elections in 2016, it was no longer enough for the red-green government to continue. Since then, a coalition of the SPD, the Greens and the FDP has governed.
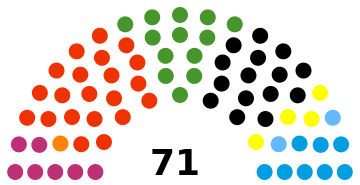
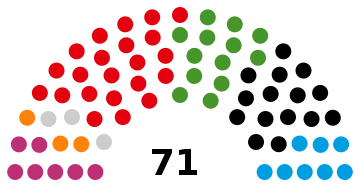
The administrative structure of the city of Kassel is based on the Hessian municipal code . According to this, the city council, as the highest body of local self-government, consists of 71 city council members elected by the city's citizens.
The magistrate, as the executive body, takes care of the day-to-day administration of the city and consists of thirteen honorary and five full-time city councilors, chaired by the mayor . The city of Kassel is divided into 23 local districts, whose citizens each elect a local advisory board. The local advisory board in turn elects a local councilor from among its members.
Historically, the council was at the head of the city of Kassel. The mayors represented the community to the council. The number of mayors ranged from four to eight. They were appointed by the guilds and the rest of the citizenry. The mayors had a seat and vote on the council and oversaw the city's finance and tax system. In the Kingdom of Westphalia , a mayor and a municipal councilor based on the French model were at the head of the city. In 1834 the Hessian municipal code came into force during the Electoral Hesse period . After that, Kassel had a lord mayor and a mayor as leading and executive officials, alongside the city council as co- managing authority.
There is a Bundestag constituency of Kassel , in the case of state elections the city is divided into the constituencies of Kassel-Stadt I and Kassel-Stadt II .
City leaders (selection)
Christian Geselle (SPD) has been Lord Mayor of Kassel since July 22, 2017 . In the election on March 5, 2017, he prevailed against five competitors with 56.6 percent of the vote.
|
|
magistrate
| Office | Surname | Political party | Department |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lord Mayor | Christian journeyman | SPD | I / Treasurer and Taxes |
| Mayoress | Ilona Friedrich | SPD | II / Citizenship and Social Affairs |
| City council | Dirk Stochla | SPD | III / Order, security and traffic |
| Councilor | Susanne Völker | independent | IV / culture |
| Councilor | Anne Janz | Green | V / school |
| City Planning Council | Christof Nolda | Green | VI / urban development, building and the environment |
Voluntary members
City Council
The city council is the highest body of the city and in Kassel consists of city council members who are organized in parliamentary groups. Its composition is determined every five years in local elections by the city's electorate. Whoever has reached the age of 18 and is a German citizen within the meaning of the Basic Law or a citizen of one of the other member states of the European Union may vote. Everyone has to have been registered in the city for at least three months. Free voters and the Pirate Party form a faction. The members of the FDP are non-attached. Two members of the FDP are now independent. Two elected members of the FDP have left the party. A non-party MP has now joined the SPD parliamentary group. So there are currently (as of April 2018) three non-attached MPs. The SPD now has 22 members instead of 21.
The local elections on March 6, 2016 produced the following results, compared to previous local elections:
| Diagram showing the election results and the distribution of seats | |
|---|---|
|
Election of the Kassel City Council 2016
percentage distribution
% 30th 20th 10
0
29.5
20.7
18.0
11.0
10.6
5.6
3.0
1.6
n. k.
Gains and losses
compared to 2011
% p 12 10 8th 6th 4th 2
0
-2 -4 -6 -8th -6.9
-3.5
-6.9
+11.0
+3.9
+3.1
+1.2
-1.1
-0.8
Remarks:
i AUF-Kassel
|
|
Distribution of seats according to parties
Distribution of seats by parliamentary group (as of April 2018)
71 city councilors and the local councils of the 23 urban districts were to be elected for the election period from April 1, 2016 to March 31, 2021.
Election results
| Nominations | 2016 | 2011 | 2006 | 2001 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Share a | Seats | Share a | Seats | Share a | Seats | Share a | Seats | |||||
| Social Democratic Party of Germany | SPD | 29.5 | 21st | 36.4 | 26th | 39.8 | 28 | 36.0 | 26th | |||
| Christian Democratic Union of Germany | CDU | 20.7 | 15th | 24.2 | 17th | 29.1 | 21st | 35.4 | 25th | |||
| Alliance 90 / The Greens | GREEN | 18.0 | 13 | 24.9 | 18th | 15.4 | 11 | 16.8 | 12 | |||
| Alternative for Germany | AfD | 11.0 | 8th | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Kassel Left for Work and Social Justice | KASSELER LINKE | 10.6 | 7th | 6.7 | 5 | 6.8 | 5 | 3.2 | 2 | |||
| Free Democratic Party | FDP | 5.6 | 4th | 2.5 | 2 | 5.5 | 4th | 5.1 | 4th | |||
| FREE VOTERS Kassel District Association | FREE VOTERS | 3.0 | 2 | 1.8 | 1 | 1.8 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Pirate Party Germany | PIRATES | 1.6 | 1 | 2.7 | 2 | - | - | - | - | |||
| UP-Kassel electoral alliance | ON-Kassel | - | - | 0.8 | 0 | 1.7 | 1 | 1.3 | 1 | |||
| Alliance for Kassel - Free Association of Voters and Pensioners Party |
BfK | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.1 | 1 | |||
| total | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | ||||
| Voter turnout in% | 42.8 | 42.4 | 37.1 | 46.2 | ||||||||
coat of arms

Blazon : "In blue a silver sloping bar, accompanied by six (2: 4 placed) and below by seven (4: 3 placed) slanted, silver clover leaves ." The city colors are blue and white.
Symbolism: The shamrocks as city symbols have been detectable as watermarks in paper since the 14th century. The sloping beam, which used to be seen as a wave beam, has also been documented since the 13th century and probably relates to the location on the Fulda. Why there are 13 clovers in particular cannot be clearly proven historically, nor is the significance of the clovers. Some experts are of the opinion that the silver bar symbolizes the Fulda, the six leaf clovers in the upper and seven in the lower part of the coat of arms represent the number of councilors on the respective sides of the river. Another reading that Kassel pupils learned earlier is that the clovers symbolized fishermen's houses on the left and right of the Fulda. Research that has not yet been recognized is based on the assumption that the clover leaves could be an abstract representation of rhombus plants .
A sloping clover leaf as in the coat of arms also appears between the mint master's mark of the Kassel mint master and in the inscription on various Weidenbaumtaler Wilhelm V of Hessen-Kassel.
Town twinning
Kassel has partnerships with the following cities:
Kassel is also a member of the Federation of European Napoleonic Cities .
Finances
Kassel was one of the most heavily indebted cities in Hesse, so the city was one of the three independent cities that, due to their poor financial situation, were entitled to place themselves under the municipal protective umbrella of the State of Hesse. At the end of 2012, a corresponding contract was signed with the state of Hesse in order to achieve partial debt relief for the city. In 2016, Kassel was able to leave the state's rescue package after the city had generated a budget surplus for the third time in a row (due to increased trade tax income).
Economy and Infrastructure


At the beginning of the 19th century industrialization began in the casting industry and, corresponding to the medieval trade routes between Brabant and Silesia, the mechanization of other trades such as the cloth industry. The increase in the number of inhabitants was linked to the connection of the city to the Main-Weser-Bahn railway line and the opening of the train station shortly after the middle of the 19th century and led to an abrupt increase in the area of the old town. The suburbs were urbanized after incorporation in the transition to the 20th century, when the companies were already generating large-scale industrial sales, mostly in the areas of heavy industry, machine and vehicle construction (trucks, locomotives and wagons) and the armaments industry ( tank and aircraft construction, aircraft engines ). Kassel companies such as Henschel & Sohn and the Gerhard-Fieseler-Werke were and are known worldwide ; Wegmann , today Krauss-Maffei Wegmann ( KMW ), the Waggonfabrik Gebrüder Credé and Junkers ( engine construction plant Kassel - later AEG plant ) also produced in the city .
From 1935 onwards there was a large artificial silk production of the Spinnfaser AG (later Vereinigte Glanzstoff-Fabriken until 1984) and the Salzmann & Comp. (until 1971) and Gottschalk & Co. (until 1999).
Kassel was affected by structural change relatively early on, primarily through the takeover of the Henschel Group by ThyssenKrupp in the late 1960s. Areas of Henschel came to other companies such as Daimler AG , Bombardier and Thyssen or were continued as independent operations. The site of the Henschel aircraft engine plant in Baunatal was acquired by Volkswagen AG , which built the Volkswagen plant in Kassel there. VW has two other locations in the region, including the Original Parts Center and the plant for processing assemblies in Kassel-Bettenhausen. The adjacent AEG home appliance factory was closed in the 1990s and is now used by Alstom . The suspension railway technology ( Transrapid ) was developed in the former Henschel plant in Mittelfeld, as was the InterCityExperimental in the area of high-speed rail , from which the ICE emerged. The Bode company manufactures train and bus doors. Since the 1990s, Rheinmetall and Krauss-Maffei Wegmann have been producing armaments again on the site.
The crude oil company Wintershall and natural gas supplier Wingas as well as the potash and salt producer K + S are active in the raw materials sector .
Kassel and the region have also made a name for themselves with their institutes, associations and companies in the field of renewable energies and energy efficiency such as the Institute for Solar Energy Supply Technology (ISET), the Center for Environmentally Conscious Building. V. (ZUB), the Society for Rational Energy Use (GRE) or the Competence Network Decentralized Energy Technologies (deENet). The largest company in the photovoltaic sector is SMA Solar Technology . The Städtische Werke Kassel , a 1929 established urban own company for several years as the only local provider offers its customers 100 -% - Natural Power. In 2010, Thüga took over the minority stake of 24.9% from Vattenfall . From 2009, the “Am Lohfeldener Rüssel” industrial park was developed together with the community of Lohfelden . Numerous companies were able to settle there, both from the service sector and manufacturing companies from the mechanical engineering sector. The area is the third defined expansion area in the Kassel-Waldau industrial park, which is heavily influenced by logistics .
In 2016, Kassel generated, within its city limits, a gross domestic product of € 9.914 billion and thus ranked 37th in the ranking of German cities according to economic output.The GDP per capita in the same year was € 49,937 per capita (Hesse: € 43,496, Germany 38,180 €) and thus above the regional and national average. The GDP per labor force is € 65,398. In 2016, around 151,600 people were employed in the city. The unemployment rate fell from 10.2% in 2011, to 9.3% in 2015 and 6.7% in December 2018 (in the neighboring district of Kassel it was 3.5%).
In the Future Atlas 2016 , the independent city of Kassel was ranked 145th out of 402 rural districts, municipal associations and independent cities in Germany, making it one of the regions with a “balanced risk-opportunity mix”.
Attractions
Buildings
→ Secondary article: Architecture of Kassel under Landgrave Karl
The old town of Kassel in what is now the Mitte district was largely destroyed in 1943. Even though, due to the destruction of the war and the post-war urban planning, there is no longer a closed historical cityscape, due to its importance as a former residential town, the city is home to numerous historical buildings from many epochs, which are also dominant in urban planning.
One example is the Evangelical Brethren Church , the second oldest church building in the city. In the area of the city center there are other historical monuments: the Renthof and the Rondell , the Martinskirche with the distinctive towers of the early post-war period, the Ottoneum , the Marstall , the ruins of the armory, the Karlshospital , the Druselturm , the ruins of the garrison church, which simplifies Rebuilt Karlskirche , the Fridericianum with Zwehrenturm (temporarily used as an observatory ), the arbor of the former Red Palace , the steeple of the old Luther Church with a modern concrete building and the surrounding grave monuments of the old town cemetery.
The Ottoneum , one of the representative buildings of the baroque residence city
Today the Marstall houses the market hall and the city archive of Kassel
The building of the Elisabeth Hospital from the Renaissance period
Cradle of the democratic upheavals at the time of early liberalism: the Ständehaus on Ständeplatz, built in the style of the early neo-renaissance
Devil's Bridge in the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
There are impressive Art Nouveau buildings in the Vorderer Westen district ; These are mostly apartment buildings with diverse facades, comparable to some quarters in the southern part of the city. The workers' quarters bordering the inner city in the north of the city and in the Wesertor are just as vivid relics as the factory settlements of the Wilhelminian era and the early modern era on Otto Haesler's Rothenberg .
The architecture of the 1950s is represented by numerous buildings and is considered a modern overall monument , for example the head building of the main station, the Hotel Hessenland, the House of Youth, the stairs street , the old police headquarters (demolished in 2007) or the EAM high-rise . The architecture that has shaped and transformed the cityscape since the 1990s manifests itself in various projects such as the new construction of the police headquarters in the Golden Hole, the conversion of military properties (Hindenburg barracks , Graf Haeseler barracks , barracks on today's Marbachshöhe) and the Untereustadt. The documenta urbana on the edge of the Dönche nature reserve is considered a pilot for alternative and cooperative housing construction, as is the eco-settlement in Harleshausen. Professors of the interdisciplinary and integrated ASL course, newly founded in 1973, were pioneers of the Kassel School at the time, such as Gernot Minke and Michael Wilkens .
Numerous oak trees fall on in many places in the Kassel city area, which by the artist Joseph Beuys ' social sculpture than 7,000 oaks - local aut forest clothes instead of local aut walt clothes "were 1982-1987 planted in streets and squares.
The tallest structures in Kassel are the old church tower of the Luther Church (76 m), the Hercules (70.5 m) and the twin towers of the Martinskirche (69 m). The 186 m high Habichtswald telecommunications tower on the Essigberg , on the other hand, is not in the urban area.
Works of art and monuments
Negative of the Ashrott fountain by Horst Hoheisel in front of the Kassel town hall
Monument E. R. Nele's ramp
Green spaces and recreation
With the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe and the Karlsaue, Kassel is represented with two parks in the European Garden Heritage Network .
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe

The Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe , which is located in the western city of Kassel in the Habichtswald, has been recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since June 2013 . It is the largest mountain park in Europe. The Wilhelmshöhe Palace , the Löwenburg and Hercules, the symbol of the city, are located here. The park is listed in 48th place among the top 100 sights in Germany.
Landgrave Karl started the mountain park as a baroque park around 1700 . In the 18th and 19th centuries it was partially redesigned into an English landscape garden. In the summer months, the remarkable Kassel water games take place there twice a week .
Before there were races on the Avus and Nürburgring, idols like Caracciola , Jörns and Rosenberger drove in the Bergpark from 1923 to 1927 for the Kassel Mountain Prize. 1951–1954 motorcycle races revived this tradition, the first Hessian Federal Horticultural Show in 1955 ended these activities. Since 2005 there have been old-timer races in the Bergpark, which are intended to remind of the races of that time.
Karlsaue and Fuldaaue
In Kassel Fulda - lowlands are the Karlsaue and the Fuldaaue . Together, these two directly adjacent parks form one of the largest inner-city parks and one of the most extensive park-like local recreation areas in Germany , in which a federal horticultural show was held in 1955 (Karlsaue) and 1981 (Karls- and Fuldaaue) .
The Karlsaue is located in the area of the Südstadt district , it is an originally Baroque , inner-city park on the western Fuldaufer, which extends as far as the city center of Kassel and Friedrichsplatz . The park, which was laid out on the flat terrain of a former Fulda island, contains numerous artificially created bodies of water such as ponds, lakes and ditches, which still illustrate the basic baroque concept of the complex today. You can walk through the complex on chaussed paths. The Fuldaaue can be reached via pedestrian bridges. In the Karlsaue is the orangery with the museum for astronomy and the history of technology, the marble bath and the flower island Siebenbergen.
The Fuldaaue - common Buga, after the Federal Garden Show - is located on the Fuldaufer opposite the Karlsaue. It was laid out for the Federal Garden Show in 1981 on the site of old gravel works. The modern designed park includes a large man-made lake, the northern part of which is demarcated as a nature reserve . Many rare birds breed in the nature reserve, while the south-western, larger part of the complex is used for recreational purposes. The dam running in between separates the two very different systems in terms of landscape gardening.
The Buga is located in the Waldau district and is an urban complex, while the Karlsaue is a state park and is maintained by the State of Hesse.
Vineyard
The Henschelvilla was demolished in 1932 due to the house interest tax , after no buyer could be found.
For several years there have been efforts to reconstruct the area around the vineyard and former "Henschelgarten", which had been fallow since the end of the war. Large areas of undergrowth had been removed there since the early 2000s, in particular to prevent its use as a cruising meeting point for gays. In the immediate vicinity is the servants' house of what was then Henschelanlage on the vineyard, which is used as a private museum for sepulchral culture . In addition, the Murhard library is located on the back of the Brüder-Grimm-Platz at Wilhelmshöher Tor.
The staircases and stairways coming from Frankfurter Straße have been repaired in recent years. The Grimmwelt was built on the vineyard between 2013 and 2015 .
Bird and nature reserves
In addition to the bird sanctuaries in the area of the Fulda floodplain (Fuldaaue in Waldau , Lossedelta at the port), there is the Dönche nature reserve , which was used by the armed forces in the post-war years as a maneuvering area . It spans the open space between the districts Brasselsberg at the foothills of the Hawk Forest, Nordhausen and the adjacent high-rise estate in the south Brückenhof , and west by the documenta urbana limited as valley.
Culture
theatre
English drama groups performed at the Kassel court as early as the 16th century. Under Landgrave Moritz , the Ottoneum was completed in 1605 , and is considered the first permanent theater building in Germany. Moritz hoped for a reform of German drama, but this did not materialize. The focus remained on the English comedy. With the beginning of the Thirty Years War , theater operations in Kassel came to a standstill in 1621. Only Landgraf Karl left the former Ballhaus at the city palace converted into a comedy house after and the stables of the castle was occasionally used for operas and comedies. In 1769 Kassel received its first opera house . It arose from the reconstruction of a princely palace on today's Opernplatz, suggested by Landgrave Friedrich II. In 1909 a monumental, eclectic new building was erected on the southeast side of Friedrichsplatz , which was badly damaged during the air raids in October 1943 and demolished in the early post-war years. The subsequent building has a longer history, as a new design by the competition winner Hans Scharoun should first be implemented, which would have been based on the old development of the square in terms of urban planning. Instead, this project was discarded and replaced by the new Paul Bode building by 1959 . The director of the Kassel State Theater is Thomas Bockelmann . The orchestra of the State Theater is one of the oldest in Germany and is first mentioned in 1502 as a court orchestra.
In addition to the state theater, there are numerous cabaret and amateur theaters in Kassel. The theater in the center is also used as a children's theater.
Museums, galleries and exhibitions
The city of Kassel has a number of important museums and galleries. The basis of today's museum landscape in Kassel was the collections of the Landgraves and Electors of Hesse-Kassel of the State Museums and Palaces and Gardens . The Fridericianum , at today's Friedrichsplatz , is considered to be the first public museum building on the European continent and, as the Fridericianum art gallery, is endowed with an important reputation for contemporary works. The neighboring Ottoneum is the first permanent theater building in Germany to house the natural history collections. The City Museum of Kassel is located at Ständeplatz , and was reopened in 2016 after a renovation and redesign. The Spohr Museum is located in the Kulturbahnhof .
The documenta hall , built in 1992, is used for changing events - such as the annual presentations of the exams and master's theses at the Kassel Art College . In the Vorderen West there is the Art Temple as a temporary exhibition space for various private foundations and the Werkstatt e. V. as a literary institution. There is also the Kasseler Kunstverein, founded in 1835 .
In 2006, the administration of the State Palaces and Gardens of Hesse combined their Kassel properties from castles and museums to form the Hessen Kassel Museum Landscape (MHK). These include: Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe with the Hercules, Wilhelmshöhe Castle (collection of antiques, Old Masters Picture Gallery, Weißenstein wing) and the buildings there (Löwenburg, Ballhaus, greenhouse), Karlsaue Park with the buildings there, the orangery (astronomical-physical cabinet, planetarium) and the marble bath, the Hessian State Museum with the gate guard and the New Gallery .
The Technik Museum Kassel and the Henschel Museum are located in Rothenditmold . There are smaller private exhibition areas in Bettenhausen and the northern city center.
From October 2, 2012 to February 18, 2013, the exhibition Everything under the sky belongs to everyone took place in numerous freely accessible locations in the city center . According to the organizers, it was the "largest overseas exhibition of Chinese art in public space to date and at the same time the largest art exhibition that will take place in 2012 as part of the Chinese Year of Culture in Germany."
The GRIMMWELT , inaugurated in 2015, is dedicated to the Brothers Grimm , who spent their longest and most productive time in the city.
documenta
Since 1955, the world art exhibition documenta has taken place in an initially irregular, since 1972 every five years . It was initiated by Arnold Bode , then a professor at the Kassel Werkkunstschule, now the Kassel Academy of Art . The first documenta set out to present modern art, defamed as “ degenerate ” during the time of German fascism between 1933 and 1945, to the public again; it was an exhibition accompanying the Kassel Federal Garden Show in 1955 . Since then, art, exhibition and city have formed a tightly woven symbiosis. The presence and work of the exhibitions since then are firmly anchored in the cityscape and society, with each individual exhibition having its own character and thus ensuring an ongoing reception. The documenta 14 was from 10 June to 17 September 2017 in Kassel and April 8 and up July 16, 2017 in Athens.
music
Kassel has considerable private and state-sponsored music institutions. Examples include: the Kassel State Orchestra at the Kassel State Theater , the Kassel Army Music Corps , the Bärenreiter-Verlag , the Kassel City Music Academy and the German Archive of Music History and the International Heinrich Schütz Society . There is also the state-funded Music School Kassel e. V., the Chamber Music Association, the Dock 4 cultural center, the Schlachthof cultural center , the cultural bunker, the Kirchditmold choir, the Kassel Bach choir , the Collegium Vocale at St. Marien, Kassel , the Kassel Youth Symphony Orchestra e. V. and others. Every year in summer the HNA Summer Open Air takes place in the Karlsaue .
Music groups from Kassel are or were, among others: Caro Kiste double bass , Jawoll and Milky Chance .
Regional customs
The summer festival on the Fuldaufer, the Zissel , is known throughout the region. A tradition on St. Nicholas Day is the Glowes Eve .
dialect
The regional dialect is Kasselaner , a variety of North Hesse . The importance of the Kassel dialect disappeared in higher educational circles in the time of the Reformation in favor of the standard language, so its use in literature is rather rare.
Examples from Kasselian:
- "Gehädd da Rädde däh?" - "Nä net mä" (= Does the dog [actually: male ] belong to you?) - (= No, not me)
- "'S schigget!" (= It's enough / It's enough!)
- "Alszus straight uss" (= always straight ahead)
- "Wist a piece of Kuan then?" (= Do you want a piece of cake too?)
- "Widden Wecke?" (= Do you want a bread roll?)
- "S reint!" (= It's raining!)
- "That would be ußwiesen" (= that will prove itself / show / let's wait!)
North of Kassel runs the language boundary of the 2nd sound shift, which separates -k and -ch , -s and -t . Thus, the federal state of Hesse in the Kassel district (between Korbach and Hofgeismar) still has a Low German dialect.
Kasselaner, Kasselaner and Kasseler
The inhabitants of the city differentiate between people from Kassel, Kasselans and Kasselans. Newcomers are called Kassel, while Kasselans were born in Kassel. Kasselans were born in Kassel and both parents are Kasselans. The name is retained even if you leave the city. The origin of this differentiation, which does not create any rights or obligations, is unknown. There are similar distinctions in Halle (Saale), among others .
Sports
Soccer
With the clubs SV Kurhessen Kassel and VfL TuRa Kassel , Kassel had two football clubs at the turn of the 20th century , and KSV Hessen Kassel succeeded them . This played from the beginning of the 1980s, with the exception of the seasons 1987/88 and 1988/89 , in the 2nd Bundesliga . After bankruptcy and re-establishment in 1997/98, the rise from the district league to the upper league and in 2005/06 to the regional league followed . The team plays its home games in the Auestadion . At the end of the 17/18 season, the KSV was relegated to the Hessen League .
ice Hockey

Ice hockey was established in Kassel by the 1970s at the latest. The Kassel Huskies were a founding member of the German Ice Hockey League in 1994 and played in the top German league. Exceptions were the 2006/07 and 2007/08 seasons , the Huskies were runner-up in 1997 . After relegation and a two-year absence, the team returned to the DEL in 2008, but had to file for bankruptcy in 2009/10. In the 2011/2012 season, the parent club EJ Kassel played after a new start in the Hessenliga with the nickname "Huskies" in the Oberliga West (third class). In 2014 he was promoted to the DEL2 . The team plays its home games in the Kassel ice rink at the Auestadion.
Handball
In addition to several small clubs in and around Kassel that are in the lower leagues, Bundesliga club MT Melsungen plays its home games in Kassel's Rothenbach-Halle. Several national players from the winning team of the EM 2016 are currently playing for MT Melsungen.
rugby
In 1900 the German Rugby Association was founded in Kassel . After a long break, the Rugby Cassel e. V. again a local representative of the full contact sport. The club's teams play with 15 players each according to rugby union rules in the Regionalliga Hessen-Nord and also take part in tournaments in Olympic 7-a-side rugby .
athletics
Numerous athletics clubs are based in Kassel . The focus here is primarily on medium and long-distance running , which can be traced back in particular to the activities of the former national marathon trainer Winfried Aufenanger .
Important regular athletics events are the Askina Sports Festival (until 2011), the Kassel City Run (until 2014) and the Hercules Mountain Run to Hercules . The premiere of the Kassel Marathon took place on June 10, 2007 .
In 2011 and 2016 the German Athletics Championships were held in the Auestadion .
water sports
Water sports enthusiasts and clubs are well represented in Kassel due to its proximity to the Fulda and the attached Buga site. Rowing in particular is one of the most popular water sports. Many schools have boathouses on the banks of the Fulda and offer corresponding activities.
For a while, the former world champion in single , Marcel Hacker , rowed in Kassel.
There is also the Motor Yacht Club (MYC) and the Hochseesegelverein (HVK) Kassel. There is also a port a little north in the urban area. The DLRG (StV Kassel) is also based on the Fulda and Fuldaaue .
Kassel is also the cradle of German water skiing. In 1949 the first German water ski club WAK Kassel (water sports club Alt Kassel) was founded. In 1958 the first German water ski championships took place on the Fulda. In the same year the German Water Ski Association was founded in Kassel . The WAK Kassel provided German champions or youth champions for years.
Table tennis
The ESV Jahn Kassel was one of the leading table tennis clubs in North Hesse for many years. The men's team has played in the Oberliga (then the highest German division) since 1954 and in the 2nd Bundesliga since 1988 . In 2005 he was relegated to the regional league. In 2007 the department dissolved and merged with SVH Kassel , whose team now plays in the regional league.
tennis
Another popular sport in Kassel is tennis . The Wilhelmshöhe Open , the largest regional and only world ranking tournament in North Hesse, deserves a special mention here.
Other sports
- With the Kassel Titans , an American football team from TSV 1891 Oberzwehren , the 2009 champions of the Hessen State League come from Kassel.
- The Herkules Baseball Club (also Herkules Kassel ) is the only municipal baseball club and currently plays in the Hessian Association League.
- The bowling sports club Kassel (BSV) is represented with several teams in the Hessian national leagues as well as in the Bundesliga with the current vice-champion (Club Finale Kassel ).
- The largest martial arts club in Kassel is SV Rot-Weiß Kassel . The PSV green and white Kassel offers the martial arts departments Judo , Ju-Jitsu , Karate or Arnis to equally the Karate Team Kassel from Bettenhausen , which stands out for its youth work.
- The Hockey-Club Kassel e.V. (HCK) is represented in hockey with its youth and adult teams throughout Hesse. The 1st men of the HCK plays in the Oberliga, the highest Hessian league.
- The Golf Club Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe is located on the golf course in Wilhelmshöhe . The men's club team plays in the 1st Hessen League.
- The Radball division of SV Nordshausen plays in the Radball Bundesliga .
- The standard formation of the Rot-Weiss-Club Kassel dances in the 1st Bundesliga standard.
- UHK Kassel Rangers was the only floorball team in Kassel. On the basis of the university sports team, the Rangers play in the Floorball Hessenliga and in the German Cup, where they reached the round of 16 in the 2010/11 season and were eliminated from the later cup finalists TV Eiche Horn Bremen. There is now a university sports team; the league operation is now based with the SV Espenau Rangers in the north Hessian community Espenau in the district of Kassel .
- The Kassel Roller Derby Bashlorettes has been a roller derby team since 2011 .
Regular events
- Summer - every five years: documenta - world exhibition for contemporary art (first 1955)
- March / April: Spring fair at the new exhibition center
- April / May: Earth Day , street festival with stands on environmental issues and a cultural program
- May / June: The city festival in the city center (first June 29 to July 6, 1979)
- June / July / August: International concert series in the culture tent at the wire bridge
- July / August: Christopher Street Day - Parade, parade and street festival of the emancipatory scene in Kassel
- July / August: Zissel - the Kassel folk festival on and on the Auedamm
- June / July: Wilhelmshöhe Open - Hesse's largest international tennis tournament
- August: Wehlheider fair
- September (usually first Saturday): Museum Night (first time September 11-12, 1999)
- September: Connichi - Anime - and Manga - Convention
- September: International theater festival in the State Theater
- September: Wilhelmshöher Mountain and Lights Festival in the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
- October: Kassel Music Days
- October: Casseler Freyheit
- October: Waldauer duck fair
- November: Kassel Documentary Film and Video Festival
- November / December: two Christmas markets in the city center
Relocation during the CSD 2005
Culinary specialties
According to many Kassel citizens, the culinary specialties include the Weckewerk , a food made from meat by-products, as well as the Ahle Wurscht (high German: old sausage) and the traditional bacon cake . Green sauce is a popular side dish in all of Hesse . Kasseler is not a Kassel specialty, but was named after the Berlin butcher Cassel.
media
The Hessische / Niedersächsische Allgemeine (HNA) appears as the daily newspaper in Kassel . From 2004 to 2008 (online until 2013) the Nordhessische Neue Zeitung appeared monthly , which was distributed free of charge in businesses and residential areas. IG Metall was the publisher until 2008. The kassel newspaper , a non-commercial, free online newspaper , has existed since 2006 . The Extra-Tip advertising paper is distributed to households in Kassel twice a week .
The Hessischer Rundfunk operates its studio in Kassel and broadcasts its radio program hr4 from Kassel. Hit Radio FFH has its North Hesse studio in the HNA house and the radio station Radio Bob broadcasts across Hesse from Friedrich-Ebert-Straße. RTL Television operates a branch in the city.
The radio station Freies Radio Kassel and the television station Medienprojektzentrum Offener Kanal Kassel (receivable on analogue and digital cable nationwide) are two non-commercial citizens' stations . The German-Russian media department IdM Europa - Integration durch Medien e. V. , which among other things produces a weekly live broadcast Offene Stadt in the Offenen Kanal Kassel. The program, which is presented in German and Russian, is also broadcast in Frankfurt am Main , Offenbach, Gießen and Fulda through the public television network .
The Bärenreiter-Verlag for classical music and the Merseburger Verlag are based in Kassel .
Public facilities
Kassel is the seat (or represented by offices or offices) of the following bodies, institutions and corporations under public law :
- Regional council of the administrative district of Kassel ,
- Career center of the Bundeswehr Kassel (formerly: District Armed Forces Replacement Office ) responsible for the independent city of Kassel and the districts: Kassel, Höxter, Hersfeld-Rotenburg, Waldeck-Frankenberg and the Schwalm-Eder district
- Social insurance for agriculture, forestry and horticulture (SVLFG - head office and office)
- Deutsche Rentenversicherung Knappschaft-Bahn-See (office)
- Health care for federal railway officials (district management)
- State Office Hessen-Forst
- Hessian state authority for private broadcasting and new media
- Hessian payment centers
- Hessian state fire brigade school
- Hessian Office for Supply and Social Affairs
- Audit office of the Hessian Court of Auditors
- German Pension Insurance Hessen (Office)
- Landesbetrieb Hessisches Landeslabor
- State Welfare Association of Hesse
- Landesbetrieb Landwirtschaft
- With Christoph 7 , one of the currently (as of October 2012) 71 German rescue helicopters is stationed in Kassel.
- The city of Kassel is the only city in Northern Hesse to have a professional fire brigade with two permanently manned fire stations.
- Zweckverband Raum Kassel (ZRK), formed in 1974 as a result of the administrative reorganization in Hesse
- Municipal works , electricity and gas suppliers
- Kassel transport and supply company
- Gesundheit Nordhessen Holding , responsible for municipal hospitals
- GWG Non-profit housing association of the city of Kassel
- Kasselwasser, municipal water and sewage company
- City cleaners, municipal garbage disposal and street cleaning
Libraries and Archives

The University Library of Kassel is a library merger of the State Library and the Murhard Library of the City of Kassel and the actual sub- and departmental libraries of the university and its departments.
The city library consists of the central library, the youth library and the district and school libraries in Niederzwehren, Oberwehren and Waldau.
The documenta archive with the Harry Kramer archive and the Kassel city archive are publicly owned . In addition, there is the foundation archive of the German women's movement , the archive of the state welfare association and the state church archive of the Protestant church of Kurhessen-Waldeck .
Judiciary
-
Federal Social Court
 National Socialist architecture on Wilhelmshöher Allee : the building of the military district command IX, which was occupied in 1938 . has been the seat of the Federal Social Court since 1954.
National Socialist architecture on Wilhelmshöher Allee : the building of the military district command IX, which was occupied in 1938 . has been the seat of the Federal Social Court since 1954. -
Hessian Administrative Court
 Hessian administrative court on Brüder-Grimm-Platz
Hessian administrative court on Brüder-Grimm-Platz - Hessian Finance Court
- Kassel Social Court
- Labor Court Kassel
- Administrative court of Kassel
- Civil Senate Higher Regional Court Frankfurt / Main
- Kassel District Court
- Kassel District Court
- Public Prosecutor Kassel
- Correctional institutions Kassel I and Kassel II
Chambers
- Kassel Chamber of Crafts - Chamber district: City of Kassel and the districts of Kassel , Fulda , Schwalm-Eder-Kreis , Hersfeld-Rotenburg , Werra-Meißner-Kreis and Waldeck-Frankenberg
- Chamber of Commerce and Industry Kassel-Marburg (IHK) - Chamber district: City of Kassel and the districts of Hersfeld-Rotenburg , Kassel , Schwalm-Eder district , Waldeck-Frankenberg , Werra-Meißner district and Marburg-Biedenkopf (with the exception of some communities)
- German Trade Union Confederation (DGB) - Competent umbrella organization of the trade union and employee representation in North Hesse
Churches
- Evangelical Church of Kurhessen-Waldeck
- Evangelical Gnadauer Community Association
- Evangelical Kreuzkirche Kassel in the district Vorderer Westen
- Catholic Church Kassel (Deanery Kassel-Hofgeismar in the Diocese of Fulda )
- New Apostolic Church - Kassel district
- Free Protestant communities in the Hessen-Waldeck district
Further
Education and Research
General education schools
The oldest of the Kassel high schools is the Friedrichsgymnasium, founded in 1779 . There are two of the four Hessian experimental schools in Kassel: The Waldau Open School and the Reform School in Wilhelmshöhe. In 2006, the Waldau Open School was one of the winners of the German School Prize . Kassel offers a total of 27 elementary schools, eight comprehensive schools, four secondary and secondary schools, seven vocational high schools, seven grammar schools and grammar schools, two schools for adults (evening schools) and around ten special schools. There are also several private schools: the Montessori school, the Waldorf school, the free Christian school, the free school and the like. a.
university
From 1633 to 1653 there was already a first university in Kassel.
The new University of Kassel was founded in 1971 as a comprehensive university (GhK) and became known for its then modern educational concept, which has become known as the Kassel model .
In 2002 the name of the university was changed to University of Kassel; Associated with this was a turning away from the idea of reform and a move towards an orientation towards the classical understanding of university organization. Since 2006, the new study regulations after Bachelor / Master have successively replaced the Kassel model. In the 2014/15 winter semester, 23,696 students were studying at the twelve departments . The Kunsthochschule Kassel, founded in 1777, is partially autonomous within the university . In addition, the former engineering school in Wilhelmshöher Allee and the higher business school have been incorporated into the structure of the university.
The University of Kassel offers courses in the fields of human sciences , humanities and cultural sciences , social sciences (with sports sciences ), architecture , urban planning , landscape planning , economics , mathematics and natural sciences , ecological agricultural sciences , civil engineering and environmental engineering, mechanical engineering , electrical engineering / computer science , Kassel University of Art .
The campus close to the center at Holländischer Platz has been developed since 1974 and is located on the former factory site of the Henschel company. By 2017, the campus is to be greatly enlarged in a northerly direction in order to provide space for departments located in the remote AVZ site in Oberzwehren. The Department of Organic Agricultural Sciences also has two locations in Witzenhausen and on the Frankenhausen state domain near Grebenstein .
Other facilities
- Hessian University for Police and Administration - Kassel Department
- Federal University for Public Administration - Faculty of Agricultural Social Insurance
- Kassel School of Medicine , medical college in cooperation with the University of Southampton
- Fraunhofer Institute for Wind Energy and Energy System Technology (IWES), formerly Institute for Solar Energy Supply Technology (ISET)
- Fraunhofer Institute for Building Physics (IBP) project group Kassel
- Brothers Grimm Society
- YMCA College , private college for theology, social affairs, community education , and ethics
- CVJM-Kolleg , technical school for theology and social affairs
- Federal Armed Forces College Kassel
- Evangelical Froebel seminar, technical school for social assistance, social education, curative education and educators
- Technical college, private college for industrial professions
- Administration and Business Academy Kassel, private technical school, which can lead to a bachelor's degree in cooperation with various universities
- Hessian Vocational Academy Kassel, private university for business
- Hessian State Fire Brigade School (HLFS). Firemen and women from all over Hesse are trained here.
- The Catholic adult education of the diocese of Fulda has its seat in the regional house Adolph Kolping. She is a member of KEB-Hessen . The Kassel Catholic Family Education Center, which is part of the Catholic Family Education Association in the Diocese of Fulda e. V. belongs to their seat.
- Oskar von Miller School Kassel , vocational school
Transport and infrastructure
Traffic counts and traffic data
The city of Kassel and the road traffic and civil engineering department regularly carry out traffic counts. Video- and radar-based technical equipment is available for recording traffic data on roads (number of vehicles, classification). Calculated traffic volumes, which give an impression of the volume of traffic and an estimate of the traffic load, can be found on a map from 2010. There the traffic volume of motor vehicle traffic is given as a cross-sectional value for an average working day (DTVw5 - average daily traffic volume on working days). An update and update is planned for 2020.
Outside the city of Kassel, figures on the traffic load on individual streets can be found in the traffic volume map for Hessen , published by the Hessen Mobil state authority .
Streets
| Street | Traffic volume or traffic load (daily vehicles, status 2010 see above) |
annotation |
|---|---|---|
| Brothers Street | 47 500 | |
| Dutch street | 30,000 - 38,000 | |
| Wilhelmshöher Allee | 6,000 - 23,500 | The Wilhelmshöher Allee, which leads from the Kassel city center to the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe , is the most obvious main axis of the city due to its completely straight road, but not its busiest street. It is around four kilometers long and was widened in two lanes in the 1970s with extensive tree felling. The lowest traffic volume can be found in the western section, at Wilhelmshöhe Castle. |
| Friedrich-Ebert-Strasse | 3,500-12,000 | The lowest traffic volume can be found in the western section, at the level of the town hall. |
- Kassel is on the A 7 , A 44 and A 49 federal motorways .
- The federal highways B 3 , B 7 , B 83 and B 251 run through the city.
- Characteristic of the cityscape is the expansion of the road network that has been driven forward since the 1950s and 1960s, particularly the ring that surrounds the city center ( inner city ring ). It leads from Ständeplatz via Scheidemannplatz and Rudolf-Schwander-Straße to Lutherplatz , from there via the Am Stern intersection and Kurt-Schumacher-Straße to the Altmarktkreuzung. Then it continues along Steinweg, Friedrichsplatz, Frankfurter Straße, and leads back to Ständeplatz at the “Trompete” in Fünffensterstraße. A second part of the ring leads from Lutherplatz via Hoffmann-von-Fallersleben-Strasse, Wolfhager Strasse, Holländischer Platz and Kurt-Wolters-Strasse to the intersection of Weserstrasse and Schützenstrasse.
- The Königsstraße represents the main part of the pedestrian zone.
- Far south of Kassel are the Kassel Mountains, which are well known to motorists, but they are not in the Kassel area.
On December 31, 2010, 92,991 vehicles were registered in the city of Kassel. A traffic-calmed business area was set up for the first time in 2019 . In addition, there are already several 30 km / h zones .
Bicycle traffic
Kassel has cycle paths on a few roads with more motor vehicle traffic , but in some places the sidewalk is open for cycle traffic. Since the early 1990s there has been a network of bicycle routes provided with signposts, which are mostly topographically favorable through mostly quiet side streets and green spaces. This network was consolidated in the 2000s with further routes with bicycle signposting , which also lead to neighboring towns. Kassel is crossed along the Fulda by the Hessian long- distance cycle route R1, on which D-Route 9 also runs. In both courses there are individual sections with bicycle roads .
“Nextbike” bike rental system: the nextbike bike rental system with 400 bikes has been in operation since January 1st, 2018. The bikes are distributed over 56 stations in the city. The operator is nextbike GmbH.
Rail transport
The Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe railway station , which opened on May 29, 1991 and was newly built and built directly on the new Hanover-Würzburg line, connects Kassel to the ICE network with the following cities via various high-speed routes:
- Hamburg or Bremen - Hanover - Kassel - Fulda - Frankfurt am Main - Karlsruhe - Basel or Zurich .
- Hamburg - Hanover - Kassel - Fulda - Würzburg - Munich and Nuremberg / Vienna
- Berlin - Wolfsburg - Braunschweig - Kassel - Fulda - Frankfurt am Main - Stuttgart - Munich
In addition, Kassel is also connected to the network of intercity lines and was also reached by various inter-regional lines until 2006, until they were converted into IC connections .
The as head station built main station is located at the northwest edge of downtown. It is located on the Hannöverschen Südbahn and has lost its importance for long-distance traffic since the ICE station Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe went into operation. Today it is only served by regional traffic. In September / October 2005 construction work began there to connect the Kassel city area to the RegioTram , which was completed in August 2007.
Omnibus, tram and RegioTram
The RegioTram connects the railway network in the region directly with the Kassel tram network as a S-Bahn -like system ( Karlsruhe model ), so the city center can be reached directly from the surrounding area without changing.
The Kassel tram operated by the municipal Kasseler Verkehrs-Gesellschaft (KVG) sometimes goes to the surrounding area, for example to Baunatal and Hessisch Lichtenau . Another expansion took place with the RegioTram light rail system , which went into full operation at the end of 2006. Since then, the route has been 122 kilometers. Until 1966 there was a railway line to Hercules . In addition, the KVG operates a bus network, from 1944 to 1962 trolleybuses drove between Harleshausen , Kirchditmold and Wilhelmshöhe .
The city belongs to the North Hessian Transport Association .
Inland shipping
Today's Kassel port was built from 1893 to 1895 as part of the expansion of the Fulda . At that time the port was used for freight traffic to the seaports. The Schlagd , as it was called, was used by barges and larger ships to handle goods. Today this area is the berth for the Fulda-Weser fleet in the direction of Hann. Münden and Bad Karlshafen. The here regulated Fulda , a source river of the Weser , serves as a shipping route only for excursion boats, as well as leisure and sport boats. The existing lock systems and weirs are too small for modern cargo ships.
Airport
The Kassel region is connected to the air transport network via Kassel-Calden Airport, located northwest of the city . The expansion of the existing airport was criticized for a long time until it was approved. On April 4, 2013, the new regional airport Kassel-Calden (KSF) went into operation. The operation was in deficit from the start, but in the third year of operation it was possible to reduce it by 25% from 8.1 to 6.1 million euros a year, not least due to growth in the freight business. In 2018, the airport handled more than 100,000 for the first time with 131,816 passengers.
Hiking trails
A number of footpaths and long-distance cycle routes lead through the city . Amongst other things:
- Footpaths
- Ederseeweg (49 km), leads from Kassel to Edersee ,
- Herkulesweg (193 km), leads from Battenberg through Kassel to Heilbad Heiligenstadt ,
- Kassel-Steig (157 km), leads around Kassel and the Kassel basin ,
- Märchenlandweg (430.8 km), leads through Reinhardswald , Solling , Kaufunger Wald , Söhre , Habichtswälder Bergland and Kassel
- Long-distance cycle routes
- Hessischer Radfernweg R1 (Fulda-Radweg; 250 km), leads from the heights of the Rhön along the Fulda to Bad Karlshafen on the Weser
- D-Route 9 (Weser-Romantic Road; 1,197 km), leads from the North Sea via Bremen, Kassel, Fulda and the Taubertal to Füssen in the Allgäu
Personalities
The most famous personalities who were born in Kassel, worked in Kassel or shaped Kassel include:
- Arnold Bode , founder of Documenta
- Holger Börner , Prime Minister of the State of Hesse from 1976 to 1987
- Hans Eichel , 1975–1991 Lord Mayor of Kassel, 1991–1999 Prime Minister of the State of Hesse, 1999–2005 Federal Minister of Finance
- Ulrike Folkerts , actress ( crime scene commissioner)
- Brothers Grimm , linguists and folklorists
- Jörg-Uwe Hahn , 2009–2014 Hessian Minister of Justice, Integration and Europe and Deputy Prime Minister
- Ludwig Mond , chemist, developer of the moon process
- Paul Julius Reuter , founder of the Reuters Telegraphic Comp. Incorporated
- Ferdinand Sauerbruch , surgeon (he performed his first operations at the Deaconess Hospital)
- Philipp Scheidemann , 1919 Reich Minister President, 1919–1925 Lord Mayor of Kassel
- Elisabeth Selbert , lawyer, member of the Parliamentary Council
energy
Own generation of electricity and heat
Electricity and heat is generated in Kassel by the Städtische Werke Energie + Wärme GmbH and others. The largest systems include:
- District heating power plant Dennhäuser Strasse (38 MW el + 80 MW th )
- Combined heating and power station Dennhäuser Strasse (52.9 MW el + 54.6 MW th )
- Biomass heating power plant Mittelfeld
- Run-of-river power plant "Neue Mühle" (0.20 MW)

- "Vogt'sche Mühle" hydropower plant (0.60 MW)

- Brückenhof heating plant

- Losse heating plant
- Central heating plant
- Waste-to-energy plant (43.5 MW el and approx. 80 MW th )
District heating network
The district heating generated in Kassel is distributed via the district heating network and is available in many parts of the city. The proportion of combined heat and power in district heating provision is C KWK = 0.97. About a third of the district heating is generated by the waste incineration plant.
| Key figures | |
|---|---|
| Route length | 175.3 km |
| Acceptance points | 2.145 |
| Connected load | 443.7 MW |
power grid
In Kassel, the substations in Bergshausen and Sandershausen connect the local 110kV network with the 400kV transmission network of TenneT TSO. The two substations ensure that the 400kV overland power is first transformed into 110kV power.
This 110kV electricity is passed on to nine other, much smaller substations within Kassel. You lower the voltage further to 10kV. This electricity in turn runs via cables to the little green transformer houses that can be found all over the city. There are around 1000 of them in Kassel. It is you who ultimately convert the 10kV electricity into our 230V household electricity.
Others
European capital of the raccoons
A special feature of the Kassel fauna is the high population density with raccoons . After raccoons were released on the Edersee in 1934 , they have settled the forests around the city and then the city area itself since 1960. While the small bears were initially considered to be neozoa , they are now counted among the native fauna, especially in northern Hesse. The population density in Kassel is even higher than in large cities in their natural habitat in North America . In the districts near the forest, sightings of entire groups of raccoons are common at dusk. Scientific studies assume a population density of between 60 and 140 animals per km² in the urban area, i.e. around 10,000 raccoons in Kassel. This makes it by far the largest urban small bear population in Europe. Hunting in the urban area (which was fruitless in the past) has not taken place for years.
Motifs from Kassel on the 1000 D-Mark banknote

On the last series of D-Mark banknotes , on the 1000 D-Mark banknote, to the left of the portrait of the linguists and collectors of fairy tales, Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm , there was a collage of various historical buildings in Kassel. There you can see the Hercules Monument , the Löwenburg , Wilhelmshöhe Castle , the Fridericianum Museum , the commandant's office, the Marstall , the Grimm Brothers' residence , the Ottoneum , the Carmelite Monastery and houses on the Altmarkt .
See also
literature
- Kassel . In: Meyers Konversations-Lexikon . 4th edition. Volume 9, Verlag des Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig / Vienna 1885–1892, p. 592.
- Paul Heidelbach , Karl Kaltwasser (ed.): Kassel: A millennium Hessian city culture. Bärenreiter-Verlag, Kassel 1957.
- Erich Keyser (Ed. On behalf of the Working Group of the Historical Commissions and with the support of the German Association of Cities, the German Association of Cities and the German Association of Municipalities): Hessisches Städtebuch. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 1957. (German city book. Handbook of urban history, Volume IV 1.)
- Ernst Metz : Alt-Cassel , pen drawings by Ernst Metz, (16 pen drawings from old Kassel in the format 32.5 × 28 cm) Bremer-Druck, Kassel 1973
- Hugo Brunner : History of the royal seat of Cassel. 913-1913. To celebrate the 1000th anniversary of the city. Weidlich, Frankfurt am Main 1978, ISBN 3-8128-0019-5 .
- Karl Baedeker : Baedekers Kassel. 2nd Edition. Ostfildern-Kemnat, Munich 1989, ISBN 3-87954-016-0 .
- Heinz Körner : Kassels Südstadt; Historical development of the southern suburb. Meister, Kassel 1990.
- Berthold Hinze , Andreas Tacke : Architectural Guide Kassel. Reimer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-496-01249-8 .
- City of Kassel: Kassel Lexicon in two volumes, Kassel 2009, ISBN 978-3-933617-32-3 .
- Uwe Feldner: Small history of the city of Kassel , Herkules-Verlag, Kassel 2010, ISBN 978-3-941499-53-9
- Jens Flemming , Dietfrid Krause-Vilmar (ed.): Kassel in the modern age. Studies and research on the city's history. Schüren, Marburg 2013, ISBN 978-3-89472-906-6 .
- Folckert Lüken-Isberner: Big plans for Kassel 1919-1949, projects for urban development and urban planning. Schüren, Marburg 2016, ISBN 978-3-89472-297-5 .
Web links
- Literature about Kassel in the Hessian Bibliography
- Link catalog on Kassel at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
- Documentary on the reconstruction of the city
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office: Population status on December 31, 2019 (districts and urban districts as well as municipalities, population figures based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Figures on the population of Kassel, accessed on February 23, 2017, from serviceportal-kassel.de
- ↑ For the name spelling of documenta-Stadt, see Population of the Hessian Communities , on statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ Chronicle of the University of Kassel - https://www.uni-kassel.de/projekte/index.php?id=36108
- ↑ F. Schmidt-Döhl : The Hessian Bergland - The emergence of a landscape . Shaker Media, Aachen 2012, ISBN 978-3-86858-891-0 .
- ↑ Topographic map of the City Atlas of Kassel ( size = 1: 10,000), publisher : Stadt Kassel, Vermessung und Geoinformation, 2009
- ↑ a b c Datasheet district information 2011 of the City of Kassel, Personnel and Organization Office, Statistics Department, as of December 31, 2011 (creation and printing date February 14, 2012; sheet no. 374279)
- ↑ a b c booklet Annual Report 2009 , City of Kassel, Personnel and Organization Office, Statistics Department, as of August 2009; ISSN 1862-7064 , on stadt-kassel.de (PDF; 924.6 kB)
- ↑ Flyer Kassel Daten , Der Magistrat der Stadt Kassel (Main Office, Department of Overall Municipal Development and Statistics ), as of October 1999
- ↑ a b Issue Annual Report 2010 , City of Kassel, Personnel and Organization Office, Statistics Department, as of September 2011; ISSN 1862-7064 , on stadt-kassel.de (PDF; 738.2 kB)
-
↑ KLIMES - Planning strategies and urban planning concepts to reduce the effects of climatic extremes on the well-being and health of people in cities ( Memento from January 18, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), in: Department of Environmental Meteorology ... Completed Research Projects (University of Kassel), accessed on 18 January 2016, on Umweltmeteorologie.uni-kassel.de; see also:
Department of Environmental Meteorology ( Memento from December 2, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (University of Kassel), accessed on January 18, 2016, at archive.org (archive version from December 2, 2013) - ↑ German Weather Service: Climate Information Kassel. World Meteorological Organization, accessed January 4, 2013 .
- ^ The climate in Kassel , on wetterkontor.de
- ↑ Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (Ed.): Official Gazette of the Reichsbahndirektion in Mainz of January 15, 1927, No. 2. Announcement No. 16, p. 6.
- ^ Frank-Roland Klaube: Chronicle of the City of Kassel , Wartberg Verlag, Gudensberg-Gleichen, 1st edition 2002, p. 4 (see “913”), ISBN 3-8313-1194-3
- ↑ Werner Guth : Kassel an der Fulda - reflections on the meaning of the place name. In: Journal of the Association for Hessian History and Regional Studies, Vol. 115, vhghessen.de, 2010, pp. 1–20
- ^ A b Heinrich Gottfried Philipp Gengler : Regesta and documents on the constitutional and legal history of German cities in the Middle Ages , Erlangen 1863, pp. 467–479, on books.google.de
- ^ Thomas Vollmer, Ralf Kulla: Panzer from Kassel - The armaments production of the companies Henschel and Wegmann . Prolog-Verlag, Kassel 1994, ISBN 3-89395-004-4 . , Page 9
- ^ The year 1945. Kassel , accessed on: May 20, 2018
- ↑ Bonner Geschichtsblätter, Vol. XX, disputes about the provisional federal seat, Bonn 1967
- ↑ See Lueken-Isberner, Folckert: PORTRAIT: Kassel, stairs street , in: moderneREGIONAL, issue 15/2
- ↑ Angela Pitzschke: Lohfelden. Three villages - one place. History and Stories , 1996, p. 346
- ↑ 100 years SPD Vollmarshausen ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on spdnet.sozi.info (PDF; 5.29 MB)
- ↑ Residency limit exceeded: Now there are exactly 200,298 Kasselers , hna.de from December 15, 2015, accessed on December 15, 2015
- ↑ a b Figures on the population. Retrieved December 25, 2016 .
- ↑ Wirtschaftswoche: City Ranking 2011 - Kassel of all places! , wiwo.de of December 9, 2011, accessed on January 5, 2011
- ↑ Figure 2: Mainly religious affiliation in the Hessian communities 2011 Source: Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt Retrieved on July 14, 2019
- ↑ Census2011 - Results - Kassel - Population by gender and religion
- ↑ Map page: Muslims in Hesse - communities . March 27, 2017. Accessed June 4, 2020.
- ↑ Evangelical Church in Kassel About Us , accessed on August 27, 2019.
- ↑ Leaving churches in Kassel has risen sharply since the beginning of the year , in 50 percent more departures , from August 20, 2014, accessed on March 3, 2017, at hna.de.
- ↑ What's next for the Church? Vicar General Christof Steinert on the growing number of people leaving the church
- ↑ Tibetan Buddhists. Council of Religions City of Kassel, accessed on December 14, 2019 .
- ↑ Central Council of Afghan Hindus and Sikhs e. V. Accessed December 14, 2019 .
- ↑ The Faith of the Alevis. In: Alevi-Kassel.de. Retrieved December 14, 2019 .
- ↑ Result of the Mayor election of Kassel in 2017
- ↑ People - SD.NET RIM 4. Retrieved on February 11, 2018 (German).
- ↑ People - SD.NET RIM 4. Retrieved on February 11, 2018 (German).
- ^ Result of the municipal election on March 6, 2016. Hessian State Statistical Office, accessed in April 2016 .
- ↑ Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt: Final result of the municipal election on March 27, 2011 (with data on the 2006 election), on statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt: Final result of the municipal election on March 18, 2001 (with data on the 1997 election), on statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ Election 2001: PDS / KL (Kasseler Linke)
- ↑ Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt: Voting groups in the district and municipal elections 2001 and 1997 , on statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ City partnerships of the city of Kassel! City of Kassel, accessed on August 7, 2010 .
- ↑ Thomas Siemon: Remembering Stallupönen - 100 years of sponsorship in what was then East Prussia HNA May 31, 2015
- ↑ Hessian municipal statistics, on statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ Overview of the municipalities that are eligible for participation in the municipal protective shield ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on hessen.de (PDF; 143.79 kB)
- ↑ Municipal protective umbrella for the city of Kassel on the agreement on partial debt relief of EUR 260.5 million , joint press release by the state of Hesse and the city of Kassel, dated December 18, 2012, on stadt-kassel.de
- ↑ Kassel closes the protective screen , from January 16, 2016, on hessenschau.de
- ^ Salzmann & Companie - Rise and Fall of the Bettenhäuser Textile Company, on uni-kassel.de
- ↑ Press release about Vattenfall and Städtische Werke , thuega.de from December 20, 2010 (PDF; 160 kB)
- ↑ Lohfelden - Kassel, "Am Lohfeldener Rüssel" (intermunicipal industrial park), Economic Development Region Kassel GmbH, wfg-kassel.de
- ↑ Current results - VGR dL. Retrieved January 7, 2019 .
- ↑ Development of the unemployment rate 2000–2014 , serviceportal-kassel.de, accessed on August 2, 2015
- ^ Kassel Documenta-Stadt - statistik.arbeitsagentur.de. Retrieved October 16, 2017 .
- ↑ Zukunftsatlas 2016. Archived from the original ; accessed on March 23, 2018 .
- ↑ The TOP 100 sights in Germany , German National Tourist Board. V., germany.travel, accessed on June 4, 2015
- ↑ Demolition of the Henschel Villa in the Crisis , hna.de June 7, 2010, accessed on June 4, 2015
- ↑ GRIMMWELT Kassel on the vineyard - GRIMMWELT Kassel opening , stadt-kassel.de from September 4th, 2015
- ^ Tic Theater in the Center. In: Kinderkultur Kassel. Kulturamt Kassel, accessed on July 5, 2015 . , on kinderkultur.stadt-kassel.de
- ↑ City Museum Kassel. In: stadtmuseum-kassel.info. Retrieved September 4, 2016 .
- ↑ documenta 2017 in Kassel and Athens - all information and background information , in: HNA's collection of articles on documenta, accessed on March 21, 2017, at hna.de.
- ↑ Article German dialects , in Kleiner Brockhaussches conversations-lexikon . 1854, p. 215
- ↑ Monika Draws-Volk: Language and Dialects, p. 24
- ^ Hessenschau de, Frankfurt Germany: Hessen Kassel is relegated from the regional league. May 27, 2018, accessed on March 5, 2019 (German).
- ↑ All 14 DEL2 clubs receive a license for the 2014/15 season. ESBG Eishockeyspielbetriebsgesellschaft mbH, July 22, 2014, accessed on August 9, 2014 . , on del.org
- ^ Wilhelmshöhe Open , Kassel Tennis Club Bad Wilhelmshöhe 1896 e. V., on wilhelmshoehe-open.de
- ↑ Kassel Roller Derby ( Memento of the original from April 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on kasselrollerderby.de
- ↑ City Library (Kassel), on stadt-kassel.de
- ↑ Numbers and facts ( Memento from September 20, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) (University of Kassel), on uni-kassel.de
- ↑ Paragraph after traffic counts in the city of Kassel in the city portal online at https://www.kassel.de/buerger/verkehr_und_mobilitaet/verkehrsprojekte/verkehrzaehler.php accessed 2019-11-05, the traffic volume map at https://www.kassel.de/ traffic-and-mobility / traffic counting / 14_10_Verkehrsmodell_Analyse-Nullfall_2010_Kfz__DTVw5_.pdf
- ↑ as an excerpt from Kassel (PDF / 2.64 MB) as of 2015 online at https://mobil.hessen.de/%C3%BCber-uns/downloads-formulare/stra%C3%9Fenverkehrsz%C3%A4hlung-2015 accessed 2019-11 -05
- ↑ Andreas Hermann: In parts of Kassel's city center, Tempo 20 should soon apply. In: hna.de . May 10, 2019, accessed May 12, 2019 .
- ↑ nextbike bike rental system
- ↑ Kassel Airport | Numbers, dates and facts. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on January 31, 2018 ; accessed on March 5, 2019 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Attachments - Städtische Werke Energie und Wärme GmbH Kassel. Retrieved October 7, 2019 .
- ↑ Thomas Siemon: Full water is turned into electricity here . Vogt'sche Mühle produces electricity for 670 households - the location already existed in the 12th century. In: HNA Hessische Allgemeine . 11th August 2015.
- ^ District heating network - Städtische Werke Energie und Wärme GmbH Kassel. Retrieved October 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Müllheizkraftwerk Kassel GmbH. Retrieved October 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Excursion to the new 400/110/20 kV substation Sandershausen of the Städtische Werke Netz + Service GmbH. Retrieved October 10, 2019 .
- ^ Electricity for Kassel: A new substation is being built on Sandershäuser Berg. April 3, 2016, accessed October 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Deutsche Bundesbank (ed.): From cotton to banknotes. A new series of banknotes is created . 2nd Edition. Verlag Fritz Knapp GmbH, Frankfurt am Main 1996, ISBN 3-611-00222-4 , p. 131 .