Herne
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 33 ' N , 7 ° 13' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Arnsberg | |
| Height : | 65 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 51.42 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 156,449 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 3043 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postcodes : | 44623-44629, 44649-44653 |
|
| Primaries : | 02323, 02325 | |
| License plate : | HER, WAN | |
| Community key : | 05 9 16 000 | |
| LOCODE : | DE HEE | |
| NUTS : | DEA55 | |
| City structure: | 4 boroughs with 13 districts |
|
City administration address : |
Friedrich-Ebert-Platz 2 44623 Herne |
|
| Website : | ||
| Lord Mayor : | Frank Dudda ( SPD ) | |
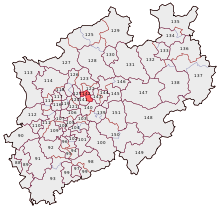
| Location of Herne in North Rhine-Westphalia | ||
Herne is a large city in the Ruhr area and in the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region in North Rhine-Westphalia . It is an independent city in the administrative district of Arnsberg and has been designated as a medium-sized center in state planning . Herne is a member of the Westphalia-Lippe Regional Association and the Ruhr Regional Association .
The city in its current boundaries is the result of several regional reforms through which the surrounding communities, including the former city of Wanne-Eickel , were incorporated into Herne or merged with this city. With around 161,000 inhabitants, Herne is one of the country's smaller cities and, after Offenbach am Main, is the second smallest city in Germany after Offenbach am Main . After Munich and Berlin, Herne has the highest population density of all cities in Germany.
In the past, Herne was characterized by hard coal mining. The mines Shamrock , Constantin , Mont Cenis and Frederick the Great were known .
geography
Herne is located between Bochum and Recklinghausen on the southern slope of the wide Emscher lowlands in the middle of a mining and industrial landscape on sandy terraces of the Emscher Valley. The highest point in the city is 130 m above sea level. NHN , the lowest point 33 m above sea level. NHN . The city limits are 42.80 km long. The largest extension of the urban area is 6.30 km in north-south direction and 12.20 km in west-east direction.
In terms of natural space , the city has about half of its share in Westenhellweg , especially in the south and south-east, and in the northern parts of the city on the Emscherland . The Wanne district lies entirely in the Emscherland.
The Ruhr Regional Association determined the spatial extent and the boundaries of the Ruhr area in 2012. In this context, the center of the Ruhr area was calculated between the westernmost and easternmost as well as the northernmost and southernmost points. The intersection and thus the center of the Ruhr Metropolis is in the Röhlinghausen district on Rolandstrasse. 49 in 51 ° 31 '3 " N , 7 ° 8' 42" O . At this point a granite stone with the inscription You are at the geographical center of the Ruhr area in Herne-Röhlinghausen was placed on the edge of the sidewalk .
Waters
The northern border of Hernes is formed on long stretches by the Emscher , in whose valley the Rhine-Herne Canal runs. Several tributaries flow into the Emscher in the Herne area. These are Börniger Bach , Sodinger Bach , Storchengraben , Landwehrbach and Roßbach , Ostbach and Mühlenbach , Westbach , Schmiedesbach , Dorneburger Bach and Hüller Bach .
natural reserve
In the interior and exterior areas of Hernes there are four nature reserves with a total area of 95 hectares . In their current form, the nature reserves were partly created on areas of the former collieries. Other areas only emerged from the renaturation of the Emscher and its tributaries in the urban area and the relocation of the Emscher to the north, from the former floodplain areas in the district of Unser Fritz / Crange .
In the interior and exterior areas of Hernes there are 24 protected landscape areas with a total area of 875 hectares. As with the nature reserves, these have been designated as areas that are intended to protect the landscape through the conversion of the Emscher and the dismantling of industrial facilities. Inner-city parks, cemeteries and legally protected biotopes are often found within the landscape protection areas .
Other protected areas are the natural monuments and avenues of Herne. There are 14 inner-city trees that are protected as natural monuments. The avenues, like the natural monuments, are protected landscape components under the Federal Nature Conservation Act. The avenues in Herne have a total length of about 10 kilometers.
Neighboring communities
The following cities border the city of Herne. They are named starting in the north in a clockwise direction : Herten , Recklinghausen and Castrop-Rauxel (all Recklinghausen district ) as well as Bochum and Gelsenkirchen (both independent cities )
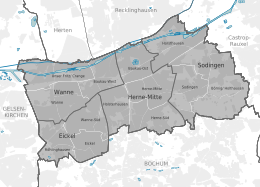
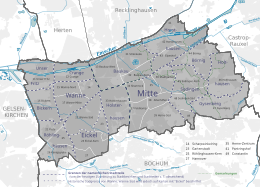
City structure

The Hernes urban area consists of four urban districts . There is a district council in each city district . The district mayor is the chairman of the district council . The city districts are divided into districts. With two exceptions, the names of the districts have been used since the Middle Ages for previously independent communities. Our Fritz is derived from the mine of the same name, and Wanne was called Bickern until 1897 . The former municipal boundaries have been adapted to modern needs when the present city districts were formed. For example, the majority of the historic building is assigned to the Herne-Mitte district, while a small area was added to the Wanne district in 1975. In addition to the city districts, there are also historical trade names such as Altenhöfen , Pantringshof or Vöde . The inhabitants of the city also identify their living environment with former colliery names such as Friedrich der Große (Piepen Fritz), Zeche Königsgrube , Teutoburgia or Constantin .
The city districts with their districts:
- Wanne district : Our Fritz / Crange, Wanne and Baukau-West
- Eickel district : Röhlinghausen, Wanne-Süd and Eickel
- District Herne-Mitte : Holsterhausen, Baukau-Ost, Herne-Mitte and Herne-Süd
- Sodingen district : Horsthausen, Sodingen and Holthausen
Today's districts and city districts differ significantly from the districts and historical affiliations of the city that have remained unchanged since 1975 ; However, the historical and well-known districts can largely be assigned to one or more statistical districts into which the districts are divided:
-
Wanne-Eickel (corresponds to the former town, district 1128; founded 1926)
- Wanne office (former districts Wanne, Crange (until 1905) and Röhlinghausen)
-
Tub
- Statistical districts Wanne-Nord , Wanne-Mitte (current district Wanne), Scharpwinkelring (now district Baukau-West); historically also the statistical district Wanne-Süd in today's district of the same name
- Crange , statistical district of the same name
- Bickern , statistical district of the same name in the Wanne district; the former district of Bickern was renamed Wanne, today only the western part is called Bickern
- Our Fritz (on the former district of Wanne), statistical district of the same name
-
Röhlinghausen , district of the same name
- Statistical districts of Pluto , Röhlinghausen-Kern and Königsgrube
-
Tub
- Amt Eickel (former districts Eickel and Holsterhausen (until 1910))
-
Herne-Eickel
- Districts of Eickel (statistical districts Eickel-Kern and Hanover ) and Wanne-Süd (statistical districts Gartenstadt and Wanne-Süd : despite its name, the latter is almost entirely on the old Eickel district)
- Holsterhausen , district of the same name and statistical district
-
Herne-Eickel
- Wanne office (former districts Wanne, Crange (until 1905) and Röhlinghausen)
- Herne until 1975
- Office of Herne
-
Baukau (district 1127)
- Statistical districts Baukau-West (district Baukau-West) and district Baukau-Ost (statistical districts Baukau-Kern and Strünkede )
-
Herne-Mitte (district 1132)
- Districts of Herne-Mitte (statistical districts Shamrock , Herne-Zentrum , Stadtgarten and Altenhöfen ) and Herne-Süd (statistical districts Feldkamp and Herne-Süd )
-
Horsthausen (district 1135), district of the same name
- Statistical districts Pantringshof , Horsthausen and Elpeshof
-
Baukau (district 1127)
- Office of Sodingen
- Börnig (district 1250), statistical district of the same name in the Holthausen district
-
Sodingen (district 1258), district of the same name
- Statistical districts of Sodingen-Kern , Sodingen-Süd and Constantin (only a colony , not the former Constantin mine ; on the Herner district)
- Holthausen (district 1261)
- Gysenberg , statistical district of the same name in the Holthausen district on the Sodingen and Holthausen districts
- Office of Herne
All parts of the city listed here, some of which are unofficial, with the exception of Unser Fritz and Gysenberg, have or had (parts of Wanne-Eickel) their own landmarks. The districts according to statistical districts differ somewhat from the historical districts:
- The small part of the Hernes district to the north of the railway line now belongs to Baukau-Kern
- The parts of Horsthausen south of the railway went to Mitte, Börnig and, to a very small extent, to Sodingen
- The east of Herne went to Sodingen
- Börnig gave the south-west to Sodingen and the east to Holthausen; the north, north of the railway line, went to Horsthausen
In particular, the area of the former town of Wanne-Eickel was clearly mixed up internally and externally. The statistical district Wanne-Süd (slightly smaller than the district of the same name), in which the historic Wanne was located, has been labeled as Eickel on maps for a long time and the railway line has become the border between the two parts to some extent. Meanwhile, Röhlinghausen, located on both sides of the railway, is now nominally no longer part of Wanne, but of Eickel.
More far-reaching is the incorporation of Baukau-West in the Wanne district and Holsterhausen, part of the former Eickel office, in the Herne-Mitte district. In addition, some of the once independent locations such as Börnig and Bickern now appear nominally at the level of the statistical districts.
climate
Due to the high density of buildings, it is usually a little warmer in Herne than in the surrounding communities. The climate in Herne is characterized by mild winters and rather warm summers, which can also be very humid.
The average annual temperature in Herne is 10.5 ° C. The coldest month is January with 2.6 ° C, the warmest July with 18.7 ° C. The amount of precipitation is approx. 750 millimeters per year, with most of the precipitation, with 85 millimeters, falling in August.
| Herne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Herne
Source:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
history
- Around 880 the name Hernes appears for the first time in a document as haranni in the oldest land register of the Werden monastery .
- 1142 Gvezelino de Strunkede appears as a witness in an Essen document. The Strünkeder knights and barons , who had their castle in the Baukau district, are in the service of the Counts and Dukes of Kleve and receive important state offices under the Brandenburg electors and Prussian kings. Until their extinction at the end of the 18th century, they remained landlords , court and church patrons of Herne.
- In 1561 the Reformation was introduced.
- In 1836 the first stagecoach drove from Bochum to Recklinghausen via Herne.
- The Cologne-Minden Railway was opened in 1847 , after which the village of Herne began to grow into an industrial city.
- In 1856 the Shamrock colliery was the first to be built in Herne.
- On April 1, 1897, Herne received city rights.
- On July 1, 1906, Herne became an independent city.
- The town hall of Herne was inaugurated in 1912 .
- In 1914 the Rhine-Herne Canal and the Wanne-West and -Est ports were completed.
- In 1928 the tram connection from Recklinghausen via Herne to Bochum was opened.
- During the Second World War , on March 31, 1945, German troops blew up the bridges over the canal and the Emscher , making Herne an immediate combat area. On April 9, 1945, the Wehrmacht , police and NSDAP evacuated the city. One day later, US troops occupied Herne relatively without a fight. During the war, the city was the target of a total of 64 Allied air raids, in which 419 people died (see also air raids on the Ruhr area )
- On January 1st, 1975 the cities of Herne and Wanne-Eickel merged to form the "new city" of Herne.
- In 1989 the Bogestra tram line U35 was opened from Bochum main station to Herne Schloss Strünkede . It is the world's first inter-city underground light rail connection.
- In 2017, Herne was included in the 27th edition of the Duden .
Religions
Herne has belonged to the Archdiocese of Cologne since its foundation and was subordinate to the Wattenscheid dean's office . From 1561 the Reformation took hold according to the Lutheran creed. After that, Herne was Protestant for many centuries. Between 1681 and 1686 a reformed congregation was also established. Both united in 1845 to form the Protestant parish of Herne, which has been part of the Evangelical Church in Prussia and its Westphalian provincial church since the transition to Prussia . Herne became the seat of a superintendent , from which the Herne parish later emerged within the Evangelical Church of Westphalia . The Reformation was also introduced in 1577 in the area that would later become the town of Wanne-Eickel. Towards the end of the 19th century, the Protestants belonged to the Gelsenkirchen District Synod. In 1933 they were assigned to the Herne parish. Today this church district is called Herne-Castrop-Rauxel and comprises a total of 15 Protestant parishes within the city of Herne and the neighboring city of Castrop-Rauxel . The former 16 parishes of the city of Herne are: Baukau, Bladenhorst-Zion, Börnig, Christ parish, Trinity parish, Kreuz parish , Luther parish, Sodingen, Crange, Eickel, Holsterhausen, Röhlinghausen, Wanne-Mitte, Wanne-Nord , Pan-South and Pan-West. The parishes of Crange and Wanne-Nord have now merged to form the parish of Crange-Wanne. Since January 1, 2009, the three parishes of Christ, Luther and Trinity have merged to form the Petrus parish and the parishes of Wanne-Süd, Wanne-Mitte and Wanne-West have become the Matthäus parish of Wanne. This means that there are now 11 parishes in the city of Herne. In July 2010, a disused church in Herne ( Paul Gerhardt Church ) was torn down . (see also church closure ).
The few Catholics in today's urban area of Herne continued to belong to the Archdiocese of Cologne until 1821, when they were assigned to the Diocese or Archdiocese of Paderborn . As a result of industrialization, more Catholics moved there. In 1859 an emergency church was built in Herne and in 1862 a separate parish was founded. In the area of the later town of Wanne-Eickel there was a strong Catholic missionary activity in the 17th century. The houses in Crange and Nosthausen in particular became centers of Catholic life. A Catholic chapel was built in Eickel as early as 1687 and in the middle of the 19th century the parish of Eickel had several daughter parishes. They all belonged to the Wattenscheid dean's office. Later, both Herne and Wanne-Eickel (1926) became the seat of their own deanery.
On July 1, 2006, the old deaneries of Herne, Wanne-Eickel and Castrop-Rauxel formed the deanery Emschertal . On January 1st, 2017 in Herne the pastoral associations with the parishes of St. Barbara (Elpeshof), St. Bonifatius , St. Trinity (Holthausen), St. Elisabeth , Herz-Jesu , St. Joseph (Horsthausen), St. Konrad , St. Marien (Baukau), St. Peter and Paul (Sodingen) and St. Pius (Pantringshof) the new parish of St. Dionysius Herne was founded. In the former deanery Wanne-Eickel with the parishes of the Most Holy Trinity, St. Barbara (Röhlinghausen), St. Franziskus (Holsterhausen), Holy Family (Holsterhausen), Sacred Heart (Wanne-North), St. Joseph (Wanne-South), St. Laurentius, St. Marien (Eickel) and St. Michael (Bickern) a merger is also planned. The Syrian Orthodox Church of Antioch, St. Petrus & Paulus e. V. (Wanne-Eickel).
In addition to the well over thirty Protestant and Catholic communities in Herne, there are also various free churches , including the Federation of Evangelical Free Churches ( Baptists ) with the Peace Church in Wanne-Eickel and the Christ Church in Herne-Mitte (both communities have existed since 1905), the Evangelical Methodist Church , the Salvation Army , the Lifeline Congregation ( Seventh-day Adventists ) and the city missions of the Evangelical Society for Germany in Eickel, Wanne and Herne. Since 1959, Pentecostal-Charismatic Christianity has also been represented by the Christian community "Elim" . There are also the Evangelical Free Churches in Herne and Wanne-Eickel, the Wanne-Eickel City Mission and the Herne-Sodingen City Mission. There are also two communities close to the Protestant regional church, one being the regional church community Wanne-Eickel and the Evangelical-Lutheran prayer community Herne Börnig.
The city first came into contact with the New Apostolic faith in 1896 through the cloth merchant Hermann Padberg . Two years later a room was found for the first believers at Neustraße 79 in Herne-Mitte. After further moving in, the New Apostolic Church opened a prayer room in Wanne-Eickel in 1929 . To date, six New Apostolic congregations have emerged in Herne and thus six church buildings have also been built or bought. More than 2000 New Apostolic Christians currently live in Herne, 550 of them are members of the Herne-Mitte congregation.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) and Jehovah's Witnesses are also represented in Herne.
There are several mosques in the urban area.
According to the 2011 census , 32.0% of the population in 2011 were Protestant, 31.8% were Roman Catholic and 36.1% were non-denominational , belonged to another religious community or did not provide any information.
Incorporations
At the beginning of the 19th century, today's urban area comprised several small towns that belonged to the Grand Duchy of Berg from 1807 . The French administration formed the Mairie Herne with the communities Baukau , Bickern , Bladenhorst , Crange , Eickel , Herne, Hiltrop , Holsterhausen, Horsthausen, Pöppinghausen and Röhlinghausen as well as the Mairie Castrop, to which u. a. the communities Börnig , Holthausen and Sodingen belonged. Mairie Herne belonged to the canton of Bochum, Mairie Castrop to the canton of Dortmund. Mayorships were formed from the two mairies in 1813 and offices in 1844 . On August 1, 1875, the office of Herne was divided. The offices of Wanne and Herne were created. Only the municipalities of Baukau, Bladenhorst, Herne, Hiltrop, Horsthausen and Pöppinghausen remained in the Herne office. After Herne received city rights on July 1, 1897 , the Herne office was dissolved. The municipalities of the previous office of Herne formed from then on the office of Baukau, from which the municipality of Hiltrop left in 1902. At the same time, the remaining office of Castrop became the office of Sodingen with the municipalities of Sodingen, Börnig and Holthausen.
On July 1, 1906, Herne left the Bochum district and became an independent city . On April 1, 1908, Baukau and Horsthausen were incorporated from the Baukau office. The remaining municipalities of the Baukau office (Bladenhorst and Pöppinghausen) then formed the Bladenhorst office , which is no longer part of the Hernes municipal area. With the incorporation of part of the municipality of Bladenhorst on April 1, 1926, the Sodingen (municipalities of Sodingen, Börnig and Holthausen) on April 1, 1928, and parts of the Gerthe municipality on August 1, 1929, the urban area of (Old) Herne reached initially its greatest extent.
The western urban area of today's Herne district also belonged to the Herne Office until 1875. But then the Wanne office in the Bochum district (Gelsenkirchen district from 1885) with the communities of Bickern, Crange, Eickel, Holsterhausen and Röhlinghausen was formed. In 1891 the Wanne office was divided, the new Eickel office was created with the communities of Eickel and Holsterhausen. The municipalities of Bickern (from August 13, 1897 Wanne), Crange and Röhlinghausen remained in the Wanne office. On October 28, 1906, Crange was incorporated into Wanne and on April 1, 1910, Holsterhausen was incorporated into Eickel. The two offices of Wanne and Eickel were combined on April 1, 1926 to form the independent city of Wanne-Eickel .
For almost five decades, two independent cities existed side by side before they were united on January 1, 1975 as part of the municipal reorganization to form the new city of Herne. Originally it was planned to incorporate Wanne-Eickel into Gelsenkirchen and from Herne to Bochum.
Population development
In 1910 Herne had more than 50,000 inhabitants. In 1933, the city's population exceeded 100,000, making it a major city . On January 1, 1975 the population of Herne reached its historical high of 193,831 due to the union with the city (since 1955) Wanne-Eickel (92,472 inhabitants 1974). On December 31, 2014, the " official population " for Herne was 154,608 according to updates by the State Office for Data Processing and Statistics North Rhine-Westphalia (only main residences and after comparison with the other state offices ). According to the population projection of the State Office, this number will decrease to 148,600 by 2040.
politics
The administration of the villages in the Herne area was incumbent on the free knights of Strünkede, who, however, very early handed over the sovereignty over their territories to the up-and-coming Counts of Kleve from the Lower Rhine . Since 1391 and 1398, with the union of the county of Kleve with the county of Mark , the rule of Strünkede was assigned to the county of Mark. The Strünkede court still existed until 1812. In French times, the municipality of Herne was formed with a mayor at its head. After the final transfer to Prussia , a mayor or bailiff heads the mayor's office or the office of Herne, to which, in addition to Herne, the municipalities of the surrounding area belonged. After the elevation to the city of 1897, a mayor headed the city administration, who received the title of mayor in 1906 after gaining district freedom .
During the time of the Nazis , the Mayor of that was NSDAP used. After the Second World War , the military government of the British occupation zone appointed a new Lord Mayor and in 1946 it introduced the local constitution based on the British model. Then there was a city council elected by the people , whose members are known as city councilors . The council initially elected the mayor from among its members as chairman and representative of the city, who was active on a voluntary basis. Furthermore, from 1946 the council also elected a full-time senior city director as head of the city administration. 1995 the dual leadership in the city administration was given up. Since then there has only been the full-time mayor. He is chairman of the council, head of the city administration and representative of the city. He was first directly elected in 1999.
City council
The council of the city of Herne currently has 60 (2009 64) members, who are distributed among the individual parties and parliamentary groups as follows:
| Political party | 2009 votes |
2009 seats |
2014 votes |
2014 seats |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | 45.4% | 29 | 44.8% | 27 | have been leading a grand coalition since June 2014 |
| CDU | 25.9% | 17th | 25.9% | 15th | |
| GREEN | 9.3% | 6th | 9.3% | 6th | |
| LEFT | 7.4% | 5 | 6.2% | 4th | |
| FDP | 6.4% | 4th | 2.8% | 2 | |
| The Pirates | - | - | 2.7% | 2 | have formed a joint council group since June 2014 |
| Alternative list Herne | 2.0% | 1 | 1.6% | 1 | |
| AfD | - | - | 4.2% | 2 | |
| Independent citizens | 3.4% | 2 | 1.6% | 1 |
Bailiffs, mayors and mayors
- 1797–1810: Christoph Johann Wilhelm Karl Natorp (1764 Bochum - 1838) Maire
- 1810–1836: Caspar Henrich Steelmenn , mayor or mayor (* 1766 Eickel) at the same time bailiff in Eickel and Bochum,
- 1836–1846: Johann Ludwig Hollweg , mayor, from 1844 bailiff. From 1847 tax recipient in Soest .
- 1847–1851: Hamme Esser , bailiff, later mayor of Lüdenscheid
- 1851–1868: Friedrich von Forell , bailiff
- 1869–1875: Gottfried Uhlenbuch , bailiff († March 30, 1875)
- 1875–1877: Paul Hesse , bailiff
- 1877–1879: Karl von Bock and Polach , bailiff, later mayor of Mülheim an der Ruhr
- 1879–1907: Hermann Schaefer , independent, bailiff, 1897 mayor, 1900 first mayor, 1907 mayor
- 1907–1913: Karl Büren (1871–1942), independent, First Mayor or Lord Mayor
- 1913–1925: Georg Sporleder , independent, First Mayor, from 1917 Lord Mayor
- 1925–1933: Curt Heinrich Täger , independent, Lord Mayor
- 1933–1942: Albert Meister , NSDAP , Lord Mayor
- 1943–1945: Hugo Peiter (1895–1978), NSDAP, Lord Mayor
- 1945–1946: Hermann Meyerhoff (1888–1970), independent, Lord Mayor
- 1946: Heinrich Crämer (1883–1960), SPD, Lord Mayor
- 1946–1948: Hermann Kleine , (1903–1970), CDU, Lord Mayor
- 1948–1951: Josef Walter , SPD, Lord Mayor
- 1951–1975: Robert Brauner , SPD , Lord Mayor
- 1975–1984: Manfred Urbanski , SPD, Lord Mayor
- 1984–1994: Wilhelm “Willi” Pohlmann , SPD, Lord Mayor
- 1994–2004: Wolfgang Becker , SPD, Lord Mayor
- 2004–2015: Horst Schiereck , SPD, Lord Mayor
- 2015 to date: Frank Dudda , SPD, Lord Mayor
Senior City Directors
- 1946–1953: Hermann Meyerhoff, DP
- 1953–1974: Edwin Ostendorf, SPD
- 1975: Acting City Director Alfred Hufeld, independent (* 1910 - 23 December 2009 in Herne) (1960–1975 City Director of the City of Wanne-Eickel )
- 1975–1987: Karl Raddatz, SPD
- 1987–1995: Roland Kirchhof, SPD
(In 1995 the office of the City Director was abolished; since then the Lord Mayor has also been head of administration)
MPs
The city of Herne includes a federal constituency . The Bundestag constituency Herne - Bochum II includes all city districts and the north and east electoral districts of the independent city of Bochum . In 2013, with 48.88 percent of the first votes cast, the direct mandate went to the first-time candidate for SPD MP Michelle Müntefering . In 2013, Ingrid Fischbach (CDU) again entered the 18th German Bundestag via the state list .
Indebtedness
The total debt of the city of Herne at the end of 2012 was 1.181 billion euros. Each resident is thus in debt with 7,646 euros.
For the budget year 2014, the city of Herne has estimated a budget deficit in ordinary income and expenses (including financial income and expenses) of EUR 47.8 million (EUR 309 per inhabitant) in the overall result plan. This corresponds to the second highest per capita budget deficit of all urban districts in North Rhine-Westphalia in 2014.
coat of arms
The coat of arms of the city of Herne shows a black jumping horse in gold, on the left above black mallets and irons set in a cross . It is a simplified combination of the coat of arms of the city of Wanne-Eickel (horse) awarded on June 14, 1929 and the coat of arms of the city of Herne (mallets and iron) awarded on July 30, 1900. The city colors are yellow-black-yellow.
The former town of Wanne-Eickel had a coat of arms with Emscherbrücher wild horse, as it is also represented in the current city coat of arms, combined with the old coat of arms of the Knights of Eickel, as it has been known since 1275, instead of the currently represented mining symbolism. The city colors of Wanne-Eickels from 1975 corresponded to the yellow-black-yellow of today's city of Herne.
The city of Herne had a coat of arms until 1975, which, based on an older model from 1900, had been in use since 1937. It showed an oak tree on "red" Westphalian soil, which was also formed as a hill and symbolized the historical name Haranni ( hair = hill). The coat of arms in the foot with a clover leaf in front of the miner's tools mallets and irons referred to the first Herner colliery Shamrock (clover leaf). The city colors of Hernes were green-white-red from 1915 to 1975.
Town twinning
Herne maintains city partnerships with the following cities :
-
 Hénin-Beaumont , Hauts-de-France , France, since 1954 (with Beaumont until 1971)
Hénin-Beaumont , Hauts-de-France , France, since 1954 (with Beaumont until 1971) -
 Wakefield , West Yorkshire , United Kingdom, since 1956
Wakefield , West Yorkshire , United Kingdom, since 1956 -
 Ometepe , Rivas Department , Nicaragua, since 1988
Ometepe , Rivas Department , Nicaragua, since 1988 -
 Belgorod , Belgorod Oblast , Russia, since 1990
Belgorod , Belgorod Oblast , Russia, since 1990 -
 Lutherstadt Eisleben , Saxony-Anhalt , Germany, since 1990
Lutherstadt Eisleben , Saxony-Anhalt , Germany, since 1990 -
 Konin , Greater Poland Voivodeship , Poland, since 1991
Konin , Greater Poland Voivodeship , Poland, since 1991 -
 Beşiktaş , Istanbul Municipality , Turkey, since 2016
Beşiktaş , Istanbul Municipality , Turkey, since 2016 -
 Luzhou , city in Sichuan Province , China, since 2018
Luzhou , city in Sichuan Province , China, since 2018
Sponsored cities are:
-
 Jauer (town and district) in Lower Silesia
Jauer (town and district) in Lower Silesia
-
 Strehlen (town and district) in Lower Silesia
Strehlen (town and district) in Lower Silesia
-
 Ortelsburg (town and district) in Warmia-Masuria
Ortelsburg (town and district) in Warmia-Masuria
External impact
On April 6, 2017, the Lord Mayor presented the new brand logo in cooperation with Stadtmarketing Herne GmbH . This is the result of a multi-stage branding process: the support campaign. While the brand logo with the words "Stadt Herne" is reserved for the administration, supporters are encouraged to use the associated statement Mit Grün. With water. In the middle. like to appropriate a coat of arms and thereby express their connection with Herne. This also corresponds to the title of the associated website: www.herne-kann-was.de
jurisdiction
Herne is the seat of two local courts. The district court of Herne on Friedrich-Ebert-Platz is responsible for the districts of Herne-Mitte and Sodingen . The local jurisdiction of the district court of Herne-Wanne extends to the districts of Wanne and Eickel, this court building is located on Wanner Hauptstrasse. In addition, Herne is the seat of the Herne Labor Court for the areas of Herne and the Recklinghausen district (excluding Gladbeck).
Economy and Infrastructure
traffic
The federal highways 42 ( Kamp-Lintfort - Dortmund ) and 43 ( Münster - Wuppertal ) run through the urban area of Hernes . Both meet in the middle of the urban area at the Herne motorway junction . In addition, the federal road 226 Bochum-Gelsenkirchen runs through the western part of the city in the Eickel and Wanne districts. The former federal highway 51 Recklinghausen-Bochum ran through the Herne-Mitte district. However, it was the national road 551 rededicated and thus is no longer the responsibility of the federal government, but the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The B 51 was replaced throughout the city by the A 43. The entire road network has a length of around 390 kilometers. It is composed as follows:
- Motorways: 14.8 kilometers,
- Federal roads: 7.5 kilometers,
- State roads: 38.8 kilometers,
- District roads: 34.2 kilometers,
- Local roads: 283.2 kilometers and
- Private roads: 8 kilometers.
Herne has several inland ports on the Rhine-Herne Canal with a connection to the Rhine and via the Dortmund-Ems Canal to the Ems and the Mittelland Canal .
After the merger of the formerly independent cities of Herne and Wanne-Eickel in 1975, Herne now has two train stations. While the Herne train station in the Herne Mitte district enables regional connections, the main train station in the Wanne district can also be reached in long-distance traffic by stopping ICE and IC trains , making it the more important of the two train stations in terms of traffic. Both are on the Duisburg – Dortmund railway line ; in Wanne-Eickel the runway branches off to Hamburg . The Herne station was opened by the Cologne-Mindener Eisenbahn as early as 1847 . The Herne-Börnig stop also exists on the Emschertal Railway from Dortmund to Dorsten ; the station in Wanne-Eickel-Unser Fritz (on the section north of Wanne-Eickel Hbf) is closed.
The pan-Herne Railway and Harbor GmbH (WHE) operates on the Rhine-Herne canal ports pan-West, pan-East and the freight village with container terminal at the West Harbor. The WHE mainly carries out transports with montane goods as well as the combined transport of the Herne industrial companies and connects to the freight station of the Wanne-Eickeler Hbf.
In the local public transport (ÖPNV) several RegionalExpress and RegionalBahn lines from DB, Abellio Rail , Eurobahn and NordWestBahn as well as the S-Bahn Rhein-Ruhr offer connections to Recklinghausen , Dortmund , Duisburg and Essen . Eurobahn runs between Hamm and Düsseldorf . Essen - Mönchengladbach or in the opposite direction Haltern - Münster offers DB Regio AG, Region NRW , Dorsten the NordWestBahn ; Abellio commutes between Bochum and Gelsenkirchen . All lines run at uniform prices within the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (VRR) ; this also applies to the U35 subway line operated by Bochum-Gelsenkirchener Straßenbahnen AG ( Bogestra ) between Herne Schloss Strünkede and Bochum Hustadt (TQ) ; Tram line 306 of the Bogestra in the districts of Wanne and Eickel between Wanne-Eickel Hauptbahnhof and Bochum Hauptbahnhof ; Buses of the HCR , the Bogestra and the Vestische trams . The extension of the U35 in the direction of Recklinghausen planned in the 1970s will probably no longer be realized for financial reasons; a cost-benefit analysis prepared by the state government of North Rhine-Westphalia within the framework of integrated overall transport planning (IGVP) comes to the conclusion that the costs for this measure are greater than the benefits (assessment: RB Arnsberg, rail project).
The U35 (Herne Schloss Strünkede ↔ Bochum Hustadt (TQ)) , tram 306 ( Wanne-Eickel Hbf ↔ Bochum Hbf ) and the bus route 311 ( Herne Bf ↔ Castrop-Rauxel Münsterplatz) have the most frequent intervals in Herne .
economy
As a result of the colliery closures, Herne experienced difficult economic times, as it was not possible to create as many jobs in other industries as were lost in mining and mining suppliers. From 2005 to 2014 the average prices for residential real estate fell by 13% - a consequence as well as an expression of the economic crisis and the decline in population.
In 2016, Herne achieved a gross domestic product (GDP) of € 3.582 billion within the city limits . In the same year, GDP per capita was € 22,918 (North Rhine-Westphalia: € 37,416 / Germany € 38,180). The city thus has the third lowest GDP per capita among all independent cities in Germany. In 2016 there were around 61,800 gainfully employed people in the city. The unemployment rate in December 2018 was 10.5% and thus well above the average for North Rhine-Westphalia of 6.4%.
Manufacturing
- Since the company was founded in 1934, the globally operating concrete pump manufacturer Schwing has had its corporate headquarters in Herne-Crange, directly on the Rhine-Herne Canal and within sight of the Cranger Kirmes .
- The international manufacturer of drive technology and refrigeration and air conditioning technology, the Vulkan Group , has had its headquarters in Crange since the 1950s . Around 1200 people are employed worldwide.
- The Steag GmbH operates in Herne Baukau a coal-fired power plant, which also heat for the regional supply in the Ruhr District Heating Network Ruhr couples out.
- The London-based and internationally active chemical company Ineos (130 employees locally) and Evonik GmbH (400 employees) operate a production facility close to the city center in Herne .
Service companies
- Börnig became known as the UPS distribution center , as all UPS deliveries from outside Europe to continental Europe are reloaded there. Also in Börnig, not far from the UPS distribution center, is the Ruhr distribution center of the pharmaceutical wholesaler Phoenix AG, which supplies pharmacies in the entire Ruhr area , Sauerland and Siegerland with pharmaceuticals around the clock .
- The listed Sanacorp Pharmahandel is also a pharmaceutical wholesaler with (2010) 200 employees.
- One of the largest bus tour operators in Germany, Anton Graf GmbH Reisen & Spedition , is based in Herne.
- In September 2007 Deutsche Annington Westfalen GmbH relocated its customer center from Recklinghausen to Herne. From here, the housing stocks for the customer service centers in Herne, Wanne-Eickel, Recklinghausen, Waltrop, Castrop-Rauxel and Datteln are looked after. The customer center is located in the main post office building at Bebelstrasse 20. The Deutsche Annington Immobilien Group (DAIG), based in Bochum, is the largest housing company in Germany with over 230,000 apartments.
The handicrafts that are important for the service-oriented city of Herne are organized by the Herne / Castrop-Rauxel district handicrafts association.
media
In Herne, a daily newspaper maintains a local editorial office. The Westdeutsche Allgemeine Zeitung , WAZ for short , reports on regional events with the local editions of Herne and Herne-Wanne-Eickel. In addition to the WAZ, there was the "Herner Zeitung", the Westfälische Rundschau and the Ruhr-Nachrichten, Dortmund, with the local edition Herne until the mid-1970s.
Since September 1, 1990, the city has had its own local radio station called Radio Herne . The weekly newspaper Herne / Wanne-Eickel appears twice a week with a circulation of 86,300 copies and is distributed free of charge to all households. The Sunday News ran until April 2018, when it was discontinued for economic reasons.
The online magazine of the cultural association "Herner Netz eV" has existed in Herne since 2001. It offers the latest news from Herne, Wanne-Eickel and the region every day.
The online newspaper “halloherne” has existed since 2009. She reports on current local events.
education
The city's Haranni high school was founded in 1872 as a private school for girls. The Pestalozzi-Gymnasium , which is also municipal, celebrated its 100th birthday in 2002 in a new building that was moved into in 1980 on Harpener Weg. The largest municipal grammar school with 1,100 students is the Otto Hahn grammar school, founded in 1957 . The Gymnasium Wanne and the Gymnasium Eickel are located in the area of the former town of Wanne- Eickel. Furthermore, there are four comprehensive schools, four secondary schools, seven secondary schools, 26 elementary schools, eight special schools and one private and one music school in Herne.
The Marienhospital in Herne is a hospital of the Ruhr University and a place for medical training for students.
In Herne-Sodingen, the further training academy of the Ministry of the Interior of North Rhine-Westphalia was built on the site of the former Mont-Cenis colliery .
The Herne observatory in Dorneburger Park offers regular sky observations, astronomical lectures and demonstrations in the planetarium .
Aid organizations
Fire and rescue services
In addition to the 150 full-time fire fighters, the city of Herne also has 200 volunteers. These ensure security within the city and also provide assistance beyond the city limits.
technical aid organization
As one of the few cities in Germany, Herne has two local branches of the technical relief organization . The two local branches are the local branch Herne and the local branch Wanne-Eickel. This peculiarity complements the fire brigade and rescue service of the city of Herne significantly, as the existing guards of the fire brigade are further supported by technical groups.
Culture and sights

Theater and cinema
With the small theater herne, Herne has its own ensemble , founded in 1995 , which had already worked together on various theater projects in the Ruhr area since 1977. In November 1998 the ensemble was able to open its own theater. It has 50 seats. By 1970 there was already a theater in Herne, the Zimmer Theater, which was closed at the time. The program of the small theater in herne includes serious works as well as boulevard and children's theater.
Since January 2004, the Mondpalast von Wanne-Eickel, under the direction of Christian Stratmann, has also been used for theatrical performances . It is the first popular theater in the Ruhr area to date . Behind the Art Nouveau facade of the former town hall building, mainly comedies are performed in which the actors of a permanent ensemble play well-known types of the area in their roles.
Since October 2004, Herne has had a modern multiplex cinema with six halls. The cinema is called Filmwelt Herne , is located on Berliner Platz and is one of the first cinemas in North Rhine-Westphalia to regularly show films in digital version .
Libraries
The city of Herne maintains two main offices of the public city library in the cultural center in the city center and in Wanne not far from the pedestrian zone , which can be used by all citizens for a small annual fee. In addition to a mobile library (“book bus”), a book delivery service for older citizens is maintained.
The Martin Opitz Library , formerly the Library of the German East, a special library with a collection area that covers the entire area of East Central, Eastern and Southeastern Europe, is located very close to the cultural center . It is supported by a foundation that the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, the city of Herne and the Federal Republic of Germany are involved in establishing. The publicly accessible library of the Emschertal Museum in Baukau offers a reference collection with a thematic focus on archeology, folklore and handicrafts in Herne and the Ruhr area.
Museums
- The Regional Association of Westphalia-Lippe maintains the LWL Museum for Archeology .
- The Emschertal Museum has three locations:
- In Renaissance -Wasserschloss Castle Strünkede a regional history collection is presented.
- In the neighboring park, in an old Wilhelminian style villa of the von Forell family, there is the Städtische Galerie in Strünkede Castle Park . The focus of the graphic collections and special exhibitions are shown there.
- In the local history and natural history museum Wanne-Eickel , you will find an exhibition about the cultural, economic and natural history of the region.
- In a hall at Riemker Strasse 50, the private Opel Museum Herne shows Opel vintage cars, but also sewing machines, bicycles and even refrigerators from the Opel brand as well as Opel souvenirs .
See also: List of museums in Herne
Buildings
Worth seeing in Herne is the already mentioned moated castle Strünkede in Baukau, which is considered the city's landmark . A medieval castle at its core, it was completed in its present Renaissance form in the early 17th century. The entire ensemble in the Strünkeder Castle Park also includes the Gothic castle chapel , the municipal gallery in a Wilhelminian style villa and the former half-timbered mill Schollbrockhaus from the 19th century, now a café. Also characteristic is the town hall (1911/1912), a neoclassical representative building with a monumental facade design by Wilhelm Kreis ; it has been a listed building since 1985. It is located in an urban planning district with interesting buildings (Post 1910, District Court 1914-1919, Reichsbank 1924 and Tax Office 1926 (both canceled in 2009), Police 1927-1929, former Sparkasse 1929-1930 (today Citizens Office)) from the first third of the 20th century. The main Protestant church is the Kreuzkirche from 1875. The parish church of St. Bonifatius is the oldest Catholic church in Hernes. In addition to the modern church, its listed neo-Gothic tower is worth mentioning, which houses a shoe shop on its ground floor.
In Börnig, the Teutoburgia settlement , a former colliery settlement of the Teutoburgia colliery , has been extensively restored in recent years . Together with the old shaft structure of the former colliery, the viewer is presented with the image of a garden city ideal of the early 20th century.
In Herne-Sodingen, the training academy of the Ministry of the Interior of North Rhine-Westphalia was built on the site of the former Mont Cenis colliery . This building contains the world's largest building-integrated solar system .
In the districts of Wanne and Eickel are the former town hall of Wanne-Eickel , the Protestant church Wanne ( Christ Church ), the Protestant church Eickel ( Johanneskirche ), the Catholic church in Wanne-Süd ( St. Joseph , "Lion Church") , the artist mine “Our Fritz” , the brine and thermal bath Wilhelmsquelle and the main train station .
The "Stadion am Schloss Strünkede" in Baukau, built around 1910, was one of the largest stadiums of the time. It can accommodate up to 32,000 people.
organ
The Kreuzkirche in Herne possesses the most important cultural and historical instrument of the city of Herne and one of the few surviving organ works in the Ruhr area with a 130-year history. The organ was built in 1877 by the organ builder Schulze and Sons from Paulinzella in Thuringia. Only a few instruments of this time survived the Second World War and the wave of new organs that began in the 1950s .
The St. Josephs Church in Herne Horsthausen has a classical organ built in Herford in 1810. It has been in use again since 1987 and is the oldest surviving and at the same time most valuable organ in Herne.
Parks and green spaces

There are various parks and recreational areas in Herne. Some examples are given below:
- The Gysenberg Forest in the south of Hernes in the Sodingen district is an urban forest and is used for local recreation for the residents. The Gysenbergpark , which was founded in 1970 as the first district park in the Ruhr area, is attached to it. A little further to the east is the Volkspark Sodingen with the Kaiser Wilhelm Tower on the Beimberg .
- The city garden is located in the city center of Herne . As a former cemetery, Behrenspark has been converted into a public green area near the pedestrian zone on Bahnhofstrasse .
- The Stadtgarten Wanne-Eickel with the hall building renamed Mondpalast is the counterpart to the Herner Stadtgarten in the formerly independent town in the west of Hernes. The Volksgarten is located in the Eickel district .
- The castle park surrounds Strünkede Castle in Herne-Baukau. The complex is landscaped with several graves . In Börnig, the KunstWald Teutoburgia is a stop on the Route of Industrial Culture .
- The Südpark was created in the southern Altenhöfen district of Herne at the source of the Westbach. In the center of the park is the “duck pond”, fed by the Westbach .
- The DSC Wanne-Eickel stadium and the DJK Wanne-Eickel 88 football pitch are located in the Wanne-Süd sports park. There is also an artificial turf pitch that is widely used by young people .
- The Königsgruber Park on the border to Bochum in the Röhlinghausen district offers extensive lawns and branched paths through small trees and shrubs as well as an airfield for model airplanes . Because of its peripheral location far away from the main roads, this park is popular with many joggers, walkers and cyclists.
The urban area is flanked by two regional green corridors of the regional association Ruhr : In the west of Hernes, the regional green corridor D leads from the Rhine-Herne Canal to the Westpark in Bochum. In the east of the city, the regional green corridor E runs between Herne and Castrop-Rauxel .
The city cemeteries are also considered to be significant green areas today. The largest is the Südfriedhof on Wiescherstrasse. The Herne forest cemetery is located in the area of the city of Herten .
Sports
Herne has several well-known football teams, of which SC Westfalia 04 Herne , who was West German champion in 1959, and DSC Wanne-Eickel played together at times in what was then the 2nd Bundesliga North . In addition to these, SV Sodingen , which caused a sensation as a league club in the 1950s before Westfalia Herne, is particularly steeped in tradition .
The women's basketball team at the Herner TC has been playing in the women's basketball league since the 2007/2008 season (with a one-year break, 2011/2012) , the men's team is active in the major league.
The archery club Sherwood BSC Herne has produced the most successful archers in Germany. The oldest shooting club in Herne is the Holthausen citizens shooting club, founded in 1857.
The baseball and softball club Herne Lizards also plays in Herne.
The ice hockey club Herner EV also played successfully in the 1st League North at times . After its bankruptcy (1999/2000) the Herner EV merged with the ESG Twister , from which the new association Herner EV Blizzards emerged. The Blizzards play in the Regionalliga NRW (West) in front of an average of approx. 1000 spectators, with attractive opponents also in front of significantly more. In the 2006/07 season they won the final against RT Bad Nauheim 6-3. In the summer of 2007, in addition to the HEG, the Herner Eissportverein 2007 was founded. In contrast to the HEG, the club, which is not financially burdened, first takes over the game operations of the 2nd team, the youngsters and the HEG women's team. Because the HEG is only entitled to participate in the - fourth-class - Regionalliga NRW 2007/08 for the first team, the first team will play as a syndicate from both clubs - outsourced to a new GmbH. Instead, the HEG should no longer be kept alive after the final conclusion of the insolvency proceedings. In 2007, the still very young club managed to qualify for the major league immediately in its first season.
The Emscher rowing club at the Wanne-Eickel lock on the Rhine-Herne Canal has had many national and international successes since it was founded in 1928. So the eighth won the German junior champion in 1965, the double foursome with helmsman became the German youth champion in 1969. The rowers Winfried Firley and Walter Käß from RV Emscher were members of the Germany Eighth and came back to Wanne-Eickel in 1972 as Vice World Champion. Thomas Domian , Olympic champion from 1988 drove temporarily for the RV Emscher. Annina Ruppel , a member of the club throughout her sporting career, won gold, silver and bronze in the German women's eight between 2001 and 2003. Bernd Heidicker , 1995/1996 as a club member, junior world champion in eight and junior vice world champion in two without a helmsman. Batsman in Germany eighth and winner of gold, silver and bronze at the 2001–2007 World Championships. Batsman for RV Emscher in the rowing league .
Important football venues in Herne are the stadium at Strünkede Castle , the venue for SC Westfalia 04 Herne, and the stadium in the Wanne-Süd sports park, which is home to DSC Wanne-Eickel. The ice arena Herne is located at Gysenbergpark , in which the Herner EV competes.
Herne has three public swimming pools. The LAGO brine, wave and outdoor pool is located in Gysenbergpark in Sodingen . The south pool , a combined indoor and outdoor pool (formerly summer pool and only outdoor pool), is located south of the city center of Herne and the Wanner indoor pool. Opposite the Wanner indoor pool is the Wilhelmsquelle brine and thermal bath in the Wanne district, which is operated by the St. Josefs Hospital. The Wananas in Wanne water park, which is particularly popular with families , fell victim to a major fire on November 10, 2011 and was reopened as an expanded new building in December 2016.
Furthermore, the fans of Borussia Dortmund use the name Herne / West for arch rivals FC Schalke 04 in order not to pronounce its name.
Regular events
Festivals and music
- As a cultural event of international importance, the Early Music Days take place in Herne in November .
- Since 2002, the Wanner Mondnächte, known beyond the city limits, have been taking place in Wanne around the Buschmannshof. The Wanner Mondnächte take on the cult around the famous moon from Wanne-Eickel , which is also sung about in the song by Friedel Hensch and the Cyprys in the title “The moon from Wanne-Eickel”. The music festival, at which some very well-known cover bands perform, takes place annually around Corpus Christi on three consecutive days.
- The KAZ Open Air, which has been taking place in the Hibernia Skatepark since 2008, has attracted nationwide attention. In the last few years bands such as Egotronic , Rantanplan , Pascow and Love A have been guests. A skate contest is also integrated into the festival.
Art fair
A regular art fair has been held in the Flottmann Halls since 1996 . Since 2005 the “KUBO” art prize for young art has been awarded there by the Herner Stadtwerke. In 2006, the organizer decided to change the name of this very successful exhibition hybrid from the militant “artificial bomb” to the variety-like “Kuboshow” without changing the socio-cultural character of the event.
Folk festivals
From the first Friday in August, the Cranger Kirmes (on Alt Wanne-Eickeler urban area) will be held for ten days . It is one of the largest folk festivals (4,700,000 visitors in 2008) in Germany after the Munich Oktoberfest (see list of German folk festivals ).
The largest public picnic in Germany takes place once a year as part of the Boulevard Festival on Bahnhofstrasse. Every year over 900 meters of festively decorated tables invite you to celebrate at the Nightlight Dinner.
Local flavor
In the townscape, the mining past lives on in some of the well-preserved winding towers.
The cities of (Alt-) Herne and Wanne, which merged in 1975, have two different telephone area codes . The license plate liberalization that took place in 2012 brought the reintroduction of the vehicle license plate "WAN", formerly for Wanne-Eickel, as an alternative to "HER". There is no Herne main station next to Herne station, but Wanne-Eickel has one. There are no longer stations in the districts in Wanne-Eickel, but at Herne ( Herne-Börnig stop , ex Wanne-Eickel – Unser Fritz ).
Wanne-Eickel can also claim a high level of awareness , for example through the song " Der Mond von Wanne-Eickel " or the Cranger Kirmes .
Personalities
Personalities of the city of Herne are the honorary citizens, sons and daughters of the city as well as other personalities who lived or are still living in Herne.
Others
Sponsorships
The city of Herne has taken on the sponsorship of a Lufthansa Airbus A340-313X with the identification D-AIGL, which Lufthansa uses on intercontinental flights. Furthermore Herne held the sponsorship of the Navy - speedboat S63 "vulture" between 1976 and its decommissioning in of 2005.
Focus city test
Of 83 cities tested, Herne performed worst in the Focus city test 2000 and was ranked 83rd behind Recklinghausen and Remscheid . The reasons for this include a lack of cultural and other leisure facilities and a low proportion of highly qualified jobs.
In 2019, Herne came second to last , ahead of Gelsenkirchen .
Trivia
Laubenstrasse in the Teutoburgia settlement in the east of Herne was used as a film set for the German film Die Vampirschwestern .
literature
- Westphalian town book ; Volume III 2nd part of the German city book. Handbook of urban history - on behalf of the working group of historical commissions and with the support of the German Association of Cities, the German Association of Cities and the German Association of Municipalities, ed. by Erich Keyser, Stuttgart 1954.
- Ludger Tewes : Middle Ages in the Ruhr Area. Settlement on the Westphalian Hellweg between Essen and Dortmund (13th to 16th centuries) , Schoeningh Paderborn 1997, ISBN 3-506-79152-4
- Ground plan for German administrative history 1815–1945. Edited by Walther Hubatsch, Volume 8: Westphalia. Marburg an der Lahn 1980, ISBN 3-87969-123-1 .
- Lots of fun. The story of a city in the Ruhr area , a film by Norbert Kozicki, FRG, 1996.
- Robert Grabski: Herne in old views. Zaltbommel / Netherlands 1977.
- Frank Braßel / Michael Clarke / Cornelia Objartel-Balliet (eds.): Nothing is as beautiful as… history and stories from Herne and Wanne-Eickel , Essen 1991, ISBN 3-88474-365-1 .
- Barbara Dorn / Michael Zimmermann: practical test. Herne and Wanne-Eickel 1933–45. Everyday Life, Resistance and Persecution under National Socialism. Bochum 1987, ISBN 3-88339-584-6 .
- Norbert Kozicki: "The Kaiser is gone!" The November Revolution in the offices of Wanne, Eickel, Herne and Sodingen. A contribution to the local history of the labor movement. Herne 1986.
- Norbert Kozicki: Herne in old views , volume 2. Zaltbommel / Netherlands 1992, ISBN 90-288-5398-7 .
- Friedhelm Wessel: Grubengold and Kumpelriviera. Wartberg-Verlag 2007, ISBN 3-8313-1812-3 .
- Friedhelm Wessel: All about Piepenfritz - everyday life in a colony. Sutton-Verlag, 2008, ISBN 978-3-86680-401-2 .
- Friedhelm Wessel: The Friedrich der Große colliery - history and stories about "Piepenfritz" in Herne. Regio-Verlag 2010, ISBN 978-3-929158-24-3 .
- Focus 50/2000, 83 cities in the test.
- Literature on Herne in the catalog of the German National Library
- Rudolf Eistermann u. a (ed.): Our Horsthausen: History and stories experienced and written down by Horsthausen pensioners. Frischtexte Verlag, Herne 1999, ISBN 978-3-933059-00-0 .
- Wolfgang Viehweger: Trace of Coal: Europe in Herne and Wanne-Eickel. Frischtexte Verlag, Herne 2000, ISBN 978-3-933059-03-1 .
- Heinz-Joachim Barsickow: Political camps and Reichstag elections in the Herne area before the First World War . Brockmeyer University Press, Bochum 2004, ISBN 3-8196-0660-2 (Bochum historical studies, modern history, vol. 18).
Web links
- Website of the city of Herne
- Wiki Hün un Perdun - The historical site of the city of Herne. Private wiki on the subject
- Herne in the Westphalia Culture Atlas
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ^ HiTS - Demography, Work, Social. Retrieved May 15, 2020 .
- ↑ The Center of the Ruhr Metropolis , Regional Association Ruhr, accessed on May 16, 2013
- ↑ Michael Muscheid: Change from district chairman to district mayor. WAZ , December 22, 2009, accessed August 5, 2017 .
- ↑ Interactive city map of Hernes with city district and city district boundaries ( Memento of the original from April 9, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , GIS project Herne
- ↑ a b Topographical Information Management, Cologne District Government, Department GEObasis NRW ( Notes )
- ^ Weather Herne, Westphalia - Wetterdienst.de
- ↑ Rudolf Kötzschke (Ed.): Die Urbare der Abtei Werden ad Ruhr (= Publications of the Society for Rhenish History XX: Rheinische Urbare). Vol. 2: A. The land register from 9. – 13. Century, ed. by Rudolf Kötzschke, Bonn 1908, reprint Düsseldorf 1978; Vol. 3: B. Stock books, lifting and interest registers from the 14th to the 17th century , Bonn 1908, reprint Düsseldorf 1978; Vol. 4, I: Introduction and Register , I. Name Register , ed. by Fritz Körholz, Düsseldorf 1978; Bd. 4, II: Introduction , Chapter IV: The economic constitution and administration of the large manor in Werden , subject register, ed. by Rudolf Kötzschke, Bonn 1958, here especially vol. 2, p. 72.
- ^ A b c d Stephanie Reekers: The regional development of the districts and communities of Westphalia 1817-1967 . Aschendorff, Münster Westfalen 1977, ISBN 3-402-05875-8 , p. 244 f .
- ↑ Summary of the fighting. In: huen-un-perdün.de. Archived from the original on February 8, 2015 ; accessed on August 5, 2016 .
- ↑ a b Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality register for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 329 .
- ↑ rp-online.de, August 8, 2017
- ↑ http://www.matthaeusgemeindewanne.de/index.php?option=com_content&view=frontpage
- ↑ Demolition of the church has started. WAZ, July 2, 2010, accessed August 5, 2016 .
- ^ New Apostolic Church - Herne district
- ↑ Census 2011 District-Free City of Herne Religion (%) , accessed on February 29, 2020
- ^ City of Herne (ed.): Herne von Ackerstr. to Zur-Nieden-Straße. City history as reflected in the street names. Stadtdruck, 1997, p. XIII.
- ↑ a b Stephanie Reekers: The regional development of the districts and communities of Westphalia 1817-1967 . Aschendorff, Münster Westfalen 1977, ISBN 3-402-05875-8 , p. 229 and 291 .
- ↑ Population development in cities and districts not belonging to the district of North Rhine-Westphalia from 2014 to 2040 ( memento of the original from May 18, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , published May 24, 2015.
- ↑ http://www.wahlresults.nrw.de/kommunalwahlen/2014/aktuell/a916000kw1400.html
- ↑ Debt ranking of the 103 independent cities in Germany . Household Control.de. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- ↑ Product area results planning in the 2014 budget of the 22 independent cities in North Rhine-Westphalia in comparison. Household control.de, accessed on November 21, 2014 .
- ↑ For the pictorial representation of the coat of arms of the city of Herne (old and new) and the former city of Wanne-Eickel , see the website of the city of Herne: City arms in the course of time .
- ↑ Michael Muscheid: Besiktas in Turkey is Herne's new twin town. Cities marriage. WAZ, August 4, 2016, accessed August 5, 2016 .
- ↑ Support campaign
- ↑ New city logo on designtagebuch.de, April 11, 2017
- ↑ Herne Labor Court
- ^ [1] , WAZ Herne-Wanne-Eickel, ICE trains stop again at Wanne-Eickel main station, accessed on December 28, 2018
- ^ Die Zeit, December 17, 2015, p. 17.
- ↑ Current results - VGR dL. Retrieved January 7, 2019 .
- ^ Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia. Federal Employment Agency, accessed on January 7, 2019 .
- ↑ STEAG - Herne power plant. Retrieved on March 11, 2019 (German).
- ↑ The halloherne UG. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on August 5, 2016 ; accessed on August 5, 2016 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ 100 objects Herne, volume 6 ( Memento from July 19, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Dagobert Ernst: Major fire at the "Wananas" leisure pool in Herne causes 15 million euros in damage. WAZ, November 10, 2011, accessed August 5, 2016 .
- ↑ The West: The New Wananas - Two Swimming Pools in One , November 23, 2016. Accessed January 6, 2017
- ↑ Wanner moon nights. Stadtmarketing Herne GmbH, archived from the original on February 11, 2015 ; accessed on August 5, 2016 .
- ↑ KAZ
- ↑ 2011 program ( Memento from May 10, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Gabriele Heimeier: 573. Cranger Kirmes sets a new visitor record. WAZ, August 11, 2008, accessed August 5, 2016 .
- ^ Sponsorships from the city of Herne
- ↑ Photo of the Lufthansa Airbus A340 D-AIGL "Herne"
- ↑ Focus Cities Test: 83 Cities in the Test , Focus No. 50 (2000), published on November 13, 2013
- ↑ Ranking revealed: Germany's most future-proof city is in the middle of Hessen , focus.de from November 22, 2019