Ems
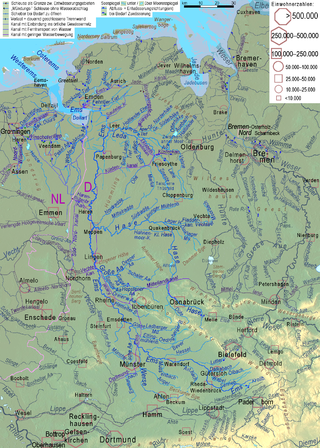
The ( Latin Amisia ; Westphalian iems , North Lower Saxony and Dutch Eems , Sater Frisian : Oamse ) is a 371 km long river to the North Sea in northwest Germany . It is the longest river that has its source in Germany and flows into the sea, and that keeps its name between the source and its mouth.
The Ems rises in the Senne near Schloß Holte-Stukenbrock in the state of Westphalia , first flows through the Westphalian Bay in a north-westerly direction, roughly parallel to the Teutoburg Forest and from the border with Lower Saxony , between the Rheine and Salzbergen , then in a north direction to the North Sea. From the Dollart onwards , the Ems forms the sometimes controversial border with the Dutch province of Groningen . It flows into the North Sea about 27 kilometers northwest of Emden between Pilsum and Eemshaven .
River data and catchment area
The Ems is 371 km long; 206 of them are navigable. Its mean flow rate is 80 m³ / s in its middle course ( Versen level ) and at its mouth it is 125 m³ / s.
The Ems catchment area is 13,160 km². It lies as a narrow, south-north extending approximate rectangle between the river system of the Rhine in the west and that of the Weser in the east. The Ems runs for more than half of its course near the western edge, so that the river system is asymmetrical. The largest tributaries, Hase and Leda , flow from the right (east) . Together they contribute more than 45 m³ / s to the water flow of the Ems. The largest left tributary is the Werse with around 6 m³ / s.
The lower reaches of the Hase and Leda, directed to the west, run in meltwater channels in front of the former ice edge layers of the Saale Cold Age ( glacial valleys ). In the southernmost former meltwater channel, between Teutoburg Forest and Wiehengebirge , lies the well-known, albeit artificial, bifurcation of the upper Hase (into the lower Hase flowing to the left and the Else flowing east ). The western edge of the catchment area is also largely due to the formation of the Ice Age: the Münsterland gravel sands separates the Ems area from that of the Stever ( Lippe ) and the Vechte in the west.
The stratified rib of the Teutoburg Forest is the most striking elevation of the Ems area, which is otherwise largely characterized by lowlands and rather low relief elevations. The Bielstein (393.6 m) is the highest point in the Ems region.
course
The Ems is divided into three sections (see Emsland ):
- Obere Ems (between the source and the Emswehr Hanekenfähr near Lingen )
- Middle Ems (between Lingen-Hanekenfähr and Papenburg)
- Lower Ems (between Papenburg and the confluence with the North Sea)
- Ems estuary
Upper Ems
source
The Ems begins as one of those numerous brooks of the Senne that do not arise in a valley of the Teutoburg Forest , but below its foot in the only slightly sloping foreland.
The source is about 130 m above sea level. NHN on the border of the town of Schloß Holte-Stukenbrock , district of Stukenbrock-Senne, and the municipality of Hövelhof . It pours and is a seepage source , i.e. H. the source stream arises from a multitude of water outlets.
Münster lowland bay
As far as Telgte , the Ems flows mainly westward with few river bends. From then on it meanders increasingly and from Greven its main direction is northwards. It drains the east (without the easternmost part further south) of the Münster lowland bay by absorbing numerous streams from the Teutoburg Forest and its foreland, but also the Axtbach , the Werse from the Beckum Mountains , which runs parallel to it for a long stretch , and the Münstersche Aa .
The first cities that the Ems flows through were centers of small independent territories in the Middle Ages: Rietberg was the seat of the County of Rietberg . The rulers of the Rheda rule resided in Rheda , the suburb of Rheda-Wiedenbrück located downstream . The name Rheda (from roadstead ) indicates that in the Middle Ages the city was the top landing place for shipping on the Ems.
At Vadrup the Ems forms the city limits of Münster for a few kilometers , but far from their urban settlement area. At Gittrup (in Münster) it is crossed by the Dortmund-Ems Canal . The “old journey” of this Münster-Gelmer canal overpass (“KÜ” for short) is an important industrial monument of the late 19th century. The canal initially runs at a distance of up to 10 km, but was created from Rheine between 3 km and very close parallel to the east of the river.
North German Lowlands
After Rheine, the Ems passes the state border between North Rhine-Westphalia, the state part of Westphalia, and Lower Saxony. After that, it hardly has any western tributaries in front of its estuary, as the Vechte, which runs parallel here , drains the area towards the IJssel , i.e. towards the Rhine delta . The water from the east, from the north of the western Osning and from the Ankumer Höhe collects the Great Aa , which flows into the Ems at Hanekenfähr . In Salzbergen , the Ems is crossed by a 100-meter-long bridge on the Autobahn 30 .
Middle Ems
Between Hanekenfähr and Lingen , the moraine ridge of the Lingener Höhe joins the river from the east . The valley of the Hase , which flows into Meppen , extends north of it . After that, the foothills of the sandy Hümmling reach close to the Ems. To the north of it lies the Wilde Moor with the nature reserve Aschendorfer Obermoor / Wildes Moor as part of the large contiguous area of the Emslandmoore . The Bourtanger Moor stretches to the west of almost the entire middle course . A little below Meppen, the Ems in the urban area of Haren passes the Emsland Euro port on the right .
Ems estuary
Inner estuary
The weir in Herbrum has formed the upper limit of the over 100 km long tidal area of the Ems, also known as the tidenem , since 1899 . The mean tidal range is three meters, at low tide there can be a tidal wave. Up to the mouth of the Leda , this estuary is still narrow like a river.
At the mouth of the Leda is the second largest of the old port cities on the Unterems, Leer , whose port, strictly speaking, does not branch off from the Ems, but from the Leda.
Below, the estuary takes on the shape of a funnel. There are a few sandbanks and islands between the Ledam estuary and Dollart: The Bingumer Sand is a real island with a summer dike . Jemgumer Sand and Midlumer Sand are each groups of small sandbanks. The Hatzumer Sand consists of some swamp and some sand.
The Ems Barrage has existed near Gandersum shortly before the Dollart since 2002 , which barely obstructs normal tidal currents, but is closed in the event of threatening floods. In contrast to similar barrages over smaller rivers, the opportunity was not used to connect the footbridges required for operation to form a bascule bridge for pedestrians and light vehicles. As a special service for the Meyer Werft in Papenburg, the barrage is not only used to prevent threatening water rises upstream, but also to raise the headwater through congestion for the transfer of ships and thus increase the water depth upstream.
22 km after the Leda estuary, the inner estuary ends at the inner Ems estuary near Pogum . This is where the (inner) outer Ems begins.
Dollard

The broad part of the estuary has the character of a bay, is officially referred to as the Outer Ems and is still considered part of the course of the river. The Emden Waterways and Shipping Office (WSA Emden) writes about the Unterems: "South of Emden it flows through the Dollar ". In fact, however, the current channel of the Ems, called from the Emden port on the Emder fairway , is separated from the tidal flats of the Geise from the Priel system of the Dollart. On the north bank of this section of the river is the largest of the port cities on the Ems, Emden . The Rheiderland lies on the south bank of the Dollart on both sides of the German-Dutch border. The Westerwoldsche Aa flows into the southernmost point of the Dollart . From here to the sea, the left bank of the Ems belongs to the Dutch province of Groningen .
The north-east facing headland of the Punt van Reide forms the western boundary of the Dollart.
Neck and outer mouth of the Ems
From the Punt van Reide in the southeast to the mouth of the Knockster Tief on the German side and the mouth of the Delfzijler Zeehavenkanaal on the Dutch side, the Außenems has a neck 3 to 4 km wide and about 5 km long. Its eastern half is divided into the outer part of the Emden fairway in the north and the mouth of the Dollart in the south by the wadden tongue of the Geisesteert . Termunten is on the south bank of the Neck . This is where the Termunterzijldiep flows , whose catchment area extends over 20 km inland to behind Winschoten .
The Outer Ems estuary connects to the neck . On the left bank is the Dutch port city of Delfzijl , founded in the Dutch War of Independence as a fortified port of the Wassergeusen . The straight line from the Dutch coast three kilometers east of the port entrance of Eemshaven to the bank of the Krummhörn near Pilsum is defined as the seaward boundary of the Ems river .
Landscape history
The course of the river Ems has changed significantly over the centuries, mainly due to the effects of the tide of the sea , here storm surges , especially on its lower course. When the Second Cosmas and Damian flood penetrated far into the interior of the Rheiderland in 1509 , today's Nesserland (the Nesse) near Emden was separated from the Rheiderland. The dollar was born. As a result, the Ems paved a different course in the following decades. In order to keep the Emden harbor on the Emd Emsbogen seaworthy , work began as early as 1583 to regulate the flow conditions in the Ems through the Nesserlander Höft , an oak sheet pile wall built south of the city at the influence of the Ems in the Dollart . Nevertheless, the Emsbogen silted up.
Land transport
At Bingum the 945 meter long Ems tunnel of the federal highway 31 (Emslandautobahn) crosses the Ems. In idle spanning Jann-Berghaus bridge , the longest folding bridge in northern Europe , the river.
The Emsland line runs parallel to the Ems ( Rheine station - Norddeich -Mole). The Leer – Groningen railway branches off to the west from this railway line . Part of the latter is the Friesenbrücke bridge east of Weener over the Ems ; it was rendered unusable by a shipwreck on December 3, 2015.
Außenems
The Outer Ems is legally divided into an inner and an outer part by the Eemshaven - Pilsum line. The inner one, with the outer mouth of the Ems, Emder Fahrwasser and Dollart, is considered part of the Ems river. The outer, northwest of the line mentioned, is assigned to the territorial sea , although the tidal flats that limit the flow channels are nautically part of the inner coastal waters .
Outer outer ems
The outer Outer Em is divided into two arms by the island of Borkum :
- The Westerems , south and west of Borkum, forms the main fairway and main drainage channel of the Ems through the Wadden Sea . The port of Eemshaven is located on the Dutch south bank.
- Osterems , east and north of Borkum, is the smaller spouse . Its flow channel is initially relatively flat and divided lengthways (see Westerbalje). It branches off to the right of the main channel and leads east of the Randzel mudflat, which adjoins Borkum to the south, to the north. It unites with the Priel Ley coming from the Leybucht and then with the Priel Memmertbalje, in the continuation of which it turns to the west and faces the open sea between the small island of Memmert in the north and the sandbank Lütje Hörn and the island of Borkum in the south.
environment
The Ems has been straightened in many places, a few places in the natural course of the river have been preserved. In recent years, sections of the river have been renatured using measures of renaturation ecology , and some of the remaining oxbow lakes have been reconnected in order to reduce the flow velocity. Three floodplain sections near Westbevern northeast of Münster are looked after by the NABU nature conservation station Münsterland . There, Heck cattle and Konik used to cultivate the grassland and transform back into one of large mammals designed landscape gradually the floodplain. Between 2010 and 2013, several kilometers between Telgte and Warendorf (area one) were renatured, whereby so-called initial channels were dug to create secondary channels, while the main canal was filled in.
From October 2016, a 2 km long oxbow river of the Ems was re-connected between Emsdetten and Saerbeck near Hembergen. On August 10, 2018, the work was ended with the opening of the oxbow and the simultaneous construction of a dam to tie off the puncture. The oxbow river became part of the river again, but the piercing was now an oxbow lake. The puncture now forms a biotope and is intended as a relief channel in the event of flooding.
2014/2015 the developed state of Lower Saxony the master plan Ems in 2050 to restore the ecosystem of the river Ems in Lower Saxony . Large sections of the Ems are FFH or EU bird protection areas . As part of the demands of the EU Commission to implement the guidelines for the designated Natura 2000 areas on the Ems, the State of Lower Saxony was threatened with infringement proceedings with fines running into the millions. The development of the master plan was the last option accepted by the EU Commission to avert such criminal proceedings.
The German part of Dollart Bay ( GKZ : 3974) is a quiet zone in the Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park . The Außenems nature reserve was established in January 2019 .
List of tributaries
The largest tributaries are the Hase in Meppen and the Leda in Leer. The river Hase is an exception with its almost continuous river name from the source to the mouth and the length above its tributaries under the Ems tributaries. Most of them have a different name for their upper reaches than their lower reaches, and many have longer secondary tributaries.
|
Left tributaries |
Right tributaries |
shipping

Most of its navigable stretch of the Ems is a federal waterway , namely as an inland waterway from Ems -km 44.8 south of Rheine to its seaward limit according to the federal waterway law at Unterems -km 67.76. The section from Rheine to Gleesen (Km 82.7) is one of the so-called other federal inland waterways. Until 1998, the section between Greven and Rheine also belonged to the federal waterways, but was assigned to the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. This section is also navigable for pleasure craft. The outer area of the Ems is part of the North Sea lake waterway . The federal waterway is administered by the waterway and shipping authorities (WSA), first from the WSA Rheine to Gleesen , then from the WSA Meppen to Papenburg and finally by the WSA Emden . Up to the confluence with the Dortmund-Ems Canal near Meppen, the Ems is used exclusively for motorized sport and leisure boat traffic.
In the further course the river serves as part of the Dortmund-Ems Canal for commercial shipping, and below Papenburg as a transport route for large ships from Meyer Werft . Because of the ever larger ship units that are manufactured at the Meyer shipyard, especially for the cruise sector, the Ems has to be dammed with the help of the Ems barrage at Gandersum . This is the only way to ensure sufficient water depth for the transfer of the cruise ships to the North Sea. So far, this "stowage" could only be carried out in the winter months (September 16 to March 14) in order to be considerate of the breeding birds in the foreland of the Ems, otherwise their eggs would be flooded. For economic reasons, Meyer Werft is also pushing for the possibility of traffic jams and a ship transfer in summer. There are currently also plans to build a canal from Papenburg to Leer to relieve the Ems at ship overpasses at Meyer Werft. An extension of the planned Ems Canal beyond Papenburg to the Dortmund-Ems Canal near Dörpen is also being considered. A feasibility study has been commissioned. The new canal construction could then mean a renaturation of the river between Papenburg and Leer.
The Ems as a federal inland waterway begins in Greven at km 0 and ends in Meppen at km 124.10. From there on, the Dortmund-Ems Canal is measured as far as Papenburg. The kilometers of the Unterems as a maritime shipping route have their km 0 in Papenburg and ends at the Eemshaven – Pilsum line at km 67.76.
In the Außenems and on the Unterems as far as Papenburg - due to an agreement with the Netherlands from 1986 - the special shipping regulations for the Ems estuary apply instead of the shipping route regulations . The inland waterways regulations apply above Papenburg .
The pilotage on the Ems is guaranteed by the Emden Lotsenbrüderschaft , whose members are also called "Emslotsen" and are deployed from their pilot stations on Borkum and in Emden.
Channel connections
The Ems is integrated into a network of shipping canals, the larger of which are important transport routes, but the smaller ones are now mainly or only used by recreational skippers:
- The Dortmund-Ems Canal was opened in 1899 and included the older (1824/25) Ems-Hase Canal . It has a connection to the Mittelland Canal in Hörstel and is connected to the Rhine in the south by the Wesel-Datteln Canal and also by the Rhine-Herne Canal . From Papenburg , the Ems is included on 59 kilometers of shipping route from the inland to the Ems estuary. Viewed upstream, the Dortmund-Ems Canal leaves the river bed of the Ems in Meppen and, after using the estuary stretch of the Hase to Hanekenfähr south of Lingen , runs parallel to the east of the Ems for about 26 kilometers. From Hanekenfähr, the canal uses the riverbed of the Ems again for 1.7 kilometers, after which the canal finally leaves the Ems.
- The Eemskanaal , laid out 1866–1867, connects the Ems in Delfzijl with Winschoterdiep and Van Starkenborghkanaal in the city of Groningen .
- The Haren-Rütenbrocker Canal , laid out 1870–1878, connects the Ems in Haren with Ter Apel , where the Stads Compascuumkanaal - Ter Apelkanaal provides connections to the south (west) and north (west). These Dutch connections are no longer classified, but still approved for recreational traffic.
- The Ems-Vechte Canal , laid out between 1870 and 1879, connects the Ems in Hanekenfähr with the Vechte in Nordhorn . The adjoining Dutch waters are no longer classified, but are still permitted for recreational traffic.
- The Ems-Jade Canal , built between 1880 and 1888, runs between Emden and Wilhelmshaven and connects the Ems with the Jade Bay .
- The coastal canal has connected the Ems with the Hunte near Oldenburg since 1935 , which then connects to the Weser.
tourism
The federal highway 31 in Lower Saxony runs largely parallel to the Ems. Above Leer it accompanies the river in the east, between Leer and Emden in the west and north. The A 31 crosses under the river west of Leer in the Emstunnel .
The Ems is accompanied and crossed by various long-distance cycle paths :
- Ems cycle path between Holte-Stukenbrock Castle and Hövelhof at the sources of the Ems and Emden at the mouth of the Ems
- German fen route
- Dollard route Between Papenburg and Delfzijl around the Dollart and the mouth of the Ems
- Dortmund-Ems Canal Route
- EmsAuenWeg between Warendorf and Rheine
- Emsland route
- Hase-Ems-Weg
- United Countries Tour
Many sections of the Ems are protected landscape areas. The natural and non-navigable areas are popular destinations for canoeists. Among other things, a part of the Ems between Lingen - Hanekenfähr and Meppen city center (total distance about 40 kilometers) is not or only partially usable by motorized boats. However, getting on and off canoes is possible and permitted at fixed moorings. There are two smaller rapids between Lingen-Schepsdorf and Lingen-Holthausen.
The Ems has twice been included in North Rhine-Westphalian state garden shows : In Rheda-Wiedenbrück in 1988 (as Flora Westfalica ) and in Rietberg in 2008. Both areas can still be used today as high-quality local recreation areas. In 2014 the 5th Lower Saxony State Garden Show took place in Papenburg.
The Ems adventure world in Schloß Holte-Stukenbrock near the Ems springs offers an interactive information tour with information on the river from the source to its mouth in the North Sea and its surroundings.
Places on the Ems
- Westphalia and the Westphalian Emsland
(Districts Gütersloh , Paderborn , Warendorf , Steinfurt ) Holte-Stukenbrock Castle , Hövelhof , Steinhorst , Westerwiehe , Schöning , Rietberg , Rheda-Wiedenbrück , Gütersloh , Harsewinkel , Herzebrock-Clarholz , Beelen , Warendorf , Eine , Telgte , Greven , Saerbeck , Emsdetten , Rheine
(Districts of Emsland and Leer , and the independent city of Emden) Salzbergen , Emsbüren , Elbergen , Lingen , Biene, Geeste , Meppen , Haren , Heede , Lathen , Fresenburg , Steinbild , Kluse , Dersum , Dörpen , Lehe , Aschendorf , Rhede , Tunxdorf , Papenburg, Weener , Leer , Jemgum , Midlum , Critzum , Ditzum , Pogum , Rorichum , Oldersum , Gandersum , Emden , Knock
- Netherlands
(Province of Groningen ) Delfzijl , Eemshaven
Nautical mileage
Nature reserve
- upstream -
- Ems-km 0 Greven, weir Schöneflieth, below the kilometer for the federal waterway
- Ems-km 10 km canal bridge Münster-Gelmer (Dortmund-Ems Canal)
- Ems-km 11 tributary of the Werse from the left
- Ems-km 26 Telgte
- Ems-km 40 Warendorf
- Ems-km 80 Rheda-Wiedenbrück
Federal waterway
- downstream -
- Ems-km 1.0 tributary of the Munster Aa from the left
- Ems-km 27.4 Emsdetten
- Ems-km 44.8 south of Rheine, beginning as a federal waterway (since January 1, 1998)
- Ems-km 46.2 Rheine with Ems weir Rheine
- Ems-km 46.6 upper lock Rheine
- Ems km 47.5 Rheine lower lock
- Ems-km 51.7 at the Bentlage lock
- Ems-km 58.1 Salzbergen
- Ems-km 71.9 Listrup lock
- Ems-km 82.7 from Gleesen to km 84.4 Emswehr Hanekenfähr shared bed with the Dortmund-Ems Canal
- Ems-km 86.5 Lingen nuclear power plant
- Ems-km 106.5 Dalum
- Ems-km 124.1 shared bed with the Dortmund-Ems Canal
- Ems-km 124.15 Meppen, tributary of the Hase from the right as the bed of the Dortmund-Ems Canal. The kilometers of the Ems ends here and is continued as far as Papenburg by the kilometers of the Dortmund-Ems Canal (DEK). From here on numerous defense arms and oxbow lakes, some of which still have the old Emskilometersteine.
- DEK-km 166.6 Meppen , beginning of the Ems as part of the Dortmund-Ems Canal
- DEK-km 174.1 Hüntel lock
- DEK-km 178.9 Haren (Ems)
- DEK-km 185.9 Hilter lock
- DEK-km 195.1 Düthe lock
- DEK-km 202.5 Confluence of the coastal canal
- DEK-km 205.9 Bollingerfähr lock
- DEK-km 212.6 Herbrum lock , tide limit
- DEK-km 225.8 Papenburg, end of the Ems as part of the Dortmund-Ems Canal, end as an inland waterway
- Unterems-km 0.0 Papenburg, beginning of the own Unterems-kilometering, beginning as a sea shipping route
- Unterems-km 14.2 Leer, tributary of the Leda from the right
- Unterems-km 30.3 Oldersum, branch of the Ems side canal
- Unterems-km 32.2 Ems Barrage near Gandersum
- Unterems-km 40.9 entrance to the port of Emden
- Unterems-km 67.76 seaward boundary of the inland waterway Ems, beginning of the Außenems as a sea waterway
Trivia
A cargo ship was named Emsriver and was attacked by Somali pirates in the Gulf of Aden on December 27, 2010 .
See also
literature
- Martin Eckoldt (Ed.): Rivers and canals. The history of the German waterways . DSV, Hamburg 1998. ISBN 3-88412-243-6
Web links
- WSA Emden: Relief map of the tidenems → Selection: "Topography"
- Implementation of the European Water Framework Directive in the international river basin district Ems , on ems-eems.de
- Ems , in Living Waters in North Rhine-Westphalia , on ems.nrw.de
- near-natural river dynamics on the Lower Saxony Ems
- Nature pleasure route of the NABU on the Ems
- The Ems near Emsbüren
- Citizens' initiative RETTET DIE EMS , on rettet-die-ems.de
- Near-natural water and floodplain development of the Ems at one - own dynamics and habitat diversity, on life-nrw.de
- The Ems renaturation at Warendorf-One
- The "Obere Ems" and its catchment area in Westphalia and in southwestern Lower Saxony
- Information platform Undine: Emsgebiet - high water, low water, hydrometeorological status, water quality
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b German basic map (DGK 5) in Topographical Information Management, Cologne District Government, Department GEObasis NRW ( information )
- ↑ a b c d State Office for Nature, Environment and Consumer Protection North Rhine-Westphalia ( Memento of the original from September 27, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 313 kB)
- ^ Deutsches Gewässerkundliches Jahrbuch Weser-Ems 2008 Lower Saxony State Agency for Water Management, Coastal Protection and Nature Conservation, accessed on January 22, 2016 (PDF, German, 6184 kB).
- ↑ a b B. Schuchardt, M. Schirmer, G. Janssen, S. Nehring and H. Leuchs: Estuaries and brackish waters ( Memento of the original from January 31, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF file; 342 kB). In: F. De Jong, J. F. Bakker, C. J. M. van Berkel, N. M. J. A. Dankers, K. Dahl, C. Gätje, H. Marencic and P. Potel (eds.): Wadden Sea Quality Status Report . Common Wadden Sea Secretariat Wilhelmshaven, Wadden Sea Ecosystem No. 9; P. 176.
- ↑ a b c d e Lengths (in km) of the main shipping lanes (main routes and certain secondary routes) of the federal inland waterways ( memento of the original from January 21, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
- ↑ Transport Infrastructure ( Memento from June 21, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), on archive.org
- ↑ Sign at the source of the Ems
-
↑
Emden Waterways and Shipping Office:
- Deepening of the Außenems to Emden ( Memento of the original from May 29, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- Planning approval for the Außenems deepening, landscaping accompanying plan (PDF, not accessible to all browsers) ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Planned nature reserve "Außenems" , nlwkn.niedersachsen.de
- ^ The Unterems (WSA Emden), on wsv.de
- ↑ Gyula Samu: A contribution to the sedimentation conditions in the Emden fairway and Emden harbor , nautical chart excerpt, p. 4, on vzb.baw.de (PDF; 33.72 MB)
- ↑ Ship accident on the Ems: heavily damaged railway bridge has to be rebuilt. In: Spiegel Online . December 4, 2015, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ Destroyed Friesenbruecke - ship had no defects. In: ndr.de. Archived from the original on December 5, 2015 ; Retrieved January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ In Ibbenbürener Volkszeitung from August 11, 2018: "Back to the old river bed"
- ↑ Questions and answers on the Ems master plan , accessed on March 26, 2015, at Umwelt.niedersachsen.de
- ↑ Krummhörn-Dollart leaflet. In: nationalpark-wattenmeer.de. March 9, 2016, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ container ship Eilbek In: meyerwerft.de , accessed on September 14 2017th
- ↑ Directory E, Ser. No. 13 and Directory F of the Chronicle ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, on wsv.de.
- ↑ List 3.2, Ser. No. 12 ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, on wsv.de.
- ↑ Kai Schöneberg: Ems Canal: A waterway as a maneuver. In: taz.de . January 2, 2009, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ Ems Canal. Feasibility study as the next step (Leer district), accessed on March 5, 2009, at presse-service.de
- ↑ 9 questions and answers about the planned Ems Canal (WWF), accessed on March 5, 2009 (PDF; 48 kB)
- ↑ Map of the Wasserschifffahrtsamt Meppen , accessed on August 8, 2011, at wsa-meppen.de
- ↑ Ems Adventure World (official homepage)