Bundesstrasse 51
| Bundesstrasse 51 in Germany | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Start of the street: |
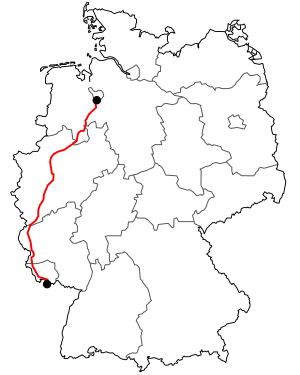
Stuhr ( 53 ° 0 ′ N , 8 ° 47 ′ E ) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End of street: |
Kleinblittersdorf ( 49 ° 7 ′ N , 7 ° 4 ′ E ) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall length: | 570 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
State : |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Development condition: | two-lane | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bundesstrasse 51 in Münster | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Course of the road
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The federal highway 51 (abbreviation: B 51 ) is a German national road . It runs in a south-westerly to southerly direction from Stuhr near Bremen through Lower Saxony , North Rhine-Westphalia , Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland to the French border near Saargemünd . Federal Motorway 1 runs roughly parallel over the entire length of 570 km .
history
Reichsstrasse 51 , introduced in 1934, linked sections with completely different origins.
The road sections between Osnabrück and Bad Iburg and between Münster and Telgte were expanded on the basis of existing old roads as early as the 18th century . The northernmost section of the route between Bremen and Münster was planned between 1811 and 1813 as a military road for Napoleon I's troops , which as Route Impériale No. 3 connect Paris with Hamburg through the Hanseatic departments annexed in 1811 and continue from Münster via Dülmen to Wesel / Venlo ( today's B 58 ) should lead. After the Napoleonic troops withdrew in 1813, the road remained largely unfinished.
In the years 1838 to 1842, the middle section of the route from Haltern via Recklinghausen to Bochum was built as the first road in Vest Recklinghausen . In the densely populated Bergisches Land , the road between Remscheid- Lennep and Cologne (Wermelskirchener Chaussee) was completed in 1775. This street was called the Cöln-Berliner Staatsstraße in 1865 .
The southern section between Cologne and Trier was started in 1826 and completed in 1841. In Saarland was started in the 18th century with the road construction. According to the city chronicle, the road between Völklingen and Bous was completed in 1734.
Original course
The federal highway 51 leads from the Hanseatic city of Bremen over the Ruhr area to the Saarland and on the French border to Lorraine .
In Bremen , south of the Weser , the B 51 begins and runs five kilometers together with the B 6 to Brinkum in Lower Saxony , municipality of Stuhr .
The B 51 passes through the flat, agriculturally used Lower Saxony part of the North German Plain via Bassum (23 km) and the district town of Diepholz (42 km), past Lower Saxony's second largest lake, the Dümmer , and over a small one through the North Rhine-Westphalian district of Minden -Lübbecke running section, to the edge of Osnabrück (110 km). Before and after Osnabrück the road crosses the nature parks of Wiehengebirge and Teutoburg Forest - south of Osnabrück four lanes to Dörenberg and further through Bad Iburg and Glandorf to the state border to North Rhine-Westphalia.
After 174 km the B 51 reaches Münster . In the inner city area, it was or is being expanded into a four-lane urban motorway . It continued through the southern Münsterland, through Haltern am See and Recklinghausen to Herne . It leads through the middle of Bochum (240 km), past the mining museum and theater , and crossed the Ruhr near Hattingen .
The old route touches the east of Wuppertal , crosses the B 7 in the Langerfeld district and now runs as the L 58 through the Bergisches Land to Remscheid- Lennep . From there on via Bergisch Born , Wermelskirchen and Burscheid to Leverkusen . It leads over the Mülheimer bridge along the banks of the Rhine (between Hohenzollern and Deutzer bridge as the Rheinufertunnel ) through Cologne (311 km), where it also meets the federal highways 8 and 9 in quick succession . A few kilometers southwest of Cologne it crosses the A 4 and the A 553 . It crosses Brühl , then crosses the short A 553 at the level of the Phantasialand , and then continues under the A 61 at Weilerswist . From here it runs almost parallel to the A1 to Euskirchen .

From Euskirchen (347 km) it now runs again as the B 51 past Bad Münstereifel (until the 1970s it ran through the middle of the city) for almost 100 km across the sparsely populated Eifel and beyond the Rhineland-Palatinate border to Prüm (409 km). The old, original route ran from Prüm through the Nimstal via Schönecken, Seffern, Bickendorf, Bitburg (now the L 5). From Bitburg (441 km) it finally leads to the Roman city and Moselle metropolis of Trier (457 km). After Trier, it approaches the Luxembourg border to within a few kilometers and comes across the Saar river for the first time near Konz .
It now accompanies this river from Saarburg as a riverside road, across the state border at Saarhölzbach into Saarland . She leaves the Saar between Mettlach and Besseringen to shorten the Saar loop near Orscholz . In the past, the B 51 between Saarburg and Mettlach did not run along the Saar, but through the Saargau , a foothills of the Hunsrück , along the current L 132 / B 407 through Perdenbach and Trassem , further along the current L 131 through Freudenburg and Weiten , from there along today's L 176. Between Besseringen (498 km) and Saarlouis (518 km), the old route corresponds to today's L 174. Then it goes through the old industrial area near Völklingen ( world cultural heritage ) to Saarbrücken (541 km). Behind this city, the B 51 continues along the Saar to its end at the French border at Sarreguemines (Saargemünd), where it merges into the French N 61 , which after a few kilometers joins the A4 to Paris or Strasbourg .
In total, the B 51 covered a distance of 569 km, although the sections in which it was replaced by a motorway cannot necessarily be included. On the other hand, the B 51 has become longer compared to the era of the Reichsstrasse because numerous bypasses were built.
Graduated Sections
The motorway-like bypass of Belm has been under traffic since mid-2019 and merges into the A 33 , the Belm through-road has been phased out. The B 51 continues at the Osnabrück-Nahne junction of the A 30 .
South of Münster, the B 51 is being replaced by the A 43 and the A 1, while the former route has largely been downgraded to the L 551. The section from the Bochum- Riemke junction to the Sprockhövel junction was phased out as of January 1, 2010, and the subsequent section to Remscheid-Lennep as of January 1, 2008.
The B 51 has also been replaced by the A 553 and again the A 1 between the junctions Brühl- Nord and Euskirchen . On January 1, 2015, the section between Euskirchen and the Blankenheim junction was downgraded to Landesstraße 194.
On January 1, 2014, the section from the beginning of Berliner Straße in Cologne's Mülheim district to the Burscheid motorway junction ( A 1 ) was downgraded to community or state roads (mostly L 188).
Further stepped sections run between Prüm and Bitburg ( A 60 ) and since the beginning of 2007 between Besseringen and Saarlouis ( A 8 ).
Supraregional importance
The importance of the B 51 as a supraregional road was hardly given in the northern course before the last gap in the A 33 was closed . However, since the gap was closed in 2019 and the Belm bypass was completed, the travel time from Bremen to Bielefeld has been shortened so much that it is hardly worth taking the B 61 from the Bremen area to the Ravensberger Land .
Between Blankenheim and Trier (with the exception of the section between Prüm and Bitburg that has been replaced by the A 60 ), the B 51 is of supraregional importance because it has to replace the A 1 that is being planned or under construction. Since considerable long-distance traffic numbers are achieved in this area, it is almost consistently three-lane, sometimes even four-lane ( motorway-like road ). The combination A 1 - B 51 - A 60 represents the shortest connection between the Cologne area and the west of Rhineland-Palatinate, Luxembourg and Lorraine , which, unlike the motorway route, is not free of intersections. The traffic between southern France or Spain and Scandinavia often uses this connection. This section is part of the E 29 .
Planning
Discussions about the inclusion of individual sections of the B 51 in the truck toll remained unsuccessful until the introduction of the truck toll for all federal highways on January 1, 2018. The temporary closure for heavy traffic in the A 64 (near Trier) to A 60 (near Bitburg) section, as has been successfully done on the B 3 in northern Hesse, for example , has so far remained unsuccessful. The most important obstacle to the closure are two two-lane bridges of the B 52 at the current end of the A 64 in the direction of A 1 / A 602 , which are in need of renovation and which could not accommodate the additional heavy traffic.
Saarland
The bypass of the Merzig district of Besseringen , which has been required since the 1960s, had been under construction since June 2011 and was completed on December 13, 2013. The costs for the 3.6 km section amounted to approx. 27.2 million euros; two viaducts over 200 m long were built. Around 16,000 vehicles passed through the town every day.
Rhineland-Palatinate
From the summer of 2004, the Trier western bypass, also known as the " Moselle ascent ", was in the planning approval process . The plan is to lead the federal highway 51 from Konz west of the Trier mountain on a new route to the Moselle heights and connect there to the A 64. However, on May 12, 2005, the Koblenz Higher Administrative Court overturned the planning approval decision . Construction in the next few years therefore appears unlikely.
For this reason, the B 51 was further expanded in the Trier city area. Between the University of Applied Sciences and the traffic lights at the Kaiser Wilhelm Bridge, the road was continuously expanded to three lanes by removing the rock below the University of Applied Sciences and upgrading the Napoleon Bridge for three lanes. In the course of this, the ailing retaining walls of the current route in the lower Gillenbachtal were repaired.
On the other hand, it is planned to relocate the B 51 in the Trier-West area from the junction of Römerstraße / level crossing in a northerly direction from Aachener Straße / Luxemburger Straße to Hornstraße. The further course is to extend from the Trierweilerweg / Über Brücken area parallel to the western route over the former premises of the railway depot and the Eybl-Bobinet company and finally return to the old and well-developed route at Im Speyer.
The official groundbreaking ceremony for the 4.3 kilometer long and around 20 million euro expensive bypass around Konz- Könen took place in February 2012, on 23 August 2017 the opening took place. The bypass begins between the branches L 136 and K 112 in the Tawern area, then bypasses the Könen district in the west and finally joins the B 419 below the Granahöhe industrial area, which merges back into the B 51 after the bridge at the mouth of the Saar.
North Rhine-Westphalia
For a long time there have been concrete plans for the expansion of the B 51 as a four-lane bypass road running east of the city center of Münster through the St. Mauritz district, which is one of the most sought-after and expensive districts of Münster . An efficient road connection between Münster and the Bielefeld region and East Westphalia was discussed as early as the 1960s. At the end of the 1960s, plans arose for a four-lane motor road that was to run south of the previous B 51. The alternative planning from 1992 envisaged a four-lane expansion of the B 51 between Münster and Telgte and was still seen as an urgent requirement until 2003.
The construction project on the route to the Schifffahrter Damm is part of the official target planning of the city of Münster in 2015. The building project is controversial among the residents, who have filed a complaint about inadequate noise protection at the Münster Higher Administrative Court. The St. Mauritz Citizens 'Initiative, Münster's oldest citizens' initiative, which was founded in 1986, has been trying to prevent the construction project from being implemented in the planned form for almost 30 years and prefers to tunnel the B 51 under the model of the Hamburg lids . As early as 1994, an environmental impact study commissioned by the then North Rhine-Westphalian Ministry of Transport recommended tunneling underground to minimize noise and exhaust emissions.
On the southern part of the section of the bypass road planned for expansion, 120,000 cars move daily at the three traffic junctions on Albersloher Weg, the bypass road itself and Wolbecker Straße. Of these, 30,000 vehicle movements are currently accounted for on the two-lane B 51. However, according to information from traffic planner Ralf Renkhoff of the city of Münster, the volume of traffic is falling. For the year 2025, an increase to around 47,000 to 52,000 vehicle movements per day is expected.
The four-lane expansion of the B 51 will be accompanied by the erection of noise barriers and the use of whispered asphalt to reduce noise emissions, according to information from the Münster district government. The planned use of whispered asphalt is criticized by residents as a politically, but not technically effective measure. Whispered asphalt can develop its noise-reducing effect at high speeds, which is why it is mainly found on motorways. No significant effect can be measured below 60 km / h. In the relevant section of the B 51 there is a speed limit of 70 km / h. In addition, the surface layer of whispered asphalt has to be replaced after six to eight years, whereas conventional asphalt has a laydown period of twelve years.
According to the city's planning, the expansion of the bypass road should be completed in full in 2025. In 2014, the federal government approved funds totaling 42 million euros for the construction work.
Before the approval for the expansion was granted, the Landesbetrieb Straßen NRW had trees and wood cut down on the 6,000 m² future construction site along the route of the B 51 in February 2015. This was criticized by Bündnis 90 / Die Grünen and the Naturschutzbund Deutschland . This was followed by a search for duds at suspicious points in the building site by the ordnance disposal service .
As early as January 2015, the property committee decided to sell land to the Landesbetrieb Straßen NRW on Wolbecker Straße, on which allotment gardens of the Morgensonne and Damaschke associations had previously been located, which directly reached the previous route of the B 51. For these areas, which are required for the expansion of the federal highway, the Green Space Office is planning to provide the tenants, whom they terminated in 2014 due to the urban development measures, with replacement areas in the urban area. The preparation of the replacement areas is associated with costs of almost 560,000 euros for the city of Münster.
After the last of 4 lawsuits before the Münster Higher Administrative Court to examine the validity of the planning approval decision for road construction from 2011 were rejected in May 2015, the groundbreaking ceremony took place on June 22, 2015 to start construction.
A bypass road around the Cologne district of Meschenich is also under construction. So far, the B 51 has crossed the town centrally, which is associated with considerable noise and pollution for the residents. The plan approval procedure has now been carried out (building law has also been in place since April 2018); In addition, the B 51 is to be relocated and expanded in the further course and thus the federal motorway 553 is to be better connected to the Cologne motorway ring via the Cologne-Eifeltor motorway junction . The groundbreaking took place on January 24, 2020.
Lower Saxony
The Belm bypass, which was partially approved in June 2019 and fully approved in August 2019, connects directly to the end of the A 33 motorway west of Belm. In the future, the A 33 will continue to be built up to the A 1, and the Belm bypass will then be connected to the motorway via an intersection-free junction. In the long term, the construction of the section between the two bypasses of Ostercappeln and Belm is also planned as a motorway-like road , so that the B 51 between the roundabout east of Ostercappeln and the A 33 would be consistently four-lane and free of intersections. The section mentioned is classified in the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030 as an additional requirement with planning rights (WB *) .
The Barnstorf through-town of the B 51 in the Diepholz district is to be replaced by a bypass road. The plan approval procedure for this was initiated in April 2008, but temporarily suspended in summer 2010 for urban planning reasons. The plans for the original route, which would have run between the Barnstorf town center and the Walsen district and would have reached close to the residential development there, were discarded. Before the project is pursued further, further route options are to be examined and a spatial planning procedure initiated. To do this, an environmental impact study must first be drawn up and an environmental impact assessment carried out. As a basis for further planning, a new route to the southeast of the Barnstorf town center and the Osnabrück – Bremen railway line is emerging . Parts of the areas planned for the original route have meanwhile been released for residential development by the Barnstorf community.
According to the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030, bypasses are also planned for Twistringen (district of Diepholz) and Bad Iburg ( district of Osnabrück ) to relieve local through-traffic in urgent need there . In Twistringen, a bypass to the northwest of the town center is planned in the 2 + 1 system ; in Bad Iburg, the area to the east of the development is to be bypassed through a tunnel.
Irrespective of the planning for a bypass, the through-road of Bad Iburg was rebuilt in four construction phases between 2011 and 2017, including the construction of two new roundabouts, narrowing the lane and creating green strips along the road. The aim was to improve safety for pedestrians and cyclists as well as to upgrade the townscape. At the same time, the city of Bad Iburg redesigned the green areas around the Charlottensee , which were used for the Lower Saxony State Garden Show in 2018.
Shared use by trams
The tram route Bochum-Gerthe - Hattingen (line 308) and Bochum Hbf - Bochum-Dahlhausen (line 318, to the stop) runs between Bochum city center (from the "Bergmannsheil" stop) and Bochum-Linden - and on a small part in Hattingen “Bochum Linden-Mitte”) of Bogestra, flush with the street in the middle of Hattinger Straße, the former B 51. The tram also ran between Recklinghausen and Bochum (line 8, 18, 28; later line 305 on the Herne-Bochum section) to Opening of the Bochum Stadtbahn ( U35 ) in 1989 on the federal road; the tracks were in the Riemke area until summer 2008 and were removed as part of the road renovation. There are also a few meters in the Höhenhaus district of Cologne, on which line 4 of the Cologne transport company runs. In Saarbrücken , the S1 line of the Saarbahn runs through St. Johanner- and Kaiserstraße, along Rathausplatz and through Großherzog-Friedrich-, Arndt- and Mainzer Straße on the B 51. From the Römerkastell stop, the S1 line then runs parallel to the B 51 to Saargemünd. In today's Leverkusen, from 1903 to 1922 drove from Reuterstr. a tram to the Binnerster Hof (today partly a pedestrian zone).
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ in the urban area of Cologne, Völklingen and Saarbrücken partially expanded to four lanes; in the urban area of Münster, bypass Brühl and Baasem – Stadtky, four-lane motorway-like expansion; Reuth – Dausfeld and Bitburg – Meckel expanded to three lanes
- ^ Otto von Mülmann : Statistics of the government district of Düsseldorf . J. Baedeker, Iserlohn 1867 ( Google Books [accessed October 28, 2011]).
- ↑ For this section there is a driving ban for trucks on the North Rhine-Westphalian public holidays Corpus Christi and All Saints' Day , which are not public holidays in Lower Saxony. For journeys on these days, freight forwarders must either obtain a special permit for a "transit" ( [1] ) or choose the diversion route via Damme (Dümmer) or the route via the A1 and the B 214 to Diepholz.
- ↑ Official Journal for the Reg.-Bez. Arnsberg. (PDF; 1.6 MB) No. 53/2009. District government Arnsberg, January 2, 2010, p. 369f , accessed on October 28, 2011 .
- ↑ Official Journal for the Reg.-Bez. Dusseldorf. (PDF; 131 kB) 189th year 2007 No. 50. (No longer available online.) District government Düsseldorf, December 12, 2007, p. 422f , archived from the original on July 22, 2014 ; Retrieved October 28, 2011 .
- ^ Official Journal for the Cologne District. (PDF; 146 kB) Volume 194, No. 27, Cologne District Government, July 7, 2014, p. 241f , accessed on June 4, 2019 .
- ^ Official Journal for the Cologne District. (PDF; 146 kB) Volume 193, No. 44. Cologne District Government, November 4, 2013, p. 446 , accessed on August 28, 2014 .
- ↑ Besseringen bypass is under construction. Saarland Ministry for Economic Affairs, Energy, Labor and Transport, June 27, 2011, accessed on October 20, 2012 .
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Development Besseringen bypass in the course of the B 51 relieves residents and improves connections to the region. ( Memento from December 14, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ highway law; Planning approval. Judgment of the Higher Administrative Court Koblenz. (No longer available online.) Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection Rhineland-Palatinate, May 12, 2005, archived from the original on July 30, 2014 ; Retrieved October 28, 2011 .
- ^ Ramsauer at groundbreaking for bypass for Konz-Könen. Trierischer Volksfreund, February 14, 2012, accessed on February 15, 2012 (newspaper article).
- ↑ https://www.volksfreund.de/b-51-ortsumgehung-konz-koenen-ist-eroeffnet_aid-5133933
- ^ Christian Kremer: First steps to the B 51 bypass. Trierischer Volksfreund, February 15, 2011, accessed on October 28, 2011 (newspaper article).
- ^ Ministry of Economics, Transport, Agriculture and Viticulture Rhineland-Palatinate Hering: bypasses Kastellaun and Konz-Könen are under construction. ( Memento from January 1, 2015 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b c b64plus.de: Chronicle of the planning: An important infrastructure project is still a long way off , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ a b c Westfälische Nachrichten : What can and cannot be included in a forecast? - Lively debate about the traffic load to be expected in the harbor district / decision postponed , Münster, Münster, Klaus Baumeister, January 30, 2015
- ^ A b c Westfälische Nachrichten : B 51 in Münster: Federal government releases 42 million for the expansion of the bypass road , Münsterland, Münster / Berlin, Klaus Baumeister, July 30, 2014
- ↑ a b c d e Michael Heß: A tunnel for Mauritz. (PDF; 83.9 kB) There is a dispute about the tunneling of the bypass road. (No longer available online.) Outside February 1, 2015, p. 10 , archived from the original on March 5, 2017 ; Retrieved February 26, 2015 .
- ↑ a b c Westfälische Nachrichten : City relies on fewer traffic jams - The port district is booming: the bypass road should bring the necessary relief , Münsterischer Anzeiger, Münster, Klaus Baumeister, January 29, 2015
- ↑ District government of Münster: Starting shot for the four-lane expansion of the B 51 between Wolbecker and Warendorfer Straße: Planning approval decision from 2011 now immediately enforceable ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Münster, August 14, 2014
- ↑ Westfälische Nachrichten : Whispering asphalt - not effective , Jürgen Tschoepe, August 26, 2011
- ^ Westfälische Nachrichten : Umgehungsstraße - Stunned Than Ever , Klaus Köster, February 5, 2015
- ↑ a b Thüringer Allgemeine : Whispered asphalt could make Tempo 30 zones unnecessary , Erfurt, Wolf-Dieter Bose, December 27, 2013
- ↑ guenther-felbinger.de: Use of whispering asphalt , Günther Felbinger, March 3, 2011
- ↑ well then: "Ignorant and inhuman" ( Memento from August 10, 2015 in the Internet Archive ), Stefan Bergmann, issue 06/2015, p. 4f.
- ^ A b Westfälische Nachrichten : Trees are falling on the B 51 , Münsterischer Anzeiger, February 10, 2015
- ^ A b Westfälische Nachrichten : More trees are falling on the B 51 , Münster, February 19, 2015
- ↑ Westfälische Nachrichten : Greens criticize tree felling , Münster, January 30, 2015
- ↑ Westfälische Nachrichten : “That’s clear-cut ” - conservationists criticize North Rhine-Westphalia for the ongoing woodcut work , Westphalia, Münsterland, Stefan Werding, February 27, 2015
- ↑ a b c Westfälische Nachrichten : Alternative quarter for allotment gardens: bypass road claims Damaschke parcels / green space office plans replacement , Münster, Münster, Lukas Speckmann, March 13, 2015
- ^ Westfälische Nachrichten : B 51: Waiting for a court date , Münster, Münster, Klaus Baumeister, February 21, 2015
- ↑ Plan approval decision. (PDF; 1.74 MB) (No longer available online.) Münster district government, September 30, 2011, archived from the original on February 27, 2017 ; Retrieved February 26, 2015 .
- ↑ Westfälische Nachrichten : B 51: Trial date has been set , Münsterischer Anzeiger Münster, kb, March 14, 2015
- ↑ First groundbreaking ceremony for B 51. Construction work begins. Westfälische Nachrichten, June 22, 2015, accessed on July 6, 2015 .
- ↑ B51: The next construction phase of the Münster bypass is being tackled. In: www.strassen.nrw.de. State Office for Road Construction North Rhine-Westphalia, June 22, 2015, accessed on July 6, 2015 .
- ↑ Planning approval documents of the city of Cologne for the planning approval procedure for the new building B51n - Meschenich bypass ", LSG L18, EZ 3, District 2
- ↑ Connection relieves the pressure on residential development in Meschenich: building permit for bypass in Kölnische Rundschau from April 28, 2018
- ↑ New streets in Meschenich: Last kilometer to the Eifeltor. In: Kölner Stadt-Anzeiger. Retrieved March 22, 2016 .
- ↑ Information from the State Office for Road Construction NRW on the subject: B51n: Continuation of the Cologne-Meschenich bypass to the A4 junction Cologne-Eifeltor (accessed September 29, 2016)
- ↑ B51: Groundbreaking ceremony for the construction of the Cologne-Meschenich bypass. State Office for Road Construction North Rhine-Westphalia, January 24, 2020, accessed on January 24, 2020 .
- ↑ Lower Saxony State Authority for Road Construction and Transport: Belm bypass in the course of the A 33 / B 51 . Retrieved June 14, 2019
- ↑ Now the traffic is rolling along the entire bypass in Belm , noz.de, August 9, 2019, accessed on August 12, 2019.
- ^ Project B51-G40-NI in the project information system for the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030, accessed on April 5, 2018
- ^ New construction of the Barnstorf bypass in the course of the federal highway 51. Lower Saxony State Authority for Road Construction and Transport, January 16, 2013, accessed on April 5, 2018 .
- ^ Project B51-G20-NI in the project information system for the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030, accessed on April 5, 2018
- ↑ Barnstorf municipality: development plan "Before the Walsen" - reasons for the draft , barnstorf.de, accessed on April 5, 2018 (PDF)
- ^ Project B51-G10-NI in the project information system for the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030, accessed on April 5, 2018
- ^ Project B51-G50-NI in the project information system for the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030, accessed on April 5, 2018
- ↑ Sebastian Philipp: Is the tunnel coming ?: Bad Iburger bypass is more likely. In: noz.de. December 2, 2016, accessed April 5, 2018 .
- ↑ Nds. State authority for road construction and traffic: Reconstruction of federal highway 51 in Bad Iburg ( Memento from April 5, 2018 in the Internet Archive ), strassenbau.niedersachsen.de, accessed on April 5, 2018.
- ↑ Tram in Schlebusch in front of today's "Old Mayor's Office"