Burscheid
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 5 ' N , 7 ° 7' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Cologne | |
| Circle : | Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis | |
| Height : | 195 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 27.33 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 18,346 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 671 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 51399 | |
| Area code : | 02174 | |
| License plate : | GL | |
| Community key : | 05 3 78 008 | |
| LOCODE : | DE BCD | |
City administration address : |
Höhestraße 7–9 51399 Burscheid |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Stefan Caplan ( CDU ) | |
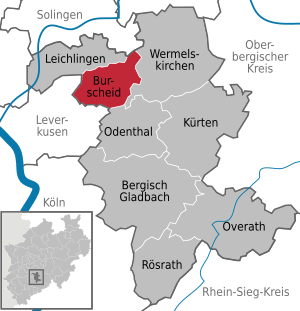
| Location of the city of Burscheid in the Rheinisch-Bergisches Kreis | ||
Burscheid is a small town in the Rheinisch-Bergisches Kreis in North Rhine-Westphalia with around 19,000 inhabitants. The city is characterized by many smaller villages and by its city center with market square and church. Burscheid was mentioned for the first time in 1175. On August 18, 1856, the then rural community was granted city rights by King Friedrich Wilhelm IV of Prussia.
geography
Districts
The main locations are Burscheid downtown and Hilgen . Alongside the main town, Hilgen is the largest and most important town in the city. It is mentioned for the first time in 1510 in a tax list of the church of Wermelskirchen, is on the B 51 and borders on Wermelskirchen .
Other locations:
Bellinghausen - Benninghausen - Berringhausen - Berghamberg - Blasberg - Bruchermühle - Büchel - Claasmühle - Dierath - Dohm - Dünweg - Dürscheid - Drauberg - oak cookies - Engelrath - Echhausen - wing - Geilenbach - barley mill - Großbruch - Großhamberg - Griesberg - Grünscheid - Hahnensiefen - Hanscheider Hof - Hamberg - Heide - Heddinghofen - Herkensiefen - Hilgen - Hinterweg - Hürringhausen - Imelsbach - Irlen - Irlerhof - Kaltenherberg - Kämersheide - Kamp - Kämpchen - Kippekofen - Kleinbruch - Kotten - Kretzheide - Kleinhamberg - Kuckenberg - Lambertsmühle - Le Lamerbusch - Lämgesmie - Landscheid - Le Lamerbusch - Lämgesmie - Landscheid - Liesendahl - Linde - Löh - Luisental - Lungstraße - Massiefen - Maxhan - Müllersbaum - Nagelsbaum - Neuenhaus - Nüxhausen - Ösinghausen - Paffenlöh - Repinghofen - Rötzinghofen - Schneppendahl - Sieferhof - Spiegelhof - Sträßchen - Thielenmühle - Wietsche
Nature reserves
history
Remains of a former ring wall in the Eifgental, the so-called Eifgenburg, are witnesses of the first settlement. Pottery fragments found there date the complex to around the 10th century. The first tower of today's Protestant church was built in the 11th century. "Bursceit" is officially mentioned for the first time in 1175 as a village belonging to the St. Gereon monastery in Cologne. Until 1806, Burscheid was a parish in the office of Miselohe in the Duchy of Berg . After Napoleon occupied and formed the Grand Duchy of Berg, Burscheid formed a mairie in the Arrondissement of Düsseldorf and in the Canton of Opladen . The brief French rule was followed by the incorporation of the Bergisches Land into the Kingdom of Prussia (1815); Burscheid became a rural community within the Rhine Province and belonged to the former Opladen district .
Good geological soil conditions and a favorable climate influenced the development of Burscheid. Early on, the company specialized in grassland and dairy farming and established the good reputation of the Bergische Obstkammer. Butter, eggs, cheese and last but not least Bergisches Apfelkraut found sales in all the markets of the Rhenish cities.
Around the 16th century the foundations for the development of the Burscheider industry were laid. The use of water power and the abundance of wood in the forests made it possible to build numerous mills, among others. a. Fruit, oil, powder and bone mills, later steel hammers and grinding bowls. The Lambertsmühle, Thielenmühle, Irlermühle, Dürscheider Mühle, Grünscheider Mühle, Gerstenmühle u. a. are witnesses of living history today.
In 1843 Burscheid became the seat of a factory court.
With the invention of a special copper-asbestos sealing ring by the locomotive driver Friedrich Wilhelm Goetze and the associated establishment of the Goetzewerke (later Goetze AG and now Federal-Mogul), the city strengthened its industrial character.
As a result of the industrial upturn, Burscheid received city rights on August 18, 1856. At that time the young city had a little over 5000 inhabitants. Sufficient jobs and the city's financial strength contributed largely to the rapid population growth.
Burscheid was connected to the railway network in October 1881, when the Wermelskirchen - Opladen section of the Wuppertal-Oberbarmen-Opladen railway was opened with stations in Burscheid and Hilgen; In May 1952 the stopping points Dünweg and Burscheid Rathaus were added. Until the Second World War, the line was double-tracked, however, after war damage, it was dismantled on a single track. In May 1983, passenger traffic was restricted to the Opladen - Hilgen section, and in 1991 the line was completely closed. Today the “Panorama-Radweg Balkantrasse”, a combined foot and cycle path, runs along the route. The section from Remscheid-Lennep to Burscheid-Kuckenberg was completed in 2012, the continuation to Opladen will open on May 29, 2014. 6.2 km of the path run in the area of the city of Burscheid.
In 1996, Johnson Controls , US manufacturer of car interiors, chose Burscheid as the location of its European headquarters with development center.
In April 2010, the Rheinisch-Bergische Kreis organized the third day of Rheinisch-Bergische history in Burscheid .
Incorporations
On January 1, 1975, parts of the neighboring town of Wermelskirchen with then about 400 inhabitants were incorporated.
Population development
| year | Residents |
|---|---|
| 1792 | 4,202 |
| 1807 | 4,258 |
| 1816 | 5,068 |
| 1825 | 5,564 |
| 1835 | 6.337 |
| June 6, 1961 | 13,220 |
| May 27, 1970 | 15,391 |
| June 30, 1974 | 16,066 |
| December 31, 1990 | 17,312 |
| December 31, 2000 | 19,125 |
| December 31, 2005 | 19,122 |
| December 31, 2006 | 19,251 |
| December 31, 2007 | 18,871 |
| December 31, 2008 | 18,727 |
| January 31, 2009 | 18,958 |
| December 31, 2012 | 18,120 |
| December 31 2013 | 18,108 |
| December 31, 2014 | 18,166 |
| December 31, 2015 | 19,047 |
| December 31, 2017 | 18.195 |
politics
City council
The local elections on May 25, 2014 led to the following result for the composition of the Burscheider city council:
| Party / list | Share of votes | +/-% p | Seats | +/- |
| CDU | 38.4% | + 7.4 | 16 | + 3 |
| SPD | 21.0% | - 1.2 | 8th | - 1 |
| Green | 10.6% | - 0.7 | 4th | - 1 |
| left | 3.5% | + 3.5 | 1 | + 1 |
| FDP | 4.7% | - 4.7 | 2 | - 2nd |
| BfB | 16.9% | - 4.4 | 7th | - 1 |
| UWG | 4.3% | - 2.2 | 2 | - 1 |
| total | 40 |
In the previous term, the city council had 42 seats.
mayor
In the local elections on May 25, 2014, Stefan Caplan (CDU) was elected mayor with 62.1 percent of the vote.
Partner communities
Partner municipalities are Egg in the Austrian Bregenzerwald (since 1968) and Bourscheid in the Luxembourg Ardennes (since 2004).
traffic

Burscheid is conveniently located on the federal motorway 1 Cologne-Dortmund. The B 51 Cologne-Wuppertal also runs through the city. The state road 291 also connects Burscheid to the Autobahn 3 via Leverkusen-Opladen . On January 1, 2018, 14,860 vehicles were registered in Burscheid, of which 12,446 were cars.
In 1994 the train service between Opladen and Remscheid-Lennep ended ; Burscheid had three stations on the connection known as the Balkan Express .
In local public transport, the RVK bus line 260 runs from Remscheid via Burscheid to Cologne every 30 minutes during peak hours and every 60 minutes during off-peak hours. There are other bus connections to Leverkusen-Opladen, Solingen and Bergisch Gladbach.
In addition, the night bus route 26 runs on Fridays and Saturdays at 01:00 and 02:00 from Cologne bus station directly via the A3 and A1 to Burscheid and Hilgen. The night bus route 25 also connects Burscheid and Leverkusen on Fridays and Saturdays between 12:25 a.m. and 3 a.m.
The outside areas that are not connected to public transport are served by the voluntarily operated “ Burscheid Citizens' Bus ” according to schedule.
Burscheid belongs to the tariff area of the VRS .
economy
The main employers are the automotive suppliers Federal Mogul (formerly Goetze AG) with around 1800 employees and Adient with around 1800 employees at the Burscheid location. Fietz GmbH is the third largest employer.
A total of around 1400 businesses are registered in Burscheid. 136 companies have more than three employees. 4,639 commuters are compared to 4,355 commuters (as of 2006).
music
Burscheid is considered the music city of the Bergisches Land with a tradition since 1811. In 1812 the Musicalische Academie became Burscheid e. V. founded by Jakob Salentin von Zuccalmaglio , it is the oldest amateur orchestra in Germany. The orchestral association Hilgen 1912 e. V. - Oelberger Musikverein Burscheid 1876 - won the title of best German amateur orchestra in symphonic wind music in 1996, 2000, 2004.
Other music associations in Burscheid are the Chorgemeinschaft Burscheid e. V. (founded 1842), the male choir Dürscheid 1889 e. V., the women's choir Dürscheider Dreiklang e. V. (founded 1986), the Singschule Dürscheid e. V. (founded 2004), the mixed choir Wiehbacher Echo Heddinghofen (founded 1926), the Catholic church choir St. Laurentius Burscheid, the Protestant choir Burscheid and the brass group of the CVJM Burscheid.
The basis of the music city Burscheid is the music school Burscheid e. V. with currently around 800 students (founded in 1972). In addition, the Orchester School Burscheid e. V.
Children's and youth center Megafon
The children and youth center Megafon is a facility sponsored by the Catholic Youth Agency Leverkusen, Rhein-Berg, Oberberg gGmbH. The city of Burscheid is the lessor of the newly built property. The new building was completed in 2015 after a two-year construction period. The location of the megaphone is Montanusstraße 15 on the old station area of the city of Burscheid.
The Megafon children's and youth center is a modern facility for open child and youth work. The facility offers leisure-time educational development opportunities, is active in the musical and cultural field and offers support with questions relating to integration and career orientation.
The target group of the facility are young people from 8 to 21 years of age.
The aim of the youth center is to support young people on their way to growing up.
Sports
Since around every fifth Burscheider is a member of a sports club, Burscheid was honored by the State Sports Association of North Rhine-Westphalia with the title “the sporty community”.
Sports clubs in Burscheid
- Burscheider Turngemeinde 1867
- Ball game club 1911 Burscheid
- Disabled sports Burscheid 1963
- Burscheider badminton club
- Burscheider shooting club 1864
- DLRG local group Burscheid
- Working dog club Burscheid
- HSG Bergische Panther
- Hilgener Rifle Club 1923
- Motorsport fans "Kolbenring" Burscheid
- Rural riding and driving club Burscheid-Paffenlöh 1926
- Burscheid cycling community in 1978
- Chess friends Burscheid 1929
- Grün-Weiß Burscheid tennis club
- Table tennis club Grün-Weiß 1948 Burscheid
- Gymnastics Federation Großösinghausen 1884
- Gymnastics community Hilgen 04
- Hiking friends 1981 Burscheid
Sports facilities in Burscheid
Kuno-Hendrichs-Sportanlage Hilgen - Sporthalle Auf dem Schulberg - Max-Siebold-Halle Hilgen - Hans-Hoersch-Halle - Hugo-Pulvermacher-Halle - Karl-Zimmer-Halle - School Gym Hilgen - Gym Ösinghausen - Gym of the Realschule Auf dem Schulberg - Sports field Griesberg - Burscheider Bad - school sports facility in Hagen - beach sports facility in Hagen
Attractions
- Eifgenburg - the ring wall system from the 9th / 10th centuries Century, located in the Eifgental, testifies to the first settlement of today's Burscheider city area. The Eifgenburg is an archaeological ground monument.
- Haus Landscheid is a historic knight's seat that belonged to a knight Heinrich von Nesselrode in 1371 . A replacement building was erected between 1718 and 1725. After being used as a restaurant and conference venue from 1983, the building stood empty from 1998 to 2009. From 2009 to 2010 it was extensively renovated and expanded and today houses a hotel, restaurant and therapy center.
- The Lambertsmühle is located in the Wiehbachtal in the southwest of the city and has been restored step by step since 1994, for example the mill wheel has been repaired. In the future, the building ensemble with its historic half-timbered building and the outbuildings will house the town's local museum. The museum's exhibition is intended to document the path from grain to bread and make it a practical experience.
- Other historical mills worth seeing in Burscheid are the Thielenmühle (here in 1887 Friedrich Goetze founded the later Goetze AG, now Federal-Mogul), Grünscheider Mühle, Dürscheider Mühle, Barley Mill and Brucher Mühle .
- The Evangelical Church on the market was built in 1767. It is a typical Bergische Baroque church with a remarkable altar, pulpit and organ prospect. The first predecessor church was built in the same place in the 13th century, for which Hermann von Alffter , in the 15th century bell founder from Alfter near Bonn, created a bell in 1468 .
- The Wallace fountain on the corner of Hauptstrasse and Bürgermeister-Schmidt-Strasse
- There are also numerous listed buildings in the city center and especially in the Dierath district.
Personalities
Honorary citizen
- Paul Luchtenberg (1890–1973), co-founder of the FDP, Member of the Bundestag , Minister of Culture of North Rhine-Westphalia
- Wilhelm Schmidt , Mayor of Burscheid from 1894 to 1928
- Hugo Bernd Pulvermacher , Burscheider "gymnastics father"
- Erich Richartz-Bertrams († 1973), industrialist and patron
sons and daughters of the town
- Carl Pulfrich (1858–1927), physicist and optician
- Ewald Sträßer (1867–1933), composer and conductor
- Max Kohl (1881–1976), Burscheider industrialist and Righteous Among the Nations
- Otto Thiel (1884–1959), politician (DVP)
- Carl Lauterbach (1906–1991), painter and collector
- Günter Wallraff (* 1942), journalist
- Carla Schulz-Hoffmann (* 1946), art historian
- Torsten Günther (* 1976), business lawyer and football referee
Other personalities
- Josef Wilhelm Bruns, first Roman Catholic pastor in Burscheid after the Reformation
- Johannes Löh (1752–1841), Protestant pastor and pioneer of the Burscheider popular education
- Friedrich Wilhelm Goetze (1856–1924), inventor, founder of Goetze AG
- Karlheinz Stockhausen (1928–2007) once attended the Burscheider Citizens' School.
- Günter Kärner (* 1933), cantor and composer
- Rüdiger Vollborn (* 1963), former Bundesliga goalkeeper of the neighboring soccer club Bayer 04 Leverkusen and Junior World Champion 1981
- Hansi Gnad (* 1963), former national basketball player
- Uwe Boll (* 1965), German director, producer and screenwriter
- Silke Gnad (* 1966), former national handball player
literature
- One hundred years city of Burscheid 1856–1956. Published by City of Burscheid, Burscheid 1956.
- 125 years of the city of Burscheid, Festschrift 125 years 1856–1981. Published by the city of Burscheid, Burscheid 1981.
- Burscheid, from the life of a mountain town. Self-published by the Verkehrs- und Verschönerungsverein, Burscheid 1935.
- Lydia Kieven: cultural guide Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis. Heider, Bergisch Gladbach 1998, ISBN 3-87314-334-8 , pp. 95-108.
- Rheinisch-Bergischer calendar . Yearbook since 1920.
- H. Liesendahl: Burscheid and its surroundings. Burscheid 1907. (ND 1987).
- F. Hinrichs: Burscheid. In: Berg.Volksbote. Burscheid 1935/36.
- P. Luchtenberg: Burscheid - evidence of its past. Leverkusen 1941.
- R. Berges: St. Laurentius. Burscheid 1961.
- What sustains us, the history of the Evangelical Church Community in Burscheid. Burscheid 1976.
- Hans Werner Hinrichs: Burscheid, history and stories, citizens write for citizens. Ed. City of Burscheid. Baltin-Verlag, Gevelsberg 1980.
- NJ Breidenbach: The writing / arithmetic book of Anna E. Jacobi. A Hilgen merchant family. In: Rheinisch-Bergischer Calendar. 1991.
- M.-L. Mettlach: Looked at the sign - Burscheider street names. Berg, Gladbach 1994.
- R. Löhmer: Burscheid, Dabringhausen, Dhünn, Wermelskirchen. Development of the spelling of its 290 localities over the course of time. Burscheid 2005.
- NJ Breidenbach: Hinterweger Hof and Hilgen-Nüxhausen. In: Altenberger Blätter . Issue 35, Odenthal 2006, ZDB -ID 1458565-0 .
- W. Küpper, E. Schiffler (Ed.): Chronicle - 500 years of Hilgen. Burscheid-Hilgen 2010.
- NJ Breidenbach: Old farms and houses in the Wupperviereck in Wermelskirchen, Burg Castle, Remscheid, Hückeswagen, Wipperfürth, Kürten, Lindlar, Odenthal, Burscheid. Wermelskirchen 2011, ISBN 978-3-9802801-2-9 , pp. 372-385.
- M.-L. Mettlach: In: 200 years of the Music Academy in Burscheid. In: Rheinisch-Bergischer Calendar. 2012.
- NJ Breidenbach: Catholic Church in Burscheid. On the church history of St. Laurentius and Liebfrauen up to 1900. In: Altenberger Blätter. Issue 69, Odenthal 2017.
Web links
- Official website of the city of Burscheid
- Literature on Burscheid in the catalog of the German National Library
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ↑ Panorama bike path Balkantrasse. In: burscheid.de/tourismus, accessed on September 23, 2017.
- ↑ NW 4.11 Panorama Cycle Path Balkantrasse: Leverkusen-Opladen - Remscheid-Lennep. In: bahntrassenradeln.de, accessed on September 23, 2017.
- ↑ a b c Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 298 .
- ↑ Figures from 1792 to 1835 according to Georg von Viebahn: Statistics and Topography of the Düsseldorf Government District. Volume 1, Düsseldorf 1836, p. 111; bsb-muenchen-digital.de (PDF) accessed on September 23, 2017.
- ↑ Martin Bünermann, Heinz Köstering: The communities and districts after the municipal territorial reform in North Rhine-Westphalia . Deutscher Gemeindeverlag, Cologne 1975, ISBN 3-555-30092-X , p. 56, 76 .
- ↑ structural data . Website of the city of Burscheid; Retrieved April 4, 2016.
- ^ City of Burscheid - Council election 2014. In: wahlen.citkomm.de, accessed on September 23, 2017.
- ↑ Mobility in North Rhine-Westphalia - data and facts 2018/2019. In: Road traffic. Ministry of Building, Housing, Urban Development and Transport of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia, p. 66 (PDF; 14.2 MB, holdings on January 1, 2018).
- ↑ Children's and Youth Center Megafon accessed on June 28, 2018
- ↑ Hermann von Alffter . In: Hans Vollmer (Hrsg.): General lexicon of fine artists from antiquity to the present . Founded by Ulrich Thieme and Felix Becker . tape 16 : Hansen – Heubach . EA Seemann, Leipzig 1923, p. 488-489 .
- ↑ Katja Nienhaus: Boogie-Woogie on the organ. In: Bergischer Volksbote. December 22, 2007.