Basic need
Basic needs are needs that are of great importance in a hierarchical division of human needs and that are primarily satisfied within the framework of the everyday subsistence process.
There is no general definition of basic needs or a general understanding of which needs are included. The term is used in a wide variety of sciences (e.g. anthropology , medicine , psychology , economics , theology or law ) and in political discussions.
Models for the hierarchical division of needs
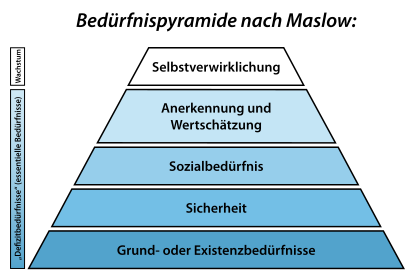
Basic needs according to Maslow
A well-known hierarchical model of needs is Maslow's hierarchy of needs :
In this model, basic needs are found in the lower levels:
- basic physical needs (also called basic biological needs): breathing (clean air ); Warmth ( clothing ); Drinking (clean drinking water ); Eating (healthy food ); Sleep (rest and relaxation)
- Security: Accommodation / Apartment ; Health ; Protection from danger; Order ( laws , rituals )
- Social relationships: circle of friends , partnership , love , charity , sexuality , care , communication
The model does not provide a demarcation or definition that explains what basic needs are. The lowest level of the model describes basic physical needs.
Urgency needs
In economics, needs are differentiated according to the urgency of their fulfillment.
- Existential needs are also required in times of need: sufficient food and water, air, clothing, living space, work and medical care.
- Basic needs include clean air, clean water, and food. There are also sleep, accommodation, clothing, health care, security and partnership .
- Cultural needs describe the desire for culture , for example aesthetics , creative expression and education .
- Luxury needs encompass the need for luxury goods and services (jewelry, cars, etc.), even if theypromotemisery, suffering and outrage in other places. Thereis nolimit to desire .
The use of the term in the political discussion
In the political debate, the concept of basic need is mainly used in the area of social, tax and development aid policy.
Social policy
In the public discussion, the term basic needs is mostly used in connection with the poverty line or social benefits . The aim of social policy in Germany is to guarantee everyone the socio-economic subsistence level. The prerequisite for this is the definition of the underlying basic needs. In Germany, this is done using a shopping basket that is collected in a representative survey of the 20% of the poorest households (“Income and Consumption Sample” (EVS)). The costs for this represent the standard rate of social assistance .
Tax policy
In tax policy, basic needs are the subject of public discussion in two areas. On the one hand, there is a constitutional requirement to keep the socio-economic subsistence level tax-free.
In the area of sales tax, there are split sales tax rates in most countries. Goods and services that serve to meet basic needs are subject to lower tax rates than others. The catalog of goods and services that are subject to the reduced tax rate (for Germany: Appendix 2 to the Value Added Tax Act ) represents a possible definition of basic needs.
Basic needs in development aid policy
In development aid, the basic needs strategy is based on the idea of basic needs.
The International Labor Organization (ILO) defined basic needs as follows: According to this, minimum requirements such as “adequate food , housing and clothing ” and “certain household appliances and furniture ” must be available. In addition, essential services such as health and educational facilities as well as the provision of sanitary facilities and clean drinking water are among the basic needs.
Change in the perception of basic needs
The public opinion , which was a "basic need", subject to strong shift in values .
Above all, the basic psychological and spiritual needs that manifest themselves in certain expectations are largely culturally and socially shaped and can be subject to change. Thus it can be observed that in times of existential crises ( wars , famines, etc.) the psychological and spiritual needs take a back seat to the satisfaction of the basic physical needs or seem to disappear completely. But they express themselves in susceptibilities z. B. for new religious offers. On the other hand, the expectation that these derived or "higher" needs will be satisfied even comes to the fore in times of existential security and can reach an equally great urgency.
Application in various sciences
psychology
The psychology considers the subjective satisfaction (eg. Maslow's hierarchy of needs ) and is supported by four columns (core values) that the well-being in a dynamic equilibrium will be: security, change (change), freedom and solidarity .
A more recent psychological theory that works with the concept of basic needs is Deci and Ryan's self-determination theory. These authors postulate three basic psychological needs, the need for competence, for autonomy / self-determination (autonomy) and for social integration (relatedness). The basic needs are understood here as mechanisms of adaptation of the individual to his physical and socio-cultural environment, the satisfaction of which affects the quality of behavior and the well-being associated with the exercise of this behavior.
There are many other psychological theories that list different basic needs. Klaus Grawe postulates four basic needs:
- Need for attachment
- Need for orientation and control
- Need for self-esteem and self-esteem protection
- Need for pleasure gain and avoidance of discomfort
The social psychologist Erich Fromm attached crucial importance to the “striving for tension and excitement” in his work Anatomy of Human Destructiveness . In his opinion, this basic need is an elementary drive that can be expressed both in constructive (creativity, social commitment, career aspiration, etc.) and in destructive action (vandalism, anti-social behavior, cruelty, etc.) - depending on the possibilities open to the individual Offer.
Examples of other basic psychological needs
- To be loved and loved .
- Security : the political and economic situation.
- Connectedness : belonging to a group; security
- Change : A certain tension is necessary, otherwise one sinks into lethargy .
- Recognition and success : confirmation from others, working atmosphere , expressing / accepting praise, dealing with criticism, feeling of being used
- Freedom , self-determination and creativity
- Self-esteem : self-esteem, self-confidence, stability, no self-pity, self-awareness, ability to be self-critical
- Distraction : the necessity of the relaxation process as an antipole to everyday processes to maintain psychological resilience
- Memorable experiences , permanent and reliable human encounters , successes at work, difficulties that have been overcome.
According to Schulz von Thun , these basic needs can be summarized in four: to be valuable, to be loved, to be free, to be connected.
Medicine and Nursing Science
The medicine looks at the functions of the body to its fulfillment in (at least) three aspects:
- Physiology as the study of the normal functioning of the organs to sustain one's own life. Usually there are norm values with a certain range within which they are defined.
- Rehabilitation as a medical subdiscipline wants to enable patients to participate independently in their work and everyday life again. Important remedies for this are occupational therapy , physiotherapy and the supply of aids.
- In medical ethics is what the health concept and the quality of life and to such questions.
The nursing science , itself a young discipline , sits under the so-called activities of daily living (ADL concept, hard of American psychology influenced) or life activities apart with these concepts and their concretization.
Other sciences
- Jurisprudence : human rights , right to life - euthanasia - death penalty , property rights and mouth robbery , non-attachability and fair taxation
- Theology : Basically the most important need here is salvation .
- Economics / Sociology : Orientate themselves, among other things, on the Maslow model (common subject matter); see also: need , need
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ University of Duisburg-Essen: Cognitive approaches to motivation ( Memento from February 22, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ TAZ of May 19, 2006
- ↑ BVerfGE 82, 60, 85 = para. 104 ff and BVerfGE 82, 60, 94 = recital 128 ff. In BVerfGE 82, 60 - Tax-free subsistence level
- ↑ Florian Steinberg: Basic Needs Strategy. Living in the “Third World”. Kiel 1985.
- ^ Richard M. Ryan, Edward L. Deci, Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. 71. In: American Psychologist 55 (2000) 68-78.
- ^ Edward L. Deci, Richard M. Ryan: The "What" and "Why" of Goal Pursuits: Human Needs and the Self-Determination of Behavior , p. 252. In: Psychological Inquiry 11 (4), 2000, 227– 268.
- ^ Klaus Grawe: Psychological Therapy. 2. corr. Edition, Hogrefe, Göttingen 2000, ISBN 3-8017-1369-5 , p. 383 ff.
- ↑ Erich Fromm: Anatomy of human destructiveness . From the American by Liselotte et al. Ernst Mickel, 86th - 100th thousand. Rowohlt, Reinbek near Hamburg 1977, ISBN 3-499-17052-3 , pp. 25-27.