Human herpes virus 8
| Human herpes virus 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Human gammaherpesvirus 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Short name | ||||||||||||||||||||
| HHV-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
The human herpes virus 8 ( scientifically V , HHV-8 ; sometimes also called Kaposi's sarcoma herpes virus , KSHV ) is a species of human pathogenic herpes viruses from the subfamily of the gamma herpes viruses . It causes Kaposi's sarcoma and certain rare malignant lymphomas .
Historical
HHV-8 was discovered in 1994 by the working group led by the US virologist Patrick S. Moore and his wife Yuan Chang at Columbia University . They used a special PCR method, the representational difference analysis . This enabled the detection of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in the tissue of Kaposi's sarcomas that came from HIV- infected patients. It quickly became clear that it was a new, previously unknown herpes virus.
Since the discovery of HIV in the early 1980s, it had become apparent that AIDS patients were more likely to develop certain malignancies. This was particularly noticeable in Kaposi's sarcoma , which was a seldom seen skin tumor before the HIV pandemic . However, Kaposi's sarcoma was about 1000 times more common in AIDS patients than in the rest of the population. It was also noteworthy that male AIDS patients were significantly more likely to develop Kaposi's sarcoma than female AIDS patients.
This led to the hypothesis that Kaposi's sarcoma could be caused by an infectious agent that revived in the immune deficiency caused by HIV and led to the formation of tumors. The increased occurrence in male homosexuals was explained by infection in the sexual practices practiced there (anal and oral sex).
Moore and Chang investigated this hypothesis and eventually discovered the virus.
Epidemiology
The detection of an infection is usually carried out serologically , i.e. by detecting antibodies against HHV-8. The seroprevalence (frequency of antibodies) is very different depending on the world region. In North America and Europe it is around 1 to 3%, in Equatorial Africa it is up to 50% in some areas. This compares HHV-8 to other human herpes viruses ( Epstein-Barr virus , varicella-zoster virus , herpes simplex virus I and II ), which have a seroprevalence of well over 50% in the adult population in Europe exhibit, relatively rare. In a study of breast cancer biopsies in Taiwan, 42% of the samples were infected with HHV-8.
transmission
HHV-8 is likely to be transmitted via saliva and other body secretions, as is the case with other herpes viruses:
- sexual transmission: oro-genital, oro-anal and oro-oral (kissing)
- Asexual transmission: saliva contact through kissing from mother to child, pre-chewed food in Africa
Diseases caused by HHV-8
The involvement of HHV-8 is considered to be certain in the development of three diseases:
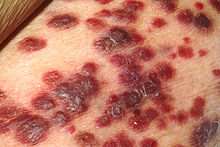
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- the so-called lymphomas in serous body cavities ( pleural cavity , pericardial cavity , peritoneal cavity ; body cavity-based lymphoma , or primary effusion lymphoma (PEL))
- certain forms of multicenter Castleman's disease
All of the diseases mentioned are rare, but occur more frequently with immune deficiency. Only a small percentage of those infected with HHV-8 will develop one of these diseases. An effective vaccination against the virus does not yet exist.
HHV-8 belongs together with the hepatitis B virus (HBV), the hepatitis C virus (HCV), the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the human papillomaviruses (HPV) and the human T-lymphotropic virus 1 to a group of human carcinogenic viruses that are responsible for 10 to 15 percent of all cancers worldwide .
Genetics and biological characteristics of the virus
HHV-8 belongs to the genus rhadinovirus of the gamma herpes viruses. As with all herpes viruses , the double-stranded DNA virus genome , which comprises around 165,000 base pairs, has a comparatively complex structure and codes for many genes. It is interesting that the HHV-8 genome contains many genes that are highly homologous to cellular human genes (e.g. interleukin -6 , cyclin D1 , BCL-2, etc.). This enables the virus to influence cell behavior in complex ways. The tumor-inducing effect is also attributed to these virus genes. Like all herpes viruses, HHV-8 is capable of viral latency ; H. the virus can apparently remain inactive in the organism for a long time and thus escape the immune system . The HHV-8 binds to integrin β-3 .
In the event of an infection, the ORF20 protein of the herpes virus forms a complex with a host protein of the innate immune system. The host protein OASL itself serves the host defense, it has an antiviral effect. When infected, this is reversed, so that OASL facilitates the infection because the virus protein ORF20 is present. The virus hits its host at its own gun.
Web links
- Patrick S. Moore's laboratory
- Human Herpesvirus-8: Related Resources HIV InSite (in English)
swell
- ↑ a b c d e ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Human alphaherpesvirus 1 , EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ↑ Y. Chang, E. Cesarman, MS Pessin, F. Lee, J. Culpepper, DM Knowles, PS Moore: Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. In: Science . 266, 1994, pp. 1865-1869. PMID 95090463
- ↑ JH Tsai, CH Tsai, MH Cheng, SJ Lin, FL Xu, CC Yang: Association of viral factors with non-familial breast cancer in Taiwan by comparison with non-cancerous, fibroadenoma, and thyroid tumor tissues. In: J med Virol. 75, 2005, pp. 276-281.
- ↑ Ulrike Wieland: Beta and Gamma Herpesviruses. Scriptum Uni Cologne, 2005 (PDF)
- ↑ D. Martin, JS Gutkind: Human tumor-associated viruses and new insights into the molecular mechanisms of cancer . In: Oncogene . tape 27 , no. 2 , 2008, p. 31-42 , PMID 19956178 .
- ↑ Kendra A. Bussey, Ulrike Lau, Sophie Schumann, Melanie Brinkmann et al .: The interferon-stimulated gene product oligoadenylate synthetase-like protein enhances replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and interacts with the KSHV ORF20 protein. In: PLOS Pathogens. 2018, DOI: 10.1371 / journal.ppat.1006937